What are the functions of Diencephalon in the brain?
The following centers are located in diencephalon:
- centers of the autonomic nervous system (of the peripheral NS),
- centers for thermoregulation
- hunger and thirst
- centers for the operation of the vegetative nervous system ( 2 ).
Is the pitutary gland part of the diencephalon?
Together with the hypothalamus – which belongs to a part of the brain known as the diencephalon – the pituitary gland controls the involuntary (vegetative) nervous system. This part of the nervous system manages the balance of energy, heat and water in the body, which includes things like body temperature, heartbeat, urination, sleep ...
What are two main parts of the diencephalon?
What are the 3 parts of the diencephalon?
- Epithalamus.
- Thalamus.
- Subthalamus.
- Metathalamus.
- Hypothalamus.
Which structures are located in the diencephalon?
What structures are located in the diencephalon quizlet?
- Thalamus.
- Hypothalamus.
- Subthalamus.
- Epithalamus.
See more

Is diencephalon a brain stem?
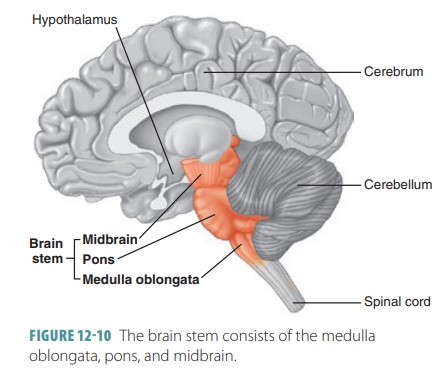
The parts of the brainstem are the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata, and sometimes the diencephalon.
What is the diencephalon part of the brain?
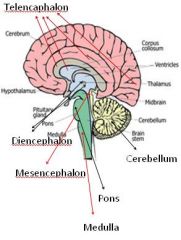
The diencephalon connects the midbrain to the forebrain. It is located deep within the brain and comprises the epithalamus, thalamus, subthalamus and hypothalamus.
What are the parts of brain stem?
AnatomyMidbrain: The top part of the brainstem is crucial for regulating eye movements.Pons: The middle portion of the brainstem coordinates facial movements, hearing and balance.Medulla oblongata: The bottom part of the brainstem helps regulate your breathing, heart rhythms, blood pressure and swallowing.
Which is not part of the brain stem?
It contains the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons and the medulla oblongata. Brainstem does not include cerebellum which is part of the hindbrain.
What is the diencephalon and brain stem?
In adults, the diencephalon is centrally located within the brain sitting at the top of the brain stem above the midbrain and under the cerebrum. It is part of the third ventricle of the brain. Along with the cerebrum, the diencephalon is part of the forebrain.
What is the diencephalon also called?
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic prosencephalon). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic mesencephalon). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in older literature.
What are the 3 parts to the brain stem?
The first two nerves originate in the cerebrum, and the remaining 10 cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem, which has three parts: the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
Which is false about the brain stem?
Which is false about the brain stem? It's responsible for the brain's highest level of thinking and perception. False- while the upper parts of the brain tackle higher level matters, the brain stem is responsible for the most basic of body functions like breathing, food digestion and blood circulation.
Where is the brain stem located?
Located towards the back of the neck, the brainstem is the lower part of the brain, and it is continuous with the spinal cord. Behind the brainstem, the cerebellum (the part of the brain largely responsible for coordination) is also protected by the lower portion of the skull.
Is thalamus part of brainstem?
Brainstem Structure and Function The brainstem can be subdivided anatomically into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus), mesencephalon (midbrain), ventral metencephalon (pons), and myelencephalon (medulla).
What is the structure and function of the diencephalon?
The diencephalon relays sensory information between brain regions and controls many autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system. This section of the forebrain also connects structures of the endocrine system with the nervous system and works with the limbic system to generate and manage emotions and memories.
What is the definition diencephalon?
Medical Definition of diencephalon : the posterior subdivision of the forebrain. — called also betweenbrain, interbrain.
