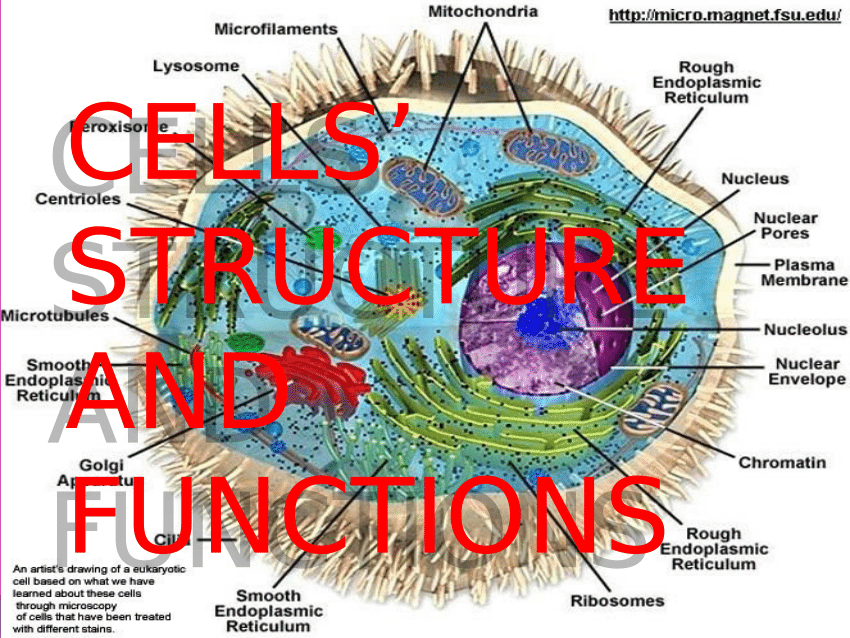
What is the structure of the cell that surrounds the organelles?
Cytoplasm, a jelly-like fluid, surrounds the organelles and the cell’s nucleus, which is a structure that contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each organelle has a certain job to perform within the cell. Types of organelles include:
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is often referred to as the control center, or brain, of the cell and contains the DNA, or genetic material. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope. For more information on DNA, see section “ DNA Definition. ”.
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton also helps guide the movement of the organelles, which are structures within the cell that execute certain functions.
Which organelle is responsible for sorting, processing, and transporting proteins and lipids?
Endoplasmic reticulum – assists with sorting, processing and transportation of protein and lipid molecules. It is the largest organelle. Golgi apparatus – bundles molecules (such as proteins and lipids) processed by the endoplasmic reticulum and transports them out of the cell.
What are the basic building blocks of life?
A cell is the basic building block of human life. The human body consists of trillions of cells. Human cells are comprised of many parts, each of which have specific functions. The cytoskeleton consists of a network of fibers that helps to retain a cell’s shape and allows the cell to move. The cytoskeleton also helps guide the movement of the organelles, which are structures within the cell that execute certain functions. Cytoplasm, a jelly-like fluid, surrounds the organelles and the cell’s nucleus, which is a structure that contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each organelle has a certain job to perform within the cell. Types of organelles include: 1 Endoplasmic reticulum – assists with sorting, processing and transportation of protein and lipid molecules. It is the largest organelle. 2 Golgi apparatus – bundles molecules (such as proteins and lipids) processed by the endoplasmic reticulum and transports them out of the cell. 3 Mitochondrion – converts food into energy that the cell can use and synthesizes adenosine triphosphate by a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell. 4 Ribosome – creates proteins for use inside and outside the cell. 5 Lysosome and peroxisome – digest foreign bacteria in the cell, rid the cell of toxic materials and recycle worn out cell components. These organelles act as the recycling center of the cell.
What are humans made of?
Humans are very complex organisms that are made of a wide range of types of cells and structures. Some of them differ from a typical eukaryotic type of cells and some of them are not even strictly part of us. Nevertheless, all of them work in unison to create a sophisticated organism that is us.
Why are most cells prokaryotic?
