Is the forehead the strongest part of the skull?
Your frontal bone forms your forehead, and the tops of your eye sockets. The fourteen bones at the front of your skull hold your eyes in place and form your facial features. Your mandible, or jawbone, is the largest, strongest bone in your face.
What bones form the forehead?
air cavities within the frontal bone (the bone that forms the forehead and extends over most of the orbits and the nasal cavity) that open into the middle meatus of the nasal cavity parietal bones The bones that lie between the temporal and occipital regions of the cranium
How can I get rid of my forehead bump?
- Properly clean your face with water. Leave the skin little wet
- Put few drops of serum on your forehead, massage the area thoroughly for best results
- In order to reduce the chances of rebirth, massage the serum daily.
What causes a sudden dent in the forehead?
So what causes these depressions?
- Pressure while sleeping and a wrong sleeping posture. One of the possible reason is pressure from an object or body part as you are sleeping or a wrong sleeping posture.
- Furrows, wrinkles and hyperactive glabellar muscles. ...
- Brow sag. ...
- Mucocele of paranasal sinuses forehead dent. ...
Is the forehead part of the scalp?
Scalp comprises the forehead and the hair-bearing regions. It extends from the supraorbital ridge anteriorly to the highest nuchal line posteriorly, while ears and zygomatic arches define its lateral borders.
Where is the forehead?
The forehead constitutes the upper third of the face. It is delineated superiorly by the hairline and inferiorly by the glabella and frontonasal groove (centrally) and the eyebrows overlying the supraorbital ridges (laterally.)
What is the forehead region called?
The frontal bone is a bowl-shaped bone in the frontal (forehead) region of the skull. It is located superior to the nasal bones and maxillae and anterior to the parietal bones.
What is front of head called?
The frontal bone, most commonly referred to as the forehead, supports the front and back of the skull. In infancy, the frontal bone is connected by frontal suture, a joint that divides the two halves of the frontal bone.
Is the forehead the thickest part of the skull?
Conclusion: The thickest area of the skull is the parasagittal posterior parietal area in male skulls and the posterior parietal area midway between the sagittal and superior temporal line in female skulls.
Why is your head called a forehead?
Forehead has the Old English roots fore, "the front part," and heafod, "top of the body," or "head."
What are the parts of skull?
The skull consists of three parts, of different embryological origin—the neurocranium, the sutures, and the facial skeleton (also called the membraneous viscerocranium). The neurocranium (or braincase) forms the protective cranial cavity that surrounds and houses the brain and brainstem.
What bone is your forehead?
frontal boneThe frontal bone forms the forehead. The two parietal bones form the upper sides of the skull; the two temporal bones form the lower sides.
Are there bones in your forehead?
The frontal bone (os frontale) is an unpaired craniofacial bone that provides partial coverage of the brain and forms the structure of the forehead and upper casing of the eye sockets.
Are forehead bones strong?
In comparing the impact strength of three facial bones on each of four cadavers, the frontal bone has been found to tolerate a force three or four times higher than the mandible and zygomatic bone which are about equal.
Where is the strongest part of skull?
Your mandible, or jawbone, is the largest, strongest bone in your face.
What is the middle of your forehead called?
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose....GlabellaLatinGlabellaTA98A02.1.03.006TA2525FMA528515 more rows
What causes forehead pain?
Forehead pain can be a symptom of eyestrain, a headache, or a sinus infection. However, it can also result from something more serious, such as physical trauma or a stroke. Forehead pain is a common symptom of infection, inflammation, vascular conditions, and physical trauma.
What is the area above the eyebrow called?
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to the nasion.
What is the bone above your eyebrow called?
The glabella – the part of the os frontale that lies between the eyebrows – ends at the top of the nasal bones. The frontal bone is thicker at the eyebrows and this is usually more pronounced in male skulls.
How deep is your forehead?
The average thickness of forehead skin is 1.70 mm and superficial fat is 1.99 mm.
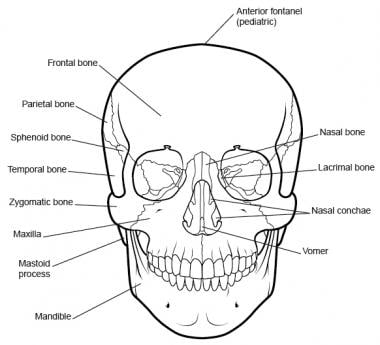
What are the parts of the skull?
Parts of the Skull. The skull consists of the rounded brain case that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures. Watch this video to view a rotating and exploded skull, with color-coded bones.
What is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain?
