What are the 7 types of bones?
List of Bones in the Human Body
- Bones at a Glance. Would you like to write for us? ...
- Frontal Bone. This bone forms the forehead, the roof of the orbital cavity (eye socket), and the root of the nose.
- Parietal Bones. ...
- Temporal Bones. ...
- Occipital Bone. ...
- Sphenoid Bone. ...
- Ethmoid Bone. ...
- Facial Bones at a Glance. ...
- Mandible. ...
- Maxilla. ...
What do bones do the maxilla articulate with?
[3] The maxilla connects with surrounding facial structures through four processes: alveolar, frontal, zygomatic and palatine. It articulates superiorly with the frontal bone, the zygomatic bone laterally, palatine bone posteriorly and with the upper teeth through the alveolar process inferiorly.
Which type of bone is considered dense bone?
- Hyaline cartilage is the most common type and is found in areas such as the trachea, ribs, and nose. ...
- Fibrocartilage is the strongest type of cartilage and composed of hyaline and dense collagen fibers. ...
- Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers and is the most flexible type of cartilage. ...
Which bone is between femur and tibia?
The knee joint is where the tibia and femur meet. Running parallel to the tibia is the fibula, the thinner and weaker bone of the lower leg. It is also known as the calf bone, as it sits slightly...
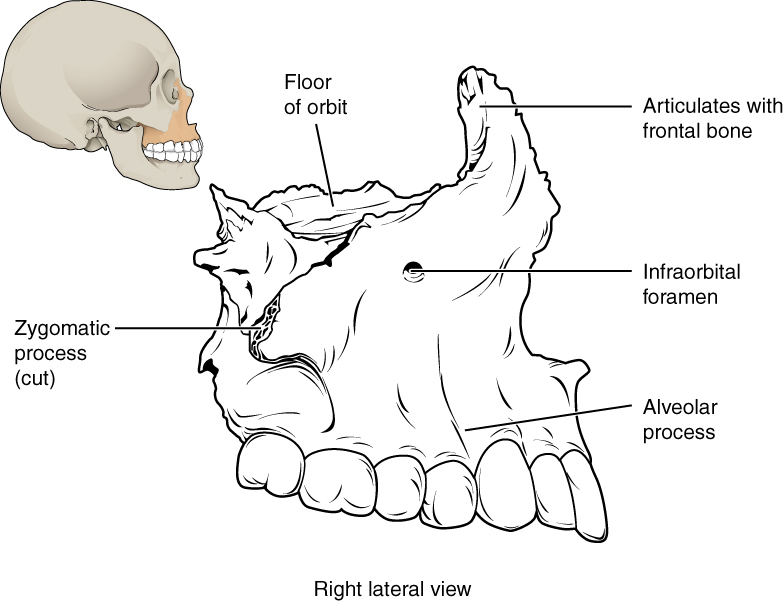
Is the maxilla 1 or 2 bones?
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. The maxilla (plural: maxillae /mækˈsɪliː/) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth.
Is the maxilla facial bone?
The primary bones of the face are the mandible, maxilla, frontal bone, nasal bones, and zygoma. Facial bone anatomy is complex, yet elegant, in its suitability to serve a multitude of functions. The image below provides an overview of the anterior features of the skull.
What bone type is maxilla?
irregular facial boneThe answer to the question, “What type of bone is the maxilla bone?” is simple – it is an irregular facial bone. You can refer to the maxilla bone as a single unit or as two paired but fused bones.
What are the 2 maxilla bones?
The two maxilla or maxillary bones (maxillae, plural) form the upper jaw (L., mala, jaw). Each maxilla has four processes (frontal, zygomatic, alveolar, and palatine) and helps form the orbit, roof of the mouth, and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity.
What are the 8 facial bones?
Facial BonesMaxilla (2)Zygomatic (2)Mandible (1)Nasal (2)Platine (2)Inferior nasal concha (2)Lacrimal (2)Vomer (1)
Which bone is not a facial bone?
The sphenoid bone is a cranial bone and NOT a facial bone. The facial bones include vomer, nasal bones...
Is the maxilla a irregular bone?
The irregular bones are: the vertebrC&, sacrum, coccyx, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid.
What type of bone is the maxilla and mandible?
Alveolar bone is that part of the maxilla and mandible which supports the teeth by forming the “other” attachment for fibres of the periodontal ligament (Fig. 1.148). It consists of two plates of cortical bone separated by spongy bone (Fig. 1.149).
What does maxilla consist of?
[3] The maxilla connects with surrounding facial structures through four processes: alveolar, frontal, zygomatic and palatine. It articulates superiorly with the frontal bone, the zygomatic bone laterally, palatine bone posteriorly and with the upper teeth through the alveolar process inferiorly.
How many maxillofacial bones what are they?
The remainder of the skull is the braincase. The fourteen bones that form the human facial skeleton. The fourteen facial bones.
What is mandible and maxilla?
The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull. It holds the lower teeth in place, it assists in mastication and forms the lower jawline. The mandible is composed of the body and the ramus and is located inferior to the maxilla. The body is a horizontally curved portion that creates the lower jawline.
What is the maxilla?
The maxilla is a bone which helps to make up the skull. It is specifically located in the mid face, forms the upper jaw, separates the nasal and oral cavities, and contains the maxillary sinuses (located on each side of the nose. One of the maxilla's most important functions is to make up the architecture of our faces and to support the rest ...
Where is the maxilla located?
The maxilla is centrally located within the skull and makes up the center of the face. The lower portion of the maxilla is connected to the upper teeth through the alveolar process. The roots of the teeth form grooves that extend up the anterior portion of the maxilla.
Why is the maxilla important?
Since it houses the upper teeth and forms a portion of the jaw, the maxilla is necessary for the process of mastication (chewing) and speaking. The mucous membrane lining the maxillary sinuses function to warm and humidify the air we breathe and to produce mucus, which functions as an immune defense.
What part of the mouth houses the upper teeth?
The maxilla houses the upper teeth, forms the roof of the mouth (palate), and also the lower portion of the orbit (bones that surround and house the eyes).
Which part of the maxilla articulates with zygomatic bone?
The palatine process also consists of the superior nasal foramina. The most lateral portion of the maxilla is called the zygomatic process because it articulates with zygomatic bone and forms the inferior orbital rim (just below the eye).
How to heal a fractured maxilla?
If the fracture is small and not extensive it may heal in time with rest, a soft diet, and pain medication. Larger more extensive fractures of the maxilla may need to be surgically repaired, especially if trauma to surrounding nerves or blood vessels has been sustained. 6 .
Which part of the maxilla articulates with the frontal bone superiorly and the nasal bones medially?
The portion of the maxilla which articulates with the frontal bone superiorly and the nasal bones medially is referred to as the frontal process. The frontal process forms several important structures including the nasolacrimal groove, the lower center of the forehead (the area in between but just below the eyebrows), and the nasal bridge. ...
How does the maxilla form the upper jaw?
The maxilla forms the upper jaw by fusing together two irregularly-shaped bones along the median palatine suture, located at the midline of the roof of the mouth. The maxillary bones on each side join in the middle at the intermaxillary suture, a fused line that is created by the union of the right and left ‘halves’ of the maxilla bone, thus running down the middle of the upper jaw. The bones help to form the upper jaw, sub-segments of the eye sockets, and the lower sections and sides of the nasal cavity. Additionally, they reduce the heaviness of the skull, help support the back teeth, and help to allow the voice to resonate.
What are the processes of the fused bones?
Each half of the fused bones contains four processes. These include the zygomatic, frontal, palatine, and alveolar processes of the maxilla.
What is the maxilla bone?
The maxilla bone or maxillary bone is a fused (paired) bone that provides part or all of the bony structure of the eye sockets, the nasal passage, the hard palate, the left and right maxillary sinuses, and the upper tooth sockets. It is the second-largest facial bone. Without the maxilla, we can neither eat properly nor speak clearly. The maxilla bone is composed of a main body with four processes or projections. It borders with nine facial and cranial bones.
What Type of Bone is the Maxilla Bone?
The answer to the question, “What type of bone is the maxilla bone?” is simple – it is an irregular facial bone. You can refer to the maxilla bone as a single unit or as two paired but fused bones.
How to feel maxilla bone?
The maxilla bone extends approximately one-third of the way along either cheek. If you press into the skin just under one of your cheekbones, you can feel the maxilla bone as it moves down to form the upper jaw. It’s easy to feel the maxilla bone. The maxillary bone is an irregular bone composed of two fused halves.
What is the frontal process of the maxillary bone?
Each rises to meet the frontal bone and each projection is, therefore, called the (right or left) frontal process of the maxilla bone. The below image is a lateral (side) view but the frontal process of the maxillary bone is very visible.
What are the borders of the maxilla?
Labeled: maxilla bone, nasal bones, and zygomatic bones. These borders and bones are: Superior surface border with the frontal bone. Posterior surface border with the ethmoid, palatine, and lacrimal bones. Medial surface border with the opposite maxilla bone, nasal bone, and vomer.
Which turbinates articulate with the inferior surface of the maxillary bone?
The lowest of the three turbinates – the inferior nasal concha – articulates with the inferior surface of the maxillary bone.
Where is the suture on the maxilla?
In the below image, the suture is to the left (red arrow). Where it continues across the frontal bone is the articulation between the nasal and frontal bones. Also take note of the many holes in the frontal bone and at the top of the maxilla border.
Which bones are associated with the maxilla?
The maxilla articulates with numerous bones: superiorly with the frontal bone, posteriorly with the sphenoid bone, palatine and lacrimal bones and ethmoid bone, medially with the nasal bone, vomer, inferior nasal concha and laterally with the zygomatic bone.
How many parts does the maxilla have?
This bone consists of five major parts, one being the body and four being projections named processes (frontal, zygomatic, palatine, alveolar). Bordered by several other bones of the viscerocranium, the maxilla on one side pairs with the corresponding bone on the opposite side via the intermaxillary suture.
What is the largest part of the bone?
The body of the maxilla is the largest part of the bone and shaped like a pyramid. It contributes to the anterior margin and floor of the bony orbit, the anterior wall of the nasal cavity and the inferior part of the infratemporal fossa.
How many ossification centers are there in the maxilla?
All five parts of the maxilla undergo intramembranous ossification through two ossification centers. In the 7th week of fetal life one differentiates between the maxilla and premaxilla (or incisive bone).
Which bone is the inferior part of the nasal cavity?
Inferior: nasal concha. Laterally: zygomatic bone. Body of the maxilla. It contains the maxillary sinuses and contributes to the floor of the orbit, anterior wall of the nasal cavity, and inferior part of the infratemporal fossa. Alveolar process.
Which process contributes to the zygomatic arch together with the zygomatic bone?
It contributes to the zygomatic arch together with the zygomatic bone. Palatine process. It constitutes the roof of the mouth and floor of the nasal cavity. This process also contains the incisive foramen and features an anterior nasal spine.
What is the role of the maxilla?
It is involved in the formation of the orbit, nose and palate, holds the upper teeth and plays an important role for mastication and communication.
What are the two bones that make up the upper jaw?
The two maxilla or maxillary bones (maxillae, plural) form the upper jaw (L., mala, jaw). Each maxilla has four processes ( frontal, zygomatic, alveolar, and palatine) and helps form the orbit, roof of the mouth, and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. Body – central portion of maxilla. [Anterior view/ Lateral view]
Where are the sinuses located?
Maxillary sinuses – two large, pyramidal-shape cavities located in the body of the maxilla bone. Each is lined by mucous membrane, and the mucous secretions drain into the mid-lateral wall of the nasal cavity through a small opening called an ostium. [Coronal view]
Where are the maxillae located?
The maxillae lie just lateral to the nasal cavity and contain the maxillary sinuses. These sinuses, the largest of the paranasal air sinuses, extend from the orbit down to the roots of the upper teeth. Laterally, the maxillae articulate with the zygomatic bones at the zygomatic processes. The maxilla, along with several other bones, ...
What is the function of the maxilla?
The function of the maxilla is to provide protection of the face, support of the orbits, hold the top half of the teeth in place, and form the floor of the nose. The functions of the maxillary sinuses: Imparts resonance to the voice. Increases the surface area and lightens the skull. Moistens and warms inspired air.
What is the maxillary sinus?
The maxillary sinus is the largest of the four bilateral air‐filled cavities in the skull. The maxillary sinus is located in the body of the maxilla and is a pyramidal‐shaped structure having as its base the medial wall (Figure 6). The pyramid has three main processes or projections: (1) the alveolar process inferiorly (bounded by the alveolar ridge), (2) the zygomatic recess (bounded by the zygomatic bone), and (3) the infraorbital process pointing superiorly. The microscopic anatomy of the sinuses reveals four basic cell types: namely, pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, nonciliated columnar cells, goblet cells, and basal cells.
What bones articulate with the zygomatic bones?
Laterally, the maxillae articulate with the zygomatic bones at the zygomatic processes. The maxilla, along with several other bones, forms the borders of the inferior orbital fissure in the floor of the orbit (Figure 1). This fissure transmits several vessels and nerves, including the maxillary nerve ...
What is the largest facial bone?
What is maxilla. The maxillary bone s, or maxillae are the largest facial bones and they form the upper jawbone and the central part of the facial skeleton (see Figure 1). The maxillae form the upper jawbone and meet each other at a median intermaxillary suture.
What is the hard palate?
The hard palate is the bony roof of the mouth, and is formed by the palatine processes of the maxillae and horizontal plates of the palatine bones. The hard palate separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity.
What is the final structure associated with the maxilla and sphenoid bone?
A final structure associated with the maxilla and sphenoid bone is the inferior orbital fissure, located between the greater wing of the sphenoid and the maxilla (see Figure 1).