Most the cells in the human body are prokaryotic because there are much more bacteria than human cells ( which are eukaryo tic) in the human body .
What organelle produces ATP?
Note that eukaryotic cells contain hundreds of copies of tiny organelles called Mitochondria (that breakdown sugar molecules and produce ATP molecules). These evolved from ancestral free-living prokaryote cells. Mitochondria are bacteria sized, have an outer membrane, and retain some of their own DNA, which is separate from the nuclear DNA, and reproduce by binary fission as their distant ancestors did.
How do biofilms form?
Biofilms form when microbes secrete a polymeric slime that acts as an adhesive, holding them to either an animate or inanimate object. More cells come along and attach themselves to the same secretion and the multicellular unit builds from there through further polysaccharide secretions, recruitment of new cells and cell division.
What is the role of genes in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells specialize by activating a much smaller subset of genes. This allows stem cells to differentiate into different kinds of blood cells, for example.
How do multicellular cells communicate?
The multicellular unit communicates internally and works together as a group. For example some cells of the group are primarily secreting adhesive polymers and holding on to an intestinal wall, while others gather nutrients from the bloodstream as well as other biological building blocks such as fibrils for further connectivity.
Which organelle provides energy for cells?
Mitochondria, the organelles that provide energy for cells are thought to originate from free-living prokaryotic organisms that became endosymbionts of an archaeal ancestor of eukaryotes but lost the ability to live without their host. They are now an integral part of our cells.
How big are eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells, ranging from around 10 to 100 μm in diameter. While many eukaryotes consist of multiple cells, there are also single-celled eukaryotes. 2. Animal cells are supported by a cytoskeleton, use mitochondria to generate energy, and use lysosomes to help remove waste.
What are plant and animal cells?
A look at animal and plant cells. 1. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have nuclei. Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus —an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope —where DNA is stored. There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such ...
What organelle does a plant cell use?
Plant cells have a cell wall and use organelles called chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis. Download Cell Lab Activities. Like animal cells and other eukaryotic cells, plant cells have a nucleus that stores their DNA. However, plant cells differ from animal cells in several important ways.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm of animal cells is filled with a variety of organelles that help the cells survive and reproduce. Here are some key cytoplasm-dwelling organelles and their functions: Organelle. Function.
Why do animals have organelles?
Animal cells contain a wide variety of organelles to help them carry out their functions.
Which part of the cell is not ribosome?
Smooth endoplasmic reti culum. Separate from the nuclear membrane, but continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and does not contain ribosomes; site of lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and detoxification; helps transport materials within the cell. Vesicles.
Do animal cells have a cell wall?
For one, animal cells don’t have a cell wall. Instead, they have a cytoskeleton, a network of filaments composed of proteins. The cytoskeleton provides support and internal transport for the cell. In addition, most animal cells have a nucleus, a special organelle that stores DNA.
Why are human cells considered eukaryotes?
All human cells are considered eukaryotes, this is because their genetic material is in the form of chromosomes within a nucleus envelope. The definition of a prokaryote is a single cell organism that does not have a distinct nucleus. Another way in which eukaryotes differ is that eukaryotes also contain organelles, such as mitochondria, ...
What is the function of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells specialize by activating a much smaller subset of genes. This allows stem cells to differentiate into different kinds of blood cells, for example. Humans, as well as other animals, plants, and fungi are all eukaryotes. Eukaryotes organisms are composed of cells with membrane bound nuclei.
What is the jelly like liquid that helps organelles to operate within the cell?
Cytoplasm, the jelly like liquid helps the organelles to operate within the cell, and contains the genetic material. However eukaryotic genetic material, known has deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is contained within the nucleus. Most prokaryotes have a flagella with helps with their movement.
Which organisms are created by prokaryotic cells?
Organism that are created with prokaryotic cells are bacteria and archaea. However each cells hold similar attributes. Example, eukaryotes and prokaryotes both contain a plasma membrane, this prevents extracellular materials entering the cell.