Identify the bony openings of the skull. The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.
How many cranial fossae are there?
Inside the skull, the floor of the cranial cavity is subdivided into three cranial fossae (spaces), which increase in depth from anterior to posterior (see Figure 4, Figure 6b, and Figure 9). Since the brain occupies these areas, the shape of each conforms to the shape of the brain regions that it contains. Each cranial fossa has anterior and posterior boundaries and is divided at the midline into right and left areas by a significant bony structure or opening.
Where are the paranasal sinuses located?
The paranasal sinuses are named for the skull bone that each occupies. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure 15). This irregular space may be divided at the midline into bilateral spaces, or these may be fused into a single sinus space. The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the paranasal sinuses. The largest sinus is the maxillary sinus. These are paired and located within the right and left maxillary bones, where they occupy the area just below the orbits. The maxillary sinuses are most commonly involved during sinus infections. Because their connection to the nasal cavity is located high on their medial wall, they are difficult to drain. The sphenoid sinus is a single, midline sinus. It is located within the body of the sphenoid bone, just anterior and inferior to the sella turcica, thus making it the most posterior of the paranasal sinuses. The lateral aspects of the ethmoid bone contain multiple small spaces separated by very thin bony walls. Each of these spaces is called an ethmoid air cell. These are located on both sides of the ethmoid bone, between the upper nasal cavity and medial orbit, just behind the superior nasal conchae.
Where is the superior nasal concha?
The superior nasal concha is located just lateral to the perpendicular plate, in the upper nasal cavity.
What is the anterior skull?
The anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the face. This view of the skull is dominated by the openings of the orbits and the nasal cavity. Also seen are the upper and lower jaws, with their respective teeth (Figure 2).
How many bones are there in the skull?
In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit. The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. Figure 1. Parts of the Skull.
What is the frontal bone?
The frontal bone, most commonly referred to as the forehead, supports the front and back of the skull. In infancy, the frontal bone is connected by frontal suture, a joint that divides the two halves of the frontal bone. As an infant starts to grow, this frontal suture fuses the frontal bone together into one solid piece.
Which part of the frontal bone is the top of the nose?
The orbital part of the frontal bone forms the top of orbit bone and ethmoid sinuses, which are located between your eyes and nose. Two openings at the front and back of the orbital part of the frontal bone allow for nerves to run through to the sinuses. Last, the nasal part of the frontal bone helps form the structure of the nose itself .
What to do if you think you have a frontal bone injury?
If you think you have a frontal bone injury, your safest bet is to get it checked by your healthcare provider. who can diagnose you correctly, ruling out a more serious brain injury in addition to providing you with the best treatment plan possible.
Which bone is the largest?
The squamous part of the frontal bone is the largest section. The outside of the squamous part is flat, but the inside is concave, consisting of frontal sinuses, a supraorbital notch, which allows for the supraorbital nerve to provide sensory function to the nose and a large part of the upper eyelids, and the superciliary arch ...
What is the function of the frontal bone?
The primary functions of the frontal bone are to protect the brain and support the structures of the head, such as the nasal passages and eyes. In between the brain and frontal bone is cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid is in between the meninges, which surround the brain. These padded layers and cerebrospinal fluid keep the brain safe, ...
What are the symptoms of a fractured frontal bone?
Other anatomical variations of the frontal bone include a fracture anywhere within the bone itself, which is usually diagnosed by one of the following signs: Pain. Swelling. Facial asymmetry.
How many articulating bones are there in the frontal bone?
The frontal bone is also surrounded by seven articulating bones to create joints.
What are the hollow spaces in the skull called?
Deep to the supraorbital ridges is a pair of hollow spaces known as the frontal sinuses . The frontal sinuses connect to the nasal cavity and, like the nasal cavity, are lined with mucous membrane. The exact function of the frontal sinuses is not certain, but it is believed that they reduce the weight of the skull by being hollow and increase the resonance of the skull to improve vocal tone.
What is the frontal bone?
The frontal bone is a bone of the skull found in the forehead region. It is one of eight bones that form the cranium, or brain case. The frontal bone plays a vital role in supporting and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the brain. It gives shape to the skull and supports several muscles of the head.
What bone forms the roof of the orbits and the brow?
Continued From Above... At its inferior border, the frontal bone forms the roof of the orbits and the brow. The coronal suture forms the posterior boundary of the frontal bone where it meets the parietal bones. Several important landmarks are found on the frontal bone.
What is the function of the frontal bone?
