What are the components of the cell membrane structure?
The cell membrane structure is comprised of phospholipids, membrane proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins and cholesterol. This is described as the 'fluid mosaic model'.
How does the structure of the cell membrane affect its function?
In general, membranes actively involved in metabolism contain a higher proportion of protein. The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells.
What is the backbone structure of the cell membrane?
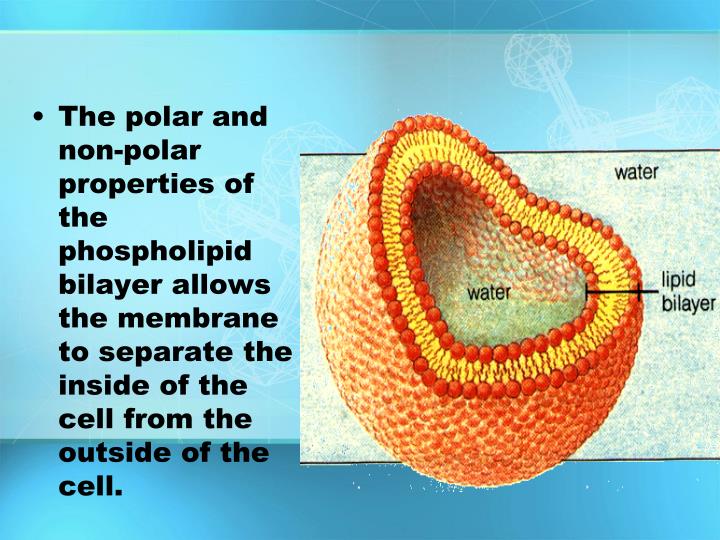
The backbone structure of the cell membrane is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules, called lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer ).
Why does the cell membrane look like a mosaic?
The cell membrane has a fluid consistency due to being made up in large part of phospholipids, and because of this, proteins move freely across its surface. The multitude of different proteins and lipids in the cell membrane give it the look of a mosaic.

Is the cell membrane static?
The physical state of membranes is dynamic, and rarely static. For example, when a cell adds extra cholesterol to a membrane, this changes the fluidity and converts the membrane from a liquid-like state to a more viscous gel-like state.
Is the cell membrane fluid or static?
Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux. The plasma membrane must be sufficiently flexible to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries.
What kind of structure is the cell membrane in?
phospholipid bilayerThe fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Is cell membrane a dynamic structure?
Cell membranes are dynamic, fluid structures, and most of their molecules are able to move about in the plane of the membrane.
Is the cell membrane static or rigid?
Although the plasma membrane encloses the cell's borders, it is far from being a static barrier; it is dynamic and constantly in flux. The plasma membrane must be sufficiently flexible to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries.
What best describes the structure of a cell membrane?
The most widely accepted model for plasma membrane structure is the fluid - mosaic model. According to this model, the plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer which has proteins embedded in it.
What is a characteristic of cell membranes?
The cell membrane is made up of phospholipid bilayer and proteins. It is a living semi-permeable membrane and regulates the solutes which can pass through it. The membrane is in general impermeable to ions because they are charged and, hence, insoluble in lipids.
What is the structure and function of the cell membrane?
Updated on October 07, 2019. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out.
What is the structure of a cell?
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
Why do we call cell membrane to be dynamic?
Cell membrane is called dynamic as it is involved in transport of molecules in and out of the cell. Cell membrane is fluid in nature because lipids present in cell membrane provide fluidity. It is known as semi permeable because only some molecules can pass through cell membrane.
What is called cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
Which model of plasma membrane is dynamic?
The fluid mosaic model incorporates the dynamic nature of bilayer membrane organization that occurs due to the constant rotational and lateral motion of the integral lipid and protein molecules.
Is the cell membrane fluid?
At physiological temperatures, cell membranes are fluid; at cooler temperatures, they become gel-like. Scientists who model membrane structure and dynamics describe the membrane as a fluid mosaic in which transmembrane proteins can move laterally in the lipid bilayer.
Why is the cell membrane referred to as fluid?
Cell membrane is fluid because individual phospholipid molecules and proteins can diffuse within their monolayer and thus move around. The fluidity is affected by: The length of the fatty acid chain.
Why do membranes have to be fluid?
Fluidity is important for many reasons: 1. it allows membrane proteins rapidly in the plane of bilayer. 2. It permits membrane lipids and proteins to diffuse from sites where they are inserted into bilayer after their synthesis.
Why is the cell membrane called a fluid mosaic?
Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membranes: Parts and Functions. The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is called such because the cell membrane is made of different parts working together, like a mosaic is made of many tiles. The different parts of the cell membrane include: Phospholipids.
What is the purpose of cell membranes?
The cell membrane contains components called glycolipids and glycoproteins, which we will discuss in the later section. These components can act as receptors and antigens for cell communication. Specific signalling molecules will bind to these receptors or antigens and will initiate a chain of chemical reactions within the cell.
What is the cell membrane structure?
The cell membrane structure is most commonly described using the 'fluid mosaic model' . This model describes the cell membrane as a phospholipid bilayer containing proteins and cholesterol which are distributed throughout the bilayer.
What factors affect the cell membrane structure?
We previously discussed the cell membrane functions which included regulating what enters and exits the cell. To perform these vital functions, we need to maintain the cell membrane shape and structure. We will explore the factors that can affect this.
Investigating cell membrane permeability
Betalain is the pigment responsible for the red color of beetroot. Disruptions to the cell membrane structure of beetroot cells cause the betalain pigment to leak out into its surroundings.
