What is tangential speed and centripetal acceleration in uniform circular motion?
The Tangential speed of the uniform circular motion is given by, v = 2π r / T. The centripetal acceleration is given by, Where, v= tangential velocity. R= radius. T= period (Time required to make one complete circle) a= centripetal acceleration. Any object moving in uniform circular motion also has an angular velocity.
What is tangential acceleration formula?
Tangential Acceleration Formula: In a circular motion, a particle may speed up or slow down or move with constant speed. When the particle is in a circular motion, it will always have an acceleration toward the centre called centripetal acceleration (even if moving with constant speed).
Is tangential speed constant at every point on the circumference?
The tangential speed at every point on the circumference is found to be constant in a uniform circular motion, and the tangential velocity vector is tangent at every point over the circumference.
What if there is no tangential acceleration?
Those special cases where there is no tangential acceleration, a → = ( 0, a ⊥) ⇔ a = a ⊥, we call them uniform. Source. Isn’t the tangential velocity always changing direction?

Is tangential acceleration in uniform circular motion?
(1) In uniform circular motion, tangential acceleration is zero.
Is tangential acceleration always constant?
(ii) For determining tangential acceleration, we need to have expression of linear speed in time. Evidently, the tangential acceleration is constant and is independent of time.
What acceleration is constant in uniform circular motion?
Because an object in uniform circular motion undergoes constant acceleration (by changing direction), we know from Newton's second law of motion that there must be a constant net external force acting on the object. Any force or combination of forces can cause a centripetal acceleration.
Why there is no tangential acceleration in uniform circular motion?
So, during a uniform circular motion tangential acceleration is zero due to its constant angular velocity. Note: It must be noted that during a uniform circular motion, the tangential acceleration is zero as the angular velocity is constant.
Is tangential acceleration constant in non uniform motion?
Non-uniform circular motion implies the movement of an object along a circular path with variable speed. Uniform circular motion implies the movement of an object along a circular path with constant speed. Angular and tangential acceleration are non-zero. Angular and tangential acceleration are zero.
What is not constant in uniform circular motion?
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) occurs when an object moves with a constant speed around a circular path. The speed remains constant, but the velocity does not because the object's direction is always changing.
What is tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is defined as the rate of change of tangential velocity of the matter in the circular path.
What is the relation between tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration during non uniform circular motion?
In non-uniform circular motion, the centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration are perpendicular to each other, but does that mean that they don't affect each other because centripetal acceleration depends on velocity (=v2/r) and tangential acceleration's direction (i.e., whether it will act along the ...
Which acceleration is not zero in an uniform circular motion?
EXPLANATION: We all know that the direction of centripetal acceleration is always towards the center and it is not equal to zero.
What is the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration during non-uniform circular motion?
The tangential component results in a change in its speed while the centripetal component of the accelerations changes direction of the velocity vector.
What changes tangential acceleration?
True, tangential acceleration is along or opposite to the direction of velocity, so it changes the magnitude of velocity. Centripetal acceleration is perpendicular to velocity, so it changes only the direction of velocity.
What is tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is defined as the rate of change of tangential velocity of the matter in the circular path.
What is the difference between tangential and normal acceleration?
The tangential acceleration is a measure of the rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity vector, i.e. speed, and the normal acceleration are a measure of the rate of change of the direction of the velocity vector.
Can an accelerating object have constant speed?
Can an object accelerate if it's moving with constant speed? Yup! Many people find this counter-intuitive at first because they forget that changes in the direction of motion of an object—even if the object is maintaining a constant speed—still count as acceleration.
Q.1. What do you mean by tangential acceleration?
Ans: The rate of change speed of the particle in the circular path is known as tangential acceleration. It is equal to the product of angular accel...
Q.2. What is the formula of centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration?
Ans: (i) We can find tangential acceleration with the help of the tangential acceleration formula, which is given as: at=dvdt or at=rα (ii) And, we...
Q.3. In which direction the tangential acceleration works?
Ans: A tangential acceleration works in the direction of a tangent at the point of circular motion. Its direction is always in the perpendicular di...
Q.4. What force causes tangential acceleration?
Ans: The tangential force component will create tangential acceleration, which will cause the object to accelerate along the tangent. Then, the obj...
Q.5. Give an example of both centripetal and tangential acceleration.
Ans: Suppose you are holding a thread to the end of which is tied to a stone. Now when you start whirling it around, you will notice that two force...
Q.6. What is Centripetal Acceleration?
Ans: Centripetal Acceleration can be defined as the component of acceleration in the radial direction (towards the centre).
Q.7. What is the difference between centripetal and tangential acceleration?
Ans: Tangential acceleration is in the direction of the tangent to the circle, whereas centripetal acceleration is in the radial direction of the c...
What is tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is the measure of how quickly the speed of a body changes when an object moves in a circular motion. Let us consider a particle ( (P)) that is moving in a circle of radius ( (r)) and centre (O,) as shown in the figure below. The position of the particle (P) at a given instant may be described by the angle (theta) between (OP) and (OX.) This angle (theta) is called the angular position of the particle with respect to (OX,) and it changes as the particle moves on the circle. Let us assume the point rotates an angle (∆θ) in the time interval of (∆t.) The rate of change of angular position is known as the angular velocity (left ( omega right).)
