Where are the dorsal and ventral cavities located on the body?
Body Cavities Labeled Diagram: The ventral cavity is located in the front of the body (red/star) and houses the organs of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Now that we have a good understanding of the dorsal and ventral cavities, each cavity can be broken down even more.
What is the function of diaphragm in the thoracic cavity?
It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities from each other by closing the inferior thoracic aperture. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that is active in inspiration. Contraction of the muscle facilitates expansion of the thoracic cavity.
What is the difference between ventral and dorsal?
Ventral and dorsal can be used to describe the position of organs in relation to one another. For example, one could say, “The small intestine is ventral to the kidneys”, which means the small intestine is in front of the kidneys. These anatomical terms can also describe different body cavities.
Where is the diaphragm located?
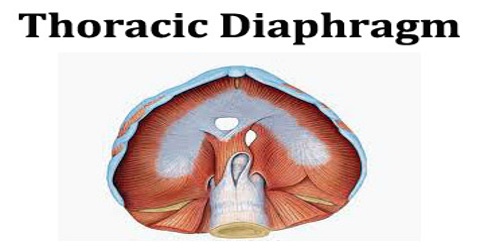
Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver The diaphragm is an unpaired, dome shaped skeletal muscle that is located in the trunk which separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities from each other by closing the inferior thoracic aperture. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that is active in inspiration.

Is diaphragm a ventral?
A ventral layer of thin cells and muscle (Fig. 16) that assists in circulation of hemolymph around the nerve cord. Cross section of an insect abdomen, showing components of the insect circulatory system and direction of hemolymph flow (adapted from Evans, Insect biology).
What region is the diaphragm located in?
The diaphragm is a thin skeletal muscle that sits at the base of the chest and separates the abdomen from the chest. It contracts and flattens when you inhale. This creates a vacuum effect that pulls air into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and the air is pushed out of lungs.
Is the diaphragm superior or inferior?
The correct answer: The diaphragm is F. inferior to the lungs.
What position is the stomach to the diaphragm?
Location. Your heart, lungs, and the upper part of your esophagus (food pipe) are in the thoracic cavity above the diaphragm. Your lower esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and kidneys are below the diaphragm, in your abdominal cavity.
What level is diaphragm?
It is located at the level of T10. The posterior and anterior vagal nerves are also found passing through this hiatus.
Is the diaphragm in the thoracic cavity?
The diaphragm is a thin dome-shaped muscle which separates the thoracic cavity (lungs and heart) from the abdominal cavity (intestines, stomach, liver, etc.).
What is the diaphragm superior to?
The diaphragm is an upward curved, c-shaped structure of muscle and fibrous tissue that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdomen. The superior surface of the dome forms the floor of the thoracic cavity, and the inferior surface the roof of the abdominal cavity.
Is the diaphragm inferior to the heart?
The heart is SUPERIOR to the diaphragm. Below. The liver is INFERIOR to the diaphragm. Toward the ventral side, toward the front or belly.
What is anterior to diaphragm?
Origin and insertion. The diaphragm is a musculotendinous structure with a peripheral attachment to a number of bony structures. It is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process and costal margin, laterally to the 11th and 12th ribs, and posteriorly to the lumbar vertebrae.
Is the stomach anterior or posterior?
The anterior surface of stomach is related to the left lobe (segments II, III and IV) of the liver, the anterior abdominal wall, and the distal transverse colon. The posterior surface of the stomach is related to the left hemidiaphragm, the spleen, the left kidney (and adrenal), and the pancreas (stomach bed).
Which body cavity has the diaphragm as the inferior wall?
thoracic cavitythoracic cavity, also called chest cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity (the body's largest hollow space) by a muscular and membranous partition, the diaphragm.
What type of muscle is the diaphragm?
skeletalThe diaphragm muscle is of the skeletal or striated type and is the major muscle of ventilation.
Is the diaphragm part of the respiratory tract?
The diaphragm in the respiratory system is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. It is also referred to the thoracic diaphragm because it's located in the thoracic cavity, or chest.
Is the diaphragm below the ribs?
The diaphragm is a mushroom-shaped muscle that sits beneath your lower-to-middle rib cage. It separates your abdomen from your thoracic area. Your diaphragm helps you breathe by lowering when you inhale, in that way, allowing your lungs to expand.
What is diaphragm in structure?
In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). Diaphragms are typically horizontal, but can be sloped such as in a gable roof on a wood structure or concrete ramp in a parking garage.
Where is the diaphragm located in a fetal pig?
2. Use your fingers to probe the chest area of the pig. You should be able to feel the hard sternum (breastbone) and the tiny ridges of the ribcage. Keep moving down until you feel the bottom edge of the rib cage; this is where the diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
What is dorsal and ventral?
Dorsal and ventral are paired anatomical terms used to describe opposite locations on a body that is in the anatomical position. The anatomical pos...
What is the difference between dorsal and ventral?