The primary functions of the frontal bone are the protection of the brain and the support of the structures of the head. The hard mineral matrix of the frontal bone provides protection for the soft brain tissue. Although the frontal bone follows the ridges of the brain very closely, a small gap between the frontal bone and brain houses the meninges and the cerebrospinal fluid of the cranium. The pressure exerted by cerebrospinal fluid on the interior of the cranium holds the brain in place and prevents the brain from colliding with the skull.
Where is the midsagittal suture located?
A midsagittal suture is often present in the glabella and squamous region , especially in infants and young children. This frontal suture is indicative of the frontal bone’s prenatal development from two individual fetal bones. The interior surface of the frontal bone contains many shallow depressions and slight ridges that follow the contours ...
Which muscle is responsible for keeping the brain in place?
The pressure exerted by cerebrospinal fluid on the interior of the cranium holds the brain in place and prevents the brain from colliding with the skull. Two major muscles of the face — the temporalis and orbicularis oculi — form origins on the frontal bone. The frontalis muscle, which forms the frontal belly of the epicranius muscle, ...
Which bone is the frontal crest?
The interior surface of the frontal bone contains many shallow depressions and slight ridges that follow the contours of the frontal lobe of the brain. A long, straight, midsagittal ridge known as the frontal crest extends from the frontal bone to follow the longitudinal fissure of the brain until it merges with the crista galli of the ethmoid bone at its inferior end.
How many bones are in the skull?
The skull is a complicated mechanical construction that consists of 28 bones, connected by sutures of different structural types – from teeth-like hardness to smooth (face cranium). The neurocranium forms the cranial cavity which protects and surrounds the brain. It is formed from the occipital bone, two parietal bones, two temporal bones, ...
What are the symptoms of a head injury?
Common symptoms of a head injury may include: lightheadedness; seizures; coordination or balance problems; nausea; a spinning sensation; abnormal eye movements; temporary ringing in the ears; vomiting;
Why does my fetal skull deform?
The precise cause is usually unknown, however, it has been suggested that, due to the cartilaginous nature of the fetal skull, compression by maternal pelvis or fetal limbs during delivery could result in skull deformation.
What are the most common types of head injuries?
physical assaults; accidents at work, home, outdoors, mountain climbing, or while playing specific sports. Concussions are the most frequent type of sports-related head injury with over 3 million sports-related concussions every year. Common symptoms of a head injury may include: lightheadedness; seizures;
What happens when you blow your head?
Head injuries caused by a blow to the head are typically associated with: falls; motor vehicle accidents;
What does it mean when you can't focus your eyes?
an inability to focus the eyes; a loss of consciousness; memory loss; a persistent headache; changes in mood; leaking of clear fluid from the nose; a loss of muscle control; serious disorientation.
Where is the tender spot on the skull?
Leavey explains, “Lacking a direct cause for a tender spot, such as being hit over the noggin with an object or suffering a fall, the vast majority of these pains are located in the relatively thin layer of skin and muscle that covers the skull.
What does it feel like to have a tender spot on your head?
The tender spot on your head, don’t be surprised, feels like the same kind of tenderness you might feel in a specific spot on your shin, where that same pressure phenomenon can occur, since there’s not much “meat” between the skin and the shin bone.
What does it mean when your skull is depressed?
A depressed fracture means that a part of your skull has been crushed in toward your brain. This kind of injury requires emergency medical treatment. Any significant head injury should be immediately evaluated by a doctor.
How to treat a depressed skull?
Bone fragments will need to be removed from the area around your brain to prevent brain damage. These types of fractures are also treated with medication for pain relief and antibiotics to prevent infection.
What does it mean when you have a dent in your head?
A dent in your head (also known as a skull depression) can indicate several medical conditions. It can also be genetic or happen because of an injury.
How long does it take for a baby to heal from a dent in the skull?
When a baby is born with a head dent or skull abnormality, the symptoms will usually resolve on their own within 6 months.
What causes bone loss in the skull?
Gorham’s disease is a rare condition that leads your bone mass to be replaced by other kinds of tissue. Gorham’s disease can cause bone loss in your skull, leading to a visible dent in some cases.
What are the symptoms of a dent in the skull?
Take note of any other symptoms, like headaches, memory loss, and vision difficulties, that could be connected to a dent in your skull. Last medically reviewed on October 21, 2019.
What to do if you have a tumor on your skull?
Treatment for cancerous tumors. In the rare case that the irregular shape of your skull reveals a malignant tumor, you will need cancer treatment. Surgery will likely be required to get rid of the cancerous tumor. The treatment you need after surgery will depend on what kind of cancer you have and how aggressive the treatment needs to be.