What is the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration?
Net acceleration: Tangential acceleration is in the direction of the tangent to the circle, whereas centripetal acceleration is in the radial direction of the circle pointing inwards to the centre. These two components are mutually perpendicular, as shown in the figure below. Thus, a particle in a circular motion having centripetal acceleration as well as tangential acceleration has a net acceleration equals to their vector sum, which is given as:
What are the two accelerations of a particle in circular motion?
Like the velocity, a particle in circular motion has two accelerations that are angular and linear acceleration . Where Angular acceleration (left ( alpha right)) is the rate of change of angular velocity. Thus, we can write that
What is the component of acceleration in the radial direction?
Centripetal acceleration: The component of acceleration in the radial direction (towards the centre) is called radial or centripetal acceleration. This component changes the direction of the linear velocity. As the direction continuously keeps on changing. So, this component can never be zero, and the value of this component is given as:
What happens when the net force is not perpendicular?
Therefore, the object is said to be accelerating in a direction that points towards the centre of the circular pathway. But what happens when the net force acting on the object is not perpendicular? In this case, there will be two-component force vectors that will point along the perpendicular and parallel to the velocity vector. The perpendicular force component will cause the object to move along a circular pathway as it creates a centripetal acceleration, and the parallel force component will cause the object to accelerate along the tangent as it creates tangential acceleration. Hence, the object will undergo non-uniform circular motion as both the direction and magnitude of the velocity of the object will change.
Is angular acceleration a vector quantity?
Angular acceleration (left ( alpha right)) is also a vector quantity. The direction of (left ( alpha right)) is also perpendicular to the plane of the circle, either parallel or antiparallel to (omega .) If the angular speed of the particle is increasing, then (left ( alpha right)) is parallel (omega ) to and if angular speed is decreasing, then (left ( alpha right)) is antiparallel to (omega .) If angular speed (or angular velocity) is constant then, angular acceleration will be zero.
What is the value of tangential acceleration?
As you can see, this is precisely the centripetal acceleration, and the value of tangential acceleration is zero.
Why does velocity have centripetal acceleration?
The velocity is changing only the direction , which is why there exists only a centripetal acceleration. If the velocity would have been changing its magnitude (in other words, if the speed was changing) then you'd see that tangential acceleration would exist. This can also be seen by the relevent formula of a body's acceleration in polar coordinates:
What acceleration does turningit require?
Turningit requires centripetal acceleration $a_perp$(perpendicular, so turning the velocity vector).
Which direction are centripetal and tangential accelerations?
The directions of centripetal and tangential accelerations can be described more conveniently in terms of a polar coordinate system, with unit vectors in the radial and tangential directions. This coordinate system, which is used for motion along curved paths, is discussed in detail later in the book.
What is the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration?
The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle. Thus, a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations:
What is the angular frequency of a particle?
Here, ω ω is a constant called the angular frequency of the particle. The angular frequency has units of radians (rad) per second and is simply the number of radians of angular measure through which the particle passes per second. The angle θ θ that the position vector has at any particular time is ωt ω t.
What is the direction of the acceleration vector?
The direction of the acceleration vector is toward the center of the circle ( Figure ). This is a radial acceleration and is called the centripetal acceleration, which is why we give it the subscript c. The word centripetal comes from the Latin words centrum (meaning “center”) and petere (meaning to seek”), and thus takes the meaning “center seeking.”
How to find the direction of acceleration?
The direction of the acceleration can also be found by noting that as Δt Δ t and therefore Δθ Δ θ approach zero, the vector Δ→v Δ v → approaches a direction perpendicular to →v. v →. In the limit Δt → 0, Δ t → 0, Δ→v Δ v → is perpendicular to →v. v →. Since →v v → is tangent to the circle, the acceleration d→ v /dt d v → / d t points toward the center of the circle. Summarizing, a particle moving in a circle at a constant speed has an acceleration with magnitude
What is the radius of a flywheel?
A flywheel has a radius of 20.0 cm. What is the speed of a point on the edge of the flywheel if it experiences a centripetal acceleration of 900.0cm/s2? 900.0 cm / s 2?
Where does the centripetal acceleration point?
Figure 4.22 The centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circle. The tangential acceleration is tangential to the circle at the particle’s position. The total acceleration is the vector sum of the tangential and centripetal accelerations, which are perpendicular.
What is the resultant acceleration of a non-uniform motion?
In case of non-uniform circular motion, there is some tangential acceleration due to which the speed of the particle increases or decreases. The resultant acceleration is the vector sum of radial acceleration and tangential acceleration.
What are some examples of circular motion?
Following are the examples of uniform circular motion: 1 Motion of artificial satellites around the earth is an example of uniform circular motion. The gravitational force from the earth makes the satellites stay in the circular orbit around the earth. 2 The motion of electrons around its nucleus. 3 The motion of blades of the windmills. 4 The tip of second’s hand of a watch with circular dial shows uniform circular motion.