What happens when diencephalon is damaged?
The diencephalon includes the hypothalamus and the thalamus. This condition is usually found in infants and young children and may result in symptoms including failure to gain weight and grow normally (failure to thrive), progressive thinness and weakness (emaciation), and hyperactivity and restlessness (hyperkinesia).
What would happen if the diencephalon is damaged?
Specifically, the diencephalon may serve as a link between limbic and cortical structures, and damage to the diencephalon can contribute to amnesia through what has been called a “disconnection syndrome” (Warrington and Weiskrantz 1982; Markowitsch 1988; Aggleton and Brown 1999).
What are the main structures of the diencephalon?
The main structures of the diencephalon include the hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus. Also located within the diencephalon is the third ventricle, one of the four brain ventricles or cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Each part of the diencephalon has its own role to play.
Where is the diencephalon located?
It is a small portion nestled under and between the two cerebral hemispheres, located just above the brain stem . Despite being small and inconspicuous, the diencephalon plays a number of critical roles in healthy brain and bodily function within the central nervous system.
What is the name of the two divisions of the prosencephalon?
Updated November 06, 2019. The diencephalon and the telencephalon (or cerebrum) comprise the two major divisions of your prosencephalon. If you were to look at a brain, you would not be able to see the diencephalon in the forebrain because it is mostly hidden from view.
What are the functions of the diencephalon?
Several structures of the diencephalon work together with other body parts to affect the following bodily functions: 1 Sense impulses throughout the body 2 Autonomic function 3 Endocrine function 4 Motor function 5 Homeostasis 6 Hearing, vision, smell, and taste 7 Touch perception
What is the function of the thalamus?
The thalamus assists in sensory perception, motor function regulation, and sleep cycle control. The thalamus acts as a relay station for almost all sensory information (with the exception of smell). Before sensory information reaches your brain's cortex, it stops at the thalamus. The thalamus processes information and passes it along. Input information then travels to the correct area of specialty and is passed to the cortex for further processing. The thalamus also plays a big role in sleep and consciousness.
Which part of the brain controls the peripheral nervous system?
The diencephalon relays sensory information between brain regions and controls many autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system. This section of the forebrain also connects structures of the endocrine system with the nervous system and works with the limbic system to generate and manage emotions and memories.
Which part of the brain processes information?
The thalamus processes information and passes it along. Input information then travels to the correct area of specialty and is passed to the cortex for further processing. The thalamus also plays a big role in sleep and consciousness.
Where is the diencephalon located?
Diencephalon Location. This brain region has a central location within the brain, it is located between the cerebral hemispheres and the brain stem , and through it travel most of the fibers that go to the cerebral cortex. The diencephalon, unlike the telencephalon that ends up forming the cerebral cortex and other internal structures such as ...
What is the largest structure in the diencephalon?
The thalamus. The thalamus corresponds to one of the largest structures in the diencephalon. It is made up mainly of grey matter, rich in neuronal bodies. Nerve impulses pass through the thalamus from the central nervous system to the peripheral and vice versa, this being the place where sensory signals are integrated for subsequent interpretation ...
What is the epithalamus?
The epithalamus is a dorsal part of the diencephalon, which is formed mainly by the habenulas -cellular nuclei with limbic and motor functions- and the pineal gland. It has important functions within the limbic system, connecting it with other parts of the brain, which for example include controlling the circadian rhythm through the pineal gland.
Which structure is responsible for the correct functioning of multiple biological processes?
In this article we will describe the structure and functions of the diencephalon, which includes such important regions as the thalamus and hypothalamus and allows for the correct functioning of multiple biological processes, such as the secretion of hormones and the regulation of the autonomic system. This structure is differentiated ...
Which part of the body controls the endocrine system?
The hypothalamus is considered one of the largest centers of endocrine control of the human body.. The signals that this part of the diencephalon emits condition a large amount of hormones in the endocrine system, thanks to the release of hormones that they cause in the pituitary gland, also known as the pituitary gland. 2.
What is the midsagittal view of the brain?
Midsagittal view of the brain. Visible are the structures situated on the medial aspect of the cortex as well as subcortical areas, which include the corpus callosum, septum pellucidum, fornix, diencephalon, and brainstem structures. These structures are closely related to each other and can collaborate to carry out specific tasks.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The functions of the hypothalamus are several of vital importance to the functioning of the body, such as homeostasis – the maintenance of normal conditions, such as body temperature, as well as plays a role in sexual desire, hunger and thirst. Also participates in sleep and memory processes, as well as in the function of sex hormones.
Where is the diencephalon located?
The diencephalon is a region of the brain located between the brain stem and the cerebrum. Its name means “between-brain” in Greek, which perfectly describes its position at the very center of the brain. Not only that, but the name also describes its role in relaying information to other brain regions. Structurally, the diencephalon is divided ...
What Is The Diencephalon Responsible For?
As already mentioned, the diencephalon is responsible for a number of functions in the brain.
What is the role of the diencephalon in the sleep cycle?
The diencephalon also regulates motor functions and sleep cycles. In tandem with the brain stem and the pons, it plays an instrumental role in the sleep process, which is essential to brain longevity.
What is the size of the diencephalon?
Namely, they are all partially controlled by the diencephalon. At just 2.2 inches in length, the diencephalon is a rather small region of the brain, especially compared to other brain regions like the cerebrum and the cerebellum.
Why is the diencephalon important?
What Is The Diencephalon And Why Is It Important? Hunger, thirst, sleep, heartbeat, childbirth – as random as these bodily functions may seem, they all have one thing in common. Namely, they are all partially controlled by the diencephalon.
Which is the largest of the four sections of the diencephalon?
Looking at the diencephalon, the hypothalamus sits at the bottom of this region. Moving up, there is the epithalamus followed by the subthalamus and the thalamus. The latter is the largest of the four sections.
What are the four main parts of the diencephalon?
Structurally, the diencephalon is divided into four main sections. They are the thalamus, subthalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. Each of these four sections has its own distinct functions in the brain.
What is the diencephalon?
The diencephalon is deep beneath the cerebrum and constitutes the walls of the third ventricle. The diencephalon can be described as any region of the brain with “thalamus” in its name. The major regions of the diencephalon are the thalamus itself, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus, which contains the pineal gland, and the subthalamus, which includes part of the basal nuclei (Figure 12.4. 1 ).
What is the brainstem?
Brainstem. The midbrain and hindbrain (composed of the pons and the medulla oblongata) are collectively referred to as the brainstem (Figure 12.4. 1 and Figure 12.4. 2 ). The structure emerges from the ventral surface of the forebrain as a tapering cone that connects the brain to the spinal cord.
What is the main connection between the cerebellum and the midbrain?
The midbrain coordinates sensory representations of the visual, auditory, and somatosensory perceptual spaces. The pons is the main connection with the cerebellum.
What is the name of the part of the brain that retains its name from embryologic development?
The diencephalon is the one region of the adult brain that retains its name from embryologic development. The etymology of the word diencephalon translates to “through brain.”. It is the connection between the cerebrum and the rest of the nervous system, with one exception. The rest of the brain, the spinal cord, ...
What is the midbrain?
Midbrain. The mesencephalon, one of the original region of the embryonic brain, becomes the midbrain, a small region between the thalamus and pons. The cerebral aqueduct passes through the center of the midbrain, such that these regions are the roof and floor of that canal.
Which part of the brain sends information to the thalamus?
The cerebrum also sends information down to the thalamus, which usually communicates motor commands. This involves interactions with the cerebellum and other nuclei in the brainstem. Inferior to the thalamus lies the subthalamic nucleus, which is part of the basal nuclei.
Which part of the brain is attached to the hypothalamus?
The cerebral peduncles of the midbrain and pyramids and their decussation of the medulla oblongata are also visible. The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothalamus, as are the mammillary bodies.