Which cell type has a nucleus?
EuKaryotes = Cells with a ‘true nucleus’ and membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. ProKaryotes = Cells with ancient packaging for the genetic material in the absence of a true nucleus (see above). Examples include bacteria, archaebacteria. So human cells have the eukaryotic organization.
Where are genes found in eukaryotic cells?
This means that their genetic material is separated from the cytoplasm in the rest of the cell, and is found in the nucleus. The large amount of genes present in eukaryotic cells means that each cell of an individual organism has a complete copy of all that species’ genes.
Which organisms have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles?
Mitochondria are bacteria sized, have an outer membrane, and retain some of their own DNA, which is separate from the nuclear DNA, and reproduce by binary fission as their distant ancestors did. EuKaryotes = Cells with a ‘true nucleus’ and membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.
What is an eukaryotic cell?
What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
Eukaryotic cells are exclusively found in plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, and other complex organisms. The examples of eukaryotic cells are mentioned below:
Which structure is found only in plant cells?
These are double-membraned structures and are found only in plant cells. These are of three types: Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis. Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red, or orange colours.
What is the membrane that separates cells from the outside environment?
Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
Why do animals have different shapes?
These do not have cell walls. Instead, they have a cell membrane. That is why animals have varied shapes. They have the ability to perform pha gocytosis and pinocytosis.
Why are cells called powerhouses?
These are also known as “powerhouse of cells” because they produce energy.
Which cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane.
What is the purpose of the sketch of an eukaryotic cell?
and Audesirk& Audesirk. It is intended to show the types of organelles in cells, although no single cell is expected to have all these organelles.
How many trillions are there in the human body?
Typical quoted numbers for cells in the human body are in the 10s of trillions, or in excess of 10 trillion or 1013. This on the order of a hundred times the estimated 200 billion or 2 x 1011stars in our galaxy.
What are living things made of?
Living things are made up of distinct units called cells. Multicellular animals including humans are made up of complex cells with multiple internal organelles. These cells are called eukaryotic cells. Single cell organisms are often referred to as microbes. Single-celled organisms like bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells. There are other prokaryotic cells which exhibit enough differences from bacteria to be classified as a separate Domain Archaea or the Archaebacteria.
Which cell is most visible to the naked eye?
Eukaryotic Cells. Most of the life that is visible to the naked eye is made up of eukaryotic cells. These cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus, and many eukaryotic cells have multiple membrane-bound organelles to carry out specific cell tasks.
Is a single cell a prokaryotic cell?
Single-celled organisms like bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells. There are other prokaryotic cells which exhibit enough differences from bacteria to be classified as a separate Domain Archaea or the Archaebacteria. All cells have genes, organelles, a cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Index. Cell Concepts.
How many cells does the human body make?
It’s difficult to measure exactly how many cells your body makes on any given day. The lifespan of each of the 200 types of cells varies considerably, so not every type of cell is produced at an equal rate.
How many cells were found in the human body?
Once they arrived at an estimate of all the different cell types, they added them all together. The number they arrived at was 30 trillion.
How many bacteria are there in the human body?
New data show that the number of bacterial cells inside a human body is around 38 trillion. This turns out to be much closer to the estimated 30 trillion human cells in the body.
What are the different types of cells?
There are about 200 different types of cells in the body. Here are just a few examples: 1 red blood cells (erythrocytes) 2 skin cells 3 neurons (nerve cells) 4 fat cells
What are the three types of blood cells?
There are three types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells (RBCs) are by far the most abundant type of cell in the human body, accounting for over 80 percent of all cells.
How many neurons are there in the brain?
There are roughly 171 billion cells in the average male brain according to new research, including about 86 billion neurons. Trusted Source. . Neurons are cells that help transmit signals throughout the brain. There are also 85 billion other cells in the brain, called glial cells, that help support the neurons.
What is the difference between the 200 different types of cells in the human body?
For this reason, each of the 200 different types of cells in the body has a different structure, size, shape, and function, and contains different organelles. For example: