What are some examples of reflexes in the nervous system?
somatic reflex examples Some examples of the somatic nervous system include: the blinking reflex, knee jerk reflex, gag reflex, and the startle reflex and rooting reflex in infants. autonomic reflex examples An example of a monosynapticreflex is the patellar (knee jerk) reflex.
What is an example of somatic nervous system?
Some examples of the somatic nervous system include: the blinking reflex, knee jerk reflex, gag reflex, and the startle reflex and rooting reflex in infants. autonomic reflex examples An example of a monosynapticreflex is the patellar (knee jerk) reflex.
What are the different types of somatic reflexes?
There are several somatic reflexes, with the most common categories of somatic reflexes including the stretch reflex, inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex. The stretch reflex, or tendon reflex, is one of the simplest monosynaptic reflexes (reflexes that have only one synapse between the afferent and efferent neurons ).
How are somatic reflexes activated?
To produce the action, the somatic reflex arc is activated when a signal from the stimulus is sent to the muscle cells, passing through afferent neurons to the CNS, and finally, to the efferent neurons. The most common categories of somatic reflexes include the stretch reflex, the inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex.
What are the somatic reflexes?
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
Why are somatic reflexes routinely assessed?

What type of reflex is the knee jerk?
stretch reflexThe patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord.
Are reflexes somatic or autonomic?
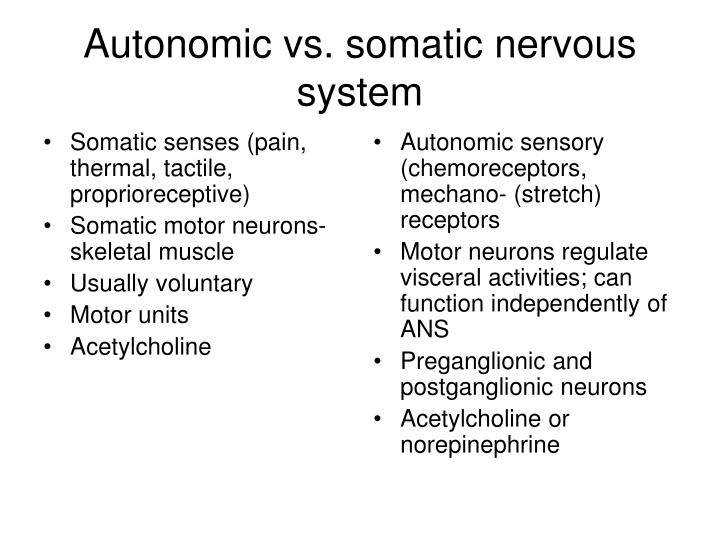
Reflexes can be categorized as either autonomic or somatic. Autonomic reflexes are not subject to conscious control, are mediated by the autonomic division of the nervous system, and usually involve the activation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
Which reflexes are somatic?
The most common categories of somatic reflexes include the stretch reflex, the inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex. Somatic reflexes have myelinated axons connecting the CNS to the skeletal muscle cells.
Which nervous system is responsible for knee jerk?
Although the knee jerk reflex is mediated by the L3 and L4 nerve roots, evidence exists that altered knee jerk expression may occur with exclusively L5 radiculopathy.
What are the 4 somatic reflexes?
In our discussion we will examine four major reflexes that are integrated within the spinal cord: the stretch reflex, the Golgi tendon reflex, the withdrawal reflex and the crossed extensor reflex.
What are examples of autonomic reflexes?
Everyday examples include breathing, swallowing, and sexual arousal, and in some cases functions such as heart rate.
What is the response in knee-jerk reflex?
knee-jerk reflex, also called patellar reflex, sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon, which lies just below the kneecap.
What is an example of a somatic response?
One common example is the knee reflex: hitting the patellar tendon just below the knee cap with a reflex hammer leads to an automatic contraction of the quadriceps – which results in the lower leg kicking out.
Are there autonomic reflexes?
Autonomic reflexes are moderated and coordinated in a hierarchical, integrated fashion by three subsystems of the autonomic nervous system: The parasympathetic system, The sympathetic system, and. The system managed by the non-myelinated vagus nerve.
Is knee-jerk a conditioned reflex?
Knee-jerk is an unconditioned reflex action.
What causes your knee to jerk?
0:351:532-Minute Neuroscience: Knee-jerk Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe knee-jerk reflex is a simple reflex arc that occurs at the level of the spinal cord. In otherMoreThe knee-jerk reflex is a simple reflex arc that occurs at the level of the spinal cord. In other words the Associated movement occurs without the involvement of the brain. The brain receives
What happens in a knee-jerk reflex quizlet?