Cell Membrane Structure
The major components of the cell membrane are phospholipids, membrane proteins (channel proteins and carrier proteins), glycolipids, glycoproteins and cholesterol.
What is the cell membrane?
Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic phospholipids?
When in water or an aqueous solution (including inside the body) the hydrophobic heads of phospholipids will orient themselves to be on the inside, as far away from the water as possible. In contrast, the hydrophilic heads will be on the outside, making contact with the water. The result is that a double layer of phospholipids is formed, with the hydrophobic heads clustering together in the center, and the hydrophilic tails forming the outside of the structure. The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
Why is cholesterol important in the cell membrane?
The amount of cholesterol in the membrane helps maintain its permeability so that the right amount of molecules can enter the cell at a time. The cell membrane also contains many different proteins. Proteins make up about half of the cell membrane.
Chemical composition of the cell membrane
It has a heterogeneous chemical composition that varies according to the type of cell . Anyway and in general it is composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Cell membrane structure
Scientists have been based on a model called ” model of the fluid mosaic “ that serves for their study and physiology of the membrane. This model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 972 and is made up of 3 layers, two external lines and two internal ones. In the middle of both is the lighter layer called the fluid mosaic pattern.
Attraction of molecules
The attractive force between the molecules allows them to slide from one side to the other.
Cell membrane wateriness
Prior to the fluid mosaic model , the membrane was considered to be a solid body , but later it was shown that it behaves like a liquid .
Selective permeability of the cell membrane
The cell membrane is characterized by being semi-permeable . In other words, it allows the membrane to select which molecules must enter and which must exit.
Processes carried out by the cell membrane
If endocytosis captures particles then the process is known as phagocytosis.
Cell membrane asymmetry
Another characteristic of the plasma membrane is that it has an asymmetric structure, since the composition of each layer that forms the cell membrane is different from one another. On the other hand, proteins also vary if they are found in one layer or another. This means that the functions of the layers are different.
How do scientists explain the cell membrane?
To better describe the properties of the cell membrane, scientists explain the cell membrane appearance and functions using the fluid mosaic model.#N#If you zoom in on the cell membrane, you will see the ocean of lipid molecules decorated with membrane proteins, cholesterols, and carbohydrates. These molecules are constantly moving in two dimensions, in a fluid fashion, similar to icebergs floating in the ocean. There is no consistent pattern or arrangement of these molecules; they are more like a mosaic.
What is the cell membrane made of?
The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted. These proteins control the movement of molecules such as water, ions, nutrients, and oxygen in and out of the cell. [In this figure] The anatomy of an animal cell with organelles labeled.
What does cell membrane look like under a microscope?
Under a compound light microscope, the cell membrane (only 5-10 nm) may be too thin to be seen. However, you can easily tell the boundary of cells if stained with proper dyes. That is where the cell membrane is.
What is the backbone of a cell?
Phospholipid bilayer as a versatile biological barrier. The backbone structure of the cell membrane is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules, called lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer ).
How do membrane proteins control the cell?
Membrane proteins control the traffic of biomolecules in and out the cells. Cells eat and excrete by changing the cell membrane. Cells talk to each other via direct or indirect contacts on their cell membranes. Signal transduction along the cell membrane of nervous cells.
Why are lipid bilayers important?
The lipid bilayers are ideally suited to keeps ions, proteins, and other charged molecules from diffusing across the membrane, even though they are only a few nanometers in width. At the same time, uncharged molecules and gases can easily cross the cell membrane.
What is the membrane of a balloon?
This soft but tough balloon is made from the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane). The cell membrane is a thin biological membrane that separates the interior of cells from the outside space and protects the cells from the surrounding environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) ...
Which region of the plasma membrane contains a greater number of positively charged ions and molecule than found in the?
Both "The region just outside of the plasma membrane contains a greater number of positively charged ions and molecule than found in the corresponding region inside the membrane" and "The extracellular fluid contains more positively charged ions than the intracellular fluid" are correct.
Which phase of the cell cycle contains half as much DNA as cells in the G2 phase?
Cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle contain half as much DNA as cells in the G2 phase.
How many new molecules does DNA replication produce?
DNA replication results in two new DNA molecules. Each of these new molecules
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, ...
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: first, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and , second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, ...
What is the innermost layer of a cell?
The innermost layer is a plasma membrane similar to the ones that surround most cells. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Some of the proteins are embedded entirely within the lipid layer, others extend to one or the other surface, and still others…
What is the membrane of a neuron?
The neuron is bound by a plasma membrane, a structure so thin that its fine detail can be revealed only by high-resolution electron microscopy. About half of the membrane is the lipid bilayer, two sheets of mainly phospholipids with a space between. One…
What are the two types of lipids in membranes?
Membrane lipids are principally of two types, phospholipids and sterols (generally cholesterol ). Both types share the defining characteristic of lipids—they dissolve readily in organic solvents—but in addition they both have a region that is attracted to and soluble in water.
How thick is the lipid bilayer?
Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, which is made up largely of phospholipids and cholesterol and which typically is between 4 and 10 nanometers (nm; 1 nm = 10 −9 metre) in thickness.
What type of bond is used to attach membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins are also of two general types. One type, called the extrinsic proteins, is loosely attached by ionic bond s or calcium bridges to the electrically charged phosphoryl surface of the bilayer. They can also attach to the second type of protein, called the intrinsic proteins.