
Full Answer
What bones make up the axial skeleton?
This includes bones in your skull (cranial and facial bones), ears, neck, back (vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone) and ribcage (sternum and ribs). Your axial skeleton protects your brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs and other important organs.
What is the thickest part of the manubrium?
Thus, the thickest part of the manubrium is that region extending between the clavicles that serves to withstand the transmission of forces from the upper appendicular to the axial skeleton. The sternocleidomastoid muscles arise from the front of the manubrium, superior to the attachment for the pectoral muscles.
How does the manubrium articulate with the sternum?
The manubrium articulates with the body of the sternum by way of the manubriosternal joint at the angle of Louis. The manubriosternal joint is a fibrocartilaginous joint or synchondrosis, which lacks a true joint cavity. The joint allows protraction and retraction of the thorax.
What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton?
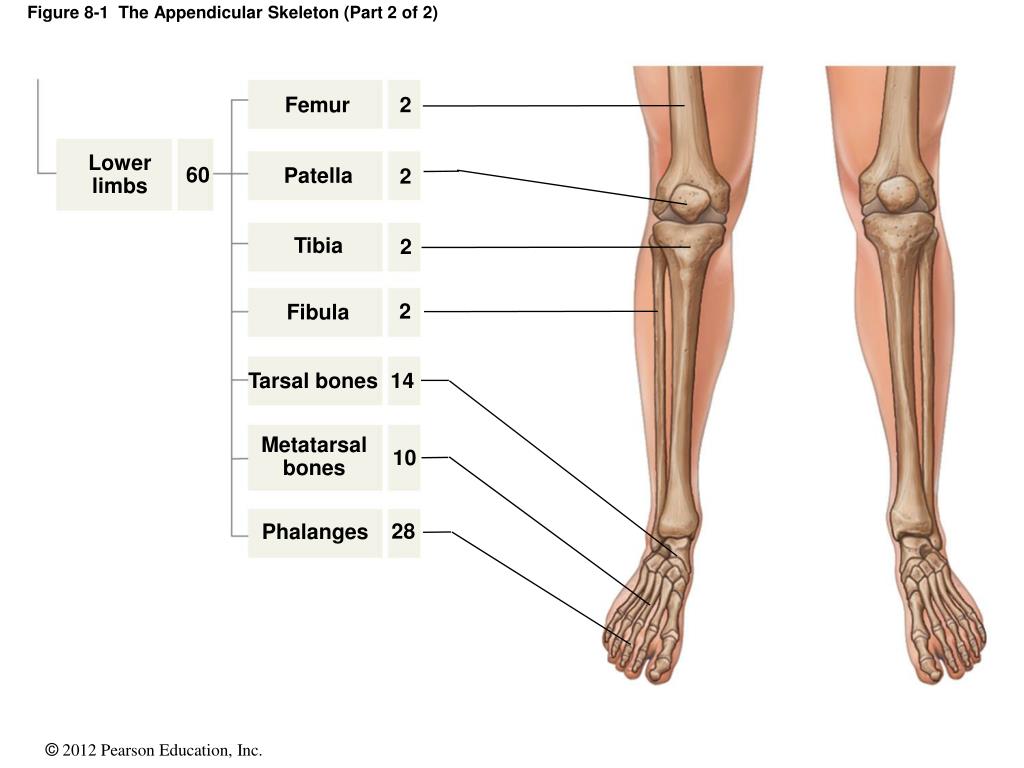
Your axial skeleton is made up of the bones in your head, neck, back and chest. Your appendicular skeleton is made up of everything else — the bones that attach (append) to your axial skeleton. Your appendicular skeleton includes the bones in your shoulders, pelvis and limbs, including your arms, hands, legs and feet.
Which is not part of the axial skeleton?
Answer and Explanation: The b. Pelvic girdle is NOT part of the axial skeleton.
What bones are part of the axial skeleton?
Your axial skeleton is made up of the 80 bones within the central core of your body. This includes bones in your skull (cranial and facial bones), ears, neck, back (vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone) and ribcage (sternum and ribs).
Does axial skeleton have sternum?
The 80 bones of the axial skeleton form the vertical axis of the body. They include the bones of the head, vertebral column, ribs and breastbone or sternum.
Is the sternum part of the axial skeleton or the appendicular skeleton?
axial skeletonThe sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the centre of the chest. It connects to the ribs through cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage. It belongs to the axial skeleton.
Where is Manubrium found in the body?
The manubrium (Latin for "handle") is the broad upper part of the sternum. It has a quadrangular shape, narrowing from the top, which gives it four borders. The suprasternal notch (jugular notch) is located in the middle at the upper broadest part of the manubrium. This notch can be felt between the two clavicles.