Tapping the patellar ligament stretches the quadriceps and excites its muscle spindles. Afferent impulses (blue) travel to the spinal cord, where synapses occur with motor neurons and interneurons. The motor neurons (red) send activating impulses to the quadriceps causing it to contract, extending the knee.
Are reflexes a part of the autonomic nervous system?
Autonomic nervous system function is based on the visceral reflex. This reflex is similar to the somatic reflex, but the efferent branch is composed of two neurons. The central neuron projects from the spinal cord or brain stem to synapse on the ganglionic neuron that projects to the effector.
Are there autonomic reflexes?
Autonomic reflexes are moderated and coordinated in a hierarchical, integrated fashion by three subsystems of the autonomic nervous system: The parasympathetic system, The sympathetic system, and. The system managed by the non-myelinated vagus nerve.
Are reflexes controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
Autonomic functions include control of respiration, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex actions such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting.
Which reflex is an autonomic reflex?
visceral reflexThe Structure of Reflexes. One difference between a somatic reflex, such as the withdrawal reflex, and a visceral reflex, which is an autonomic reflex, is in the efferent branch.
What is a somatic reflex?
A somatic reflex is an involuntary response to a stimulus, such as pulling one’s hand away after touching a hot stove. The nervous system is split...
What is a somatic reflex arc?
A somatic reflex arc is the neural pathway that occurs from the initial sensing of a stimulus to the response, such as the moving of a limb. The ba...
What are the somatic reflexes?
There are several somatic reflexes, with the most common categories of somatic reflexes including the stretch reflex, inverse stretch reflex, and t...
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
The autonomic reflex and somatic reflex often differ in their efferent branches of the reflex arc and their effector targets. In an autonomic refle...
Why are somatic reflexes routinely assessed?
It is important to assess somatic reflexes because they demonstrate the ability of nerves to respond to stimuli. Each reflex is associated with a f...
What are the most important facts to know about a somatic reflex?
A somatic reflex is an involuntary movement in response to a stimulus. To produce the action, the somatic reflex arc is activated when a signal fro...
Ex.21 Human reflex physiology Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Define reflex, Name five essential components of a reflex arc:, In general what is the importance of reflex testing in a routine physical examination? and more.
Human Reflex Physiology Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like DEFINE REFLEX, NAME FIVE ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS OF A REFLEX, IN GENERAL, WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF REFLEX TESTING IN A ROUTINE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION? and more.
The Role of Somatic Reflexes | somatic nervous system, lifelong motor ...
Protective mechanisms demonstrated by the Moro reflex when, among other things, it alerts caretakers of infant distress.; Restorative mechanisms demonstrated by the Babkin Palmomental reflex when it automatically positions a newborn’s body, face, and mouth for nourishment from the mother’s breast.; Postural reflexes such as the Hands Supporting reflex (also known as the parachute reflex ...
What are some examples of the somatic nervous system?
Some examples of the somatic nervous system include: the blinking reflex, knee jerk reflex, gag reflex, and the startle reflex and rooting reflex in infants.
Where do involuntary stimuli come from?
involuntary stimuli transmitted to skeletal muscles from neural arcs in the spinal cord
What are the somatic reflexes?
There are several somatic reflexes, with the most common categories of somatic reflexes including the stretch reflex, inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex.
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
The autonomic reflex and somatic reflex often differ in their efferent branches of the reflex arc and their effector targets. In an autonomic reflex, the efferent branch typically contains a two-step pathway, where the efferent neuron enters a ganglion (i.e., a bundle of nerve cell bodies) before reaching the effector target. In addition, autonomic reflex axons are only myelinated (i.e., insulated with a fatty sheath) in the CNS. Lastly, the effector target in the autonomic reflex is often smooth muscle cells (e.g., stomach, intestines, and bladder ). In contrast, the somatic reflex pathway contains a myelinated axon connecting from the spinal cord directly to the effector target, which is often skeletal muscle .
Why are somatic reflexes routinely assessed?
It is important to assess somatic reflexes because they demonstrate the ability of nerves to respond to stimuli. Each reflex is associated with a few cranial or spinal nerves. There are twelve cranial nerves that each connect from the brain to a specific area of the head, neck, and trunk. Therefore, a lack of response in a specific reflex may indicate an underlying issue with a nerve, such as a herniated disk. Additionally, if multiple reflexes are affected, a systemic disease, such as diabetes mellitus and thyroid disorders, may be present.