What is the frictional force between tyres and ground that provides the required centripetal force for?
When the vehicles turn on the roads, it is the frictional force between tyres and ground that provides the required centripetal force for turning. So if a particle is moving in a uniform circular motion: 1) Its speed is constant. 2) Velocity is changing at every instant. 3) There is no tangential acceleration.
What is the movement of a body following a circular path called?
The movement of a body following a circular path is called a circular motion. Now, the motion of a body moving with constant speed along a circular path is called Uniform Circular Motion. Here, the speed is constant but the velocity changes. If a particle is moving in a circle, it must have some acceleration acting towards ...
What does the tip of the second hand of a watch with circular dial show?
The tip of second’s hand of a watch with circular dial shows uniform circular motion.
When a particle is moving with constant angular velocity, the energy of the particle is conserved?
This is because in a uniform circular motion, kinetic energy remains unchanged and the momentum of the particle varies with change in velocity.
Why does the velocity vector change direction?
The velocity vector of a particle will change its direction. This is because it is always directed in the direction of the tangent to the circle.
What is the difference between centripetal and tangential acceleration?
If the speed of the particle is changing, then it has a tangential acceleration that is the time rate of change of the magnitude of the velocity: The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle.
What is uniform circular motion?
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors.
How to calculate centripetal acceleration?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Solve for the centripetal acceleration of an object moving on a circular path. 2 Use the equations of circular motion to find the position, velocity, and acceleration of a particle executing circular motion. 3 Explain the differences between centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration resulting from nonuniform circular motion. 4 Evaluate centripetal and tangential acceleration in nonuniform circular motion, and find the total acceleration vector.
What is the radius of a flywheel?
A flywheel has a radius of 20.0 cm. What is the speed of a point on the edge of the flywheel if it experiences a centripetal acceleration of
How to create greater acceleration than g?
To create a greater acceleration than g on the pilot, the jet would either have to decrease the radius of its circular trajectory or increase its speed on its existing trajectory or both.
How to describe a particle executing circular motion?
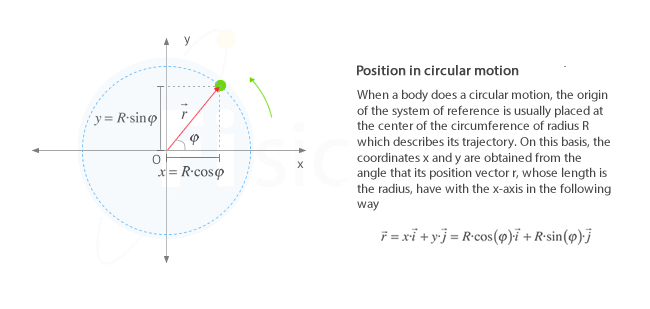
A particle executing circular motion can be described by its position vector
Where does the centripetal acceleration point?
Figure 4.22 The centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circle. The tangential acceleration is tangential to the circle at the particle’s position. The total acceleration is the vector sum of the tangential and centripetal accelerations, which are perpendicular.
What is tangential acceleration?
In the rotational motion of any object, tangential acceleration is the measure of how quickly a tangential velocity changes. Here tangential velocity will work in the direction of a tangent at the point of motion. Therefore it always acts in the perpendicular direction to the centripetal acceleration of a rotating object.
What is greater than zero?
Greater than zero: When the body has accelerated motion, that is , the magnitude of the velocity vector increases with time. Less than zero: When the body has slowed or decelerated motion, that is, the magnitude of the velocity vector decreases with time. Equal to zero: When the body has uniform motion, that is, ...
Is tangential acceleration linear or tangential?
Tangential acceleration is similar to the linear acceleration, but it is specific to the tangential direction. This is related to circular motion. Therefore, the rate of change of the tangential velocity of a particle in a circular orbit is known as Tangential acceleration. It always directs towards the tangent to the path of the body.
What is the acceleration of an object moving in a circular motion?
An object moving in a circular motion has a centripetal acceleration of 20 m/s2. If the radius of the motion is 0.5 m, calculate the frequency of the motion.
What is the acceleration of a circular object?
a= centripetal acceleration. Any object moving in uniform circular motion also has an angular velocity. The object’s velocity changes continuously and therefore there is an acceleration in the circular motion, and this acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circle which is termed as centripetal acceleration.
What is uniform circular motion?
The term circular is applied to describe the motion in a curved path. The motion of an object along a circular path covering equal distance along the circumference in the same interval of time is known as uniform circular motion. In any uniform circular motion, the speed remains constant, but the direction of the velocity changes.
Is the velocity constant in circular motion?
In any uniform circular motion, the speed remains constant, but the direction of the velocity changes. The tangential speed at every point on the circumference is found to be constant in a uniform circular motion, and the tangential velocity vector is tangent at every point over the circumference.
Is tangential velocity a vector?
Tangential velocity is the vector formed to the tangential speed; therefore, the magnitude remains constant and equal to the tangential speed of the uniform circular motion. Any object moving in uniform circular motion also has an angular velocity.