What 4 parts make up the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton includes the bones that form the skull, laryngeal skeleton, vertebral column, and thoracic cage.
Which bone is not part of the axial skeleton quizlet?
Which of the following is NOT part of the axial skeleton? Upper limbs are part of the appendicular skeleton, which is composed of the humerus, radius, and ulna. The humerus attaches to the pectoral girdle, which is composed of the scapula and clavicle. These attach to the axial skeleton at the sternum.
What 3 things make up the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate animal, including humans. The primary divisions of the skeleton system are the head, thorax, and vertebral column.
What is included in the axial skeleton quizlet?
The axial skeleton consist of: the skull, hyoid bones, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. the framework that consist of extremities, shoulders, pelvic and gridle.
What are the main components of axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton?
The axial skeleton supports the head, neck, back, and chest and thus forms the vertical axis of the body. It consists of the skull, vertebral column (including the sacrum and coccyx), and the thoracic cage, formed by the ribs and sternum. The appendicular skeleton is made up of all bones of the upper and lower limbs.
What is divided into the axial and appendicular?
The axial skeleton forms the vertical axis of the body and includes the bones of the head, neck, back, and chest of the body. It consists of 80 bones that include the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs.
What are the bones under the axial and appendicular divisions?
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton It consists of the skull, vertebral column (including the sacrum and coccyx), and the thoracic cage, formed by the ribs and sternum. The appendicular skeleton is made up of all bones of the upper and lower limbs.
What are the 3 main parts of the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the human body and consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage.
What bones are found in the axial skeleton quizlet?
The axial skeleton consist of: the skull, hyoid bones, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum.
Which bone is not part of the axial skeleton quizlet?
Which of the following is NOT part of the axial skeleton? Upper limbs are part of the appendicular skeleton, which is composed of the humerus, radius, and ulna. The humerus attaches to the pectoral girdle, which is composed of the scapula and clavicle. These attach to the axial skeleton at the sternum.
What part make on the appendicular skeleton?
The bones of the appendicular skeleton make up the rest of the skeleton, and are so called because they are appendages of the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs.
Where is the manubrium located?
In the living, the manubrium is to be found at the level of the third and fourth thoracic vertebrae and forms the anterior boundary of the superior mediastinum. The immediate relations of the upper part are therefore the thymus, left brachiocephalic vein and the brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, while its lower part is closely related to the arch of the aorta. Due to its close association with the major arteries, the manubrium can bear some evidence of arterial pathologies such as aneurysms ( Kelley, 1979a; Ortner and Putschar, 1985 ). The lateral boundaries of the manubrium come into direct contact with the parietal pleurae ( Fig. 8-2B ). It is interesting to note that at birth, the superior margin of the manubrium lies opposite the body of the second thoracic vertebra and so it is one to one-and-a-half vertebral levels higher than its final adult position ( Crelin, 1973 ).
What is the lateral border of the manubrium?
The lateral borders of the manubrium are each marked by a depression for the articulation with the first costal cartilage above (a primary cartilaginous joint) and a small demifacet for articulation with the upper half of the second costal cartilage below (a synovial joint).
What is the clinical syndrome of the manubrium?
The Clinical Syndrome. The manubrium articulates with the body of the sternum by way of the manubriosternal joint at the angle of Louis. The manubriosternal joint is a fibrocartilaginous joint or synchondrosis, which lacks a true joint cavity. The joint allows protraction and retraction of the thorax.
What causes manubriosternal joint pain?
Pain originating from the manubriosternal joint can mimic pain of cardiac origin. The manubriosternal joint is susceptible to the development of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter's syndrome, and psoriatic arthritis. The joint can also be traumatized during acceleration-deceleration injuries and blunt trauma to the chest ( Fig. 62.1 ). With severe trauma, the joint may subluxate or dislocate. Overuse or misuse can result in acute inflammation of the manubriosternal joint, which can be quite debilitating. The joint is also subject to invasion by tumor from primary malignant tumors, including thymoma, or from metastatic disease. Rarely, septic arthritis of the manubriosternal joint can occur ( Fig. 62.2 ).
Where do the sternocleidomastoid and sternohyoid muscles attach?
Both the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles take their attachment from the posterior surface, which is relatively featureless and concave both from side to side and from above to below.
Which part of the sternum is most likely to survive inhumation?
The manubrium . The manubrium is the thickest and strongest portion of the sternum and is therefore the area that is most likely to survive inhumation.
How rare are manubrial fractures?
Fractures of the manubrium are relatively rare (0.5% incidence) and most commonly arise following direct violence. There is no doubt that prior to the compulsory introduction of car seat belts in the UK, manubrial fractures following impact with the steering wheel were more common ( Helal, 1964 ).