The main difference between dorsal and ventral is the area of the body to which they refer. In general, ventral refers to the front of the body, an...
What are the dorsal and ventral body cavities?
The dorsal and ventral body cavities, two of the largest body compartments in humans, are anatomical spaces that contain various organs and other s...
What are the most important facts to know about dorsal and ventral?
Dorsal and ventral are terms that refer, respectively, to the back and front portions of the human body in the anatomical position. These terms can...
Where is the ventral aperture located in the diaphragm?
1,3 The caval foramen allows passage of the caudal vena cava. It is the most ventral aperture and is located in the central tendon to the right of midline. 3 The esophageal hiatus is located on the midline dorsal to the caval foramen.
Why is the diaphragm important?
Because it is a barrier to microorganisms, evidence suggests that use of the diaphragm lowers the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease. The relatively high failure rate of a diaphragm with a spermicide (6–16%) is due to several factors. For example, use of the diaphragm requires high motivation and commitment.
What is the term for a herniation of the diaphragm?
The degree of herniation is a dynamic process, complicating its use for prediction of disease severity or disease mechanism. The term eventration is a synonym for herniation and is most often used to describe abnormal elevation of the diaphragm in a situation where the diaphragm remains intact. This results from a number of mechanisms including a lack of diaphragmatic function secondary to nerve or muscle dysfunction, or from abnormal muscular development of the diaphragm. The terminology becomes more confusing when a severe herniation is identified arising from an intact but undermuscularized portion of the diaphragm. In these cases, clinical descriptions include Bochdalek or congenital diaphragmatic hernia with a sac membrane, sac hernia, or eventration hernia ( Ackerman et al., 2012 ). From a developmental biology perspective, it is important to differentiate these lesions since they likely occur via different mechanisms.
What is the range of a diaphragm manometer?
The appropriate measuring range of modern capacitance diaphragm manometer is from 0.1 Pa to 1 atm. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
How does a diaphragm filler work?
Instead of a rigid piston and cylinder, a diaphragm filler has a flexible diaphragm, which can be distorted to adjust its volume. The operation of a diaphragm filler is straightforward. When the cycle starts, the valve at the bottom of the supply tank is opened and the valve to the empty container is closed. Air pressure in the supply tank forces the product out of the tank and into the me asuring chamber. The top of the chamber is formed by the diaphragm with the plunger above. As product flows into the chamber, the diaphragm and plunger are lifted. When the plunger reaches a preset position, the valves are reversed and air pressure is applied to the top of the plunger, forcing the product out of the chamber and into the container. The filled container is then conveyed away and replaced by another empty container and the process cycle repeats.
What is a diaphragm forming sheet?
Diaphragm forming (Fig. 2 (e)) uses one or two “slave” sheets of a superplastic alloy to guide a smaller unclamped blank to be gradually drawn and draped into tool contact.
Why should a diaphragm be replaced?
Damage to the diaphragm can result in product leaking through into the nonproduct side, which may give rise to contamination and also makes cleaning and disinfection nearly impossible. To avoid premature rupture, the diaphragm should be replaced at regular intervals depending upon the operating conditions.
What is the difference between ventral and dorsal?
In general, ventral refers to the front of the body, and dorsal refers to the back. These terms are also known as anterior and posterior, respectively.
What is the paired anatomical term for the ventral and dorsal?
The anatomical position of a human body is defined as a body standing upright with the head facing forward, arms down at the sides with the palms turned forward, and feet parallel facing forward.
What is the ventral cavity?
On the anterior side of the body, the ventral cavity is made up of the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity. The thoracic cavity contains the heart, lungs, breast tissue, thymus gland, and blood vessels. Inside the abdominal cavity are the stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small intestine, colon, appendix, and kidneys.
What is the ventral cavity of the small intestine?
For example, one could say, “The small intestine is ventral to the kidneys”, which means the small intestine is in front of the kidneys. These anatomical terms can also describe different body cavities. The dorsal cavity contains the spinal cord, central nervous system, and spinal column, whereas the ventral cavity consists of the thoracic, ...
What are the dorsal and ventral cavities?
What are the dorsal and ventral body cavities? The dorsal and ventral body cavities, two of the largest body compartments in humans, are anatomical spaces that contain various organs and other structures. The dorsal cavity lies close to the spine in the posterior portion of the body. The dorsal cavity contains the spinal column, ...
What are the most important facts about dorsal and ventral?
What are the most important facts to know about dorsal and ventral? Dorsal and ventral are terms that refer, respectively, to the back and front portions of the human body in the anatomical position. These terms can also be referred to as posterior and anterior surfaces.
What is the ventral location of the stomach?
For example, the stomach is ventral to the spinal cord, which means that the stomach is located in front of the spinal cord.
What is the thoracic cavity?
Thoracic cavity. The upper ventral, thoracic, or chest cavity contains the heart, lungs, trachea, esophagus, large blood vessels, and nerves. The thoracic cavity is bound laterally by the ribs (covered by costal pleura) and the diaphragm caudally (covered by diaphragmatic pleura).
What is directional term?
Directional Terms. Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Superior or cranial - toward the head end of the body; upper (example, the hand is part of the superior extremity ).
What are the two main cavities in the human body?
The cavities, or spaces, of the body contain the internal organs, or viscera. The two main cavities are called the ventral and dorsal cavities. The ventral is the larger cavity and is subdivided into two parts (thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities) by the diaphragm, a dome-shaped respiratory muscle.
Which organ is found in the abdominal cavity?
The abdominal cavity contains most of the gastrointestinal tract as well as the kidneys and adrenal glands. The abdominal cavity is bound cranially by the diaphragm, laterally by the body wall, and caudally by the pelvic cavity. The pelvic cavity contains most of the urogenital system as well as the rectum.
What is the difference between medial and lateral?
Medial - toward the midline of the body (example, the middle toe is located at the medial side of the foot). Lateral - away from the midline of the body (example, the little toe is located at the lateral side of the foot).
Which cavity is the smaller?
Dorsal cavity. The smaller of the two main cavities is called the dorsal cavity. As its name implies, it contains organs lying more posterior in the body. The dorsal cavity, again, can be divided into two portions.
Which plane divides the body into right and left sides?
Sagittal Plane (Lateral Plane) - A vertical plane running from front to back; divides the body or any of its parts into right and left sides. Axial Plane ( Transverse Plane) - A horizontal plane; divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts.
Which cavity houses the esophagus, trachea, and the heart?
The thoracic cavity, which is the chest cavity that is separated from the lower parts by the diaphragm. The mediastinum houses the esophagus, trachea, and the heart and its associated blood vessels. The pleural cavity houses the lungs ('pleural' is the medical term for lungs).
Which cavity houses the lungs?
It's divided into the thoracic cavity, which houses the esophagus, trachea, heart, and lungs, and the abdominopelvic cavity, of which the abdominal cavity houses the kidneys, gallbladder, liver, small intestines, part of the large intestines, stomach, spleen,and pancreas.
How many regions are there in the abdominopelvic quadrant?
Sabrina says she remembers a little about the regions because it looked like a tic-tac-toe board drawn over the cavity. There are nine regions to study. Let go from top down, left to right. First, the top:
What are the two cavities in the abdominopelvic cavity?
The abdominopelvic cavity, which is really two cavities (abdominal and pelvic), but there's nothing to separate the two. The abdominal cavity houses the kidneys, gallbladder, liver, small intestines, part of the large intestines, stomach, spleen, and pancreas.
What is the pelvic cavity?
The pelvic cavity houses the colon, rectum, reproductive organs, and urinary bladder. Let's now take a look at the different divisions within the abdominal pelvic cavity, beginning with the abdominopelvic quadrants.
What is the right lower quadrant?
So, 'left' means the left side of the body, not your left.
Which quadrant contains the liver, kidney, stomach, spleen, pancreas, and left half
Left upper quadrant (LUQ): contains the small part of the liver, left kidney, stomach, spleen, pancreas, and left half of the transverse colon. Right upper quadrant (RUQ): contains a large portion of the liver, right kidney, bottom end of the stomach, gallbladder, and right half of the transverse colon.
What is the ventral cavity?
The ventral cavity, in humans, is actually made up of two separate cavities, separated by the diaphragm, a thin muscle which helps control the expansion and contraction of the lungs. The ventral cavity is sometimes referred to as a coelom, or true body cavity. While not all coelomates have a well-defined ventral cavity as in humans, ...
Which part of the ventral cavity must expand and contract?
The abdominopelvic portion of the ventral cavity also must expand and contract. The walls of the abdomen have thick muscles, mostly for moving the body. However, these muscles push and work on the internal organs in the cavity, stimulating them and moving food and fluids through the system. Further, the abdominal cavity ...
What are the two segments of the ventral cavity?
The ventral cavity is actually made up of several different cavities, which are separated by muscles and membranes. These smaller cavities are divided into two segments, the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.
Why do ventral cavities expand?
In humans, the ventral cavity must expand in several places to allow for various organs to expand and change shape. In the superior (top) portion of the ventral cavity, the lungs need room to expand and take in air. In the inferior (lower) portion, the stomach and intestines need room to expand when taking in food, ...
What is the function of the ventral cavity?
First and foremost, the cavity protects the organs inside from shock damage as the organism moves through the world. The space and fluid around the organs insures that any impacts incurred by ...
Which organs are lined with peritoneum?
Both the organs and the ventral cavity walls are lined with peritoneum, a thin membrane which separates the cavity from the inside of the body. The organs are also lined with a peritoneum, ...
What is the difference between the pelvic and abdominal cavity?
The abdominal cavity sits on top, while pelvic cavity sits below. The abdominal cavity houses the stomach, small intestines, most of the large intestines, kidneys, spleen, and liver. The pelvic cavity houses the internal reproductive organs and the bladder, while the large intestine briefly passes through it.