Where are the frontal lobes of the motor cortex located?
The premotor and primary motor areas of the motor cortex contain nerves that control the execution of voluntary muscle movement. Directionally, the frontal lobes are located in the anterior portion of the cerebral cortex. They are directly anterior to the parietal lobes and superior to the temporal lobes.
What is the function of the motor strip in the brain?
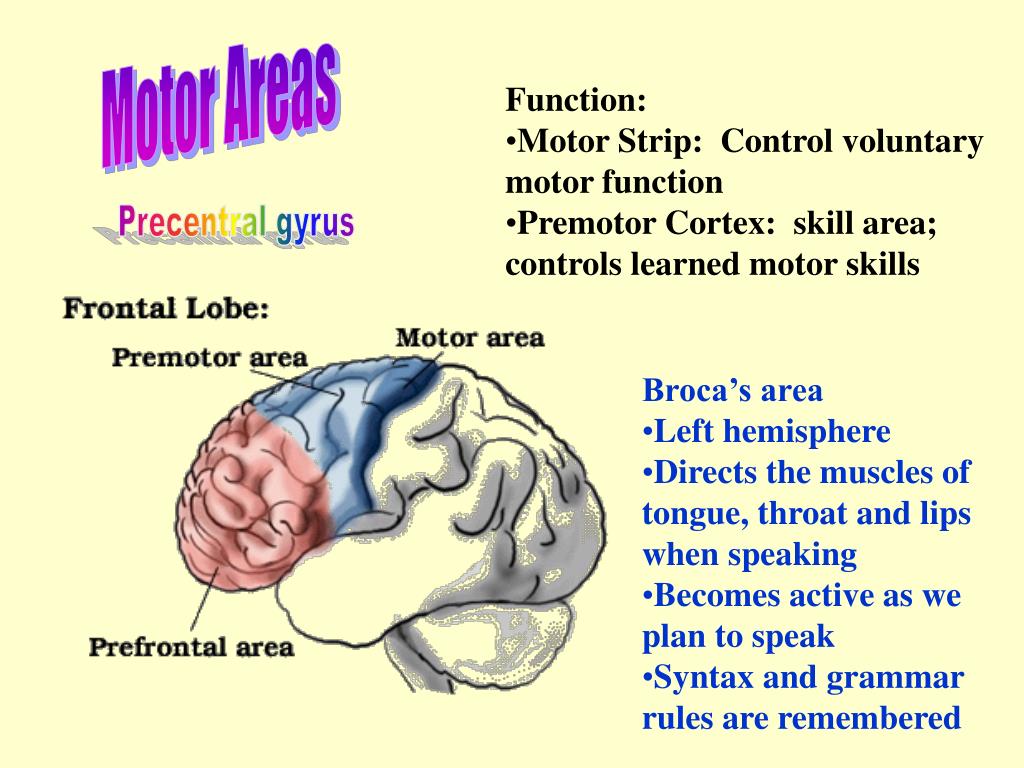
The back of the frontal lobe is a region called the motor strip, which controls and directs the body's voluntary (purposeful) physical movements. The left motor strip controls movement of the right side of the body, while the right motor strip controls movements of the left side of the body.
What are the two main areas of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobes can be subdivided into two main areas: the prefrontal cortex and the motor cortex. The motor cortex contains the premotor cortex and primary motor cortex. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for personality expression and the planning of complex cognitive behaviors.
What is the difference between the left and right motor strip?
The left motor strip controls movements of the right side of the body, while the right motor strip controls movements of the left side of the body. There are also functions that are predominantly controlled by the left frontal lobe or the right frontal lobe.
Is the motor strip part of the frontal lobe?
In the frontal lobe, there are four important gyri. Roughly parallel and anterior to the central sulcus is the Precentral Gyrus (also called the motor strip).
Which lobe is the motor strip?
frontal lobeThe primary motor cortex (Brodmann area 4) is a brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe.
Where is the motor cortex Strip?
frontal lobeThe primary motor cortex is a strip of brain tissue located in the frontal lobe. It is responsible for initiating purposeful and intentional movements. These purposeful movements include everything from moving your hands, arms, and legs to controlling facial expressions and even swallowing.
Is the sensory strip in the frontal lobe?
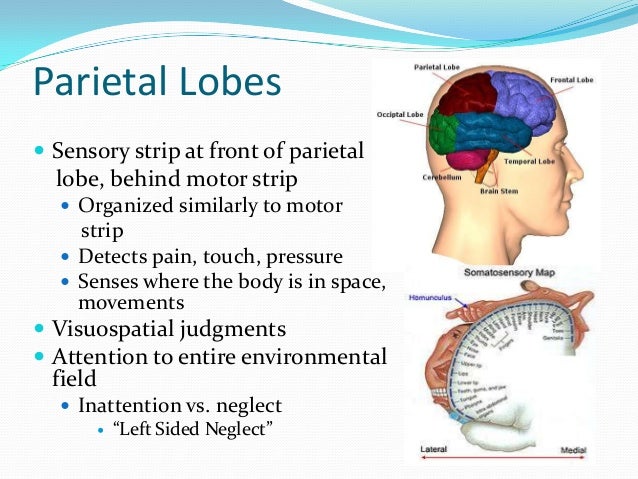
The sensory strip is a part of the brain located in the parietal lobe, near the border of the frontal lobe. The sensory strip is involved in registering sensation that are connected specific body parts or body functions. It is the band of neurons that are embedded in your cerebrum or cerebral cortex .
What's in the frontal lobe of the brain?
The frontal lobe is the part of the brain that controls high-level cognitive skills and primary motor functions. It is the center for our personality and communication abilities. The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes, and it is located at the front of the brain.
What is the sensory motor strip?
The term sensorimotor strip refers to a composite structure of the primary motor cortex and the primary somatosensory cortex. In humans and macaques it is located in portions of the precentral gyrus and the postcentral gyrus, which meet at the floor of the central sulcus ( Anthoney-1994 ).
What is the motor strip in the brain and what does it do?
The area towards the back of the frontal lobe, called the motor strip, helps to control movement. In the left hemisphere, the motor strip controls movement of the right side of the body; in the right hemisphere, it controls movement of the left side of the body.
Is the frontal lobe and frontal cortex the same thing?
The frontal lobe is part of the frontal cortex. It is a part of the brain that plays a role in memory, attention, judgment, and other vital functions. Damage to the frontal lobe can occur as a result of dementia, a traumatic injury, multiple sclerosis, a brain tumor, or a stroke.
What part of the brain contains the motor centers?
frontal lobesThe frontal lobes are the largest of the four lobes responsible for many different functions. These include motor skills such as voluntary movement, speech, intellectual and behavioral functions. The areas that produce movement in parts of the body are found in the primary motor cortex or precentral gyrus.
What part of the brain contains the sensory strip?
parietal lobeThe brain's parietal lobe is located immediately behind the frontal lobe, and is involved in processing information from the body's senses. It contains the somatosensory cortex , which is essential for processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Is the motor and sensory cortex part of the frontal lobe?
The motor cortex is situated within the frontal lobe of the brain, next to a large sulcus called the central sulcus.
Which lobe controls the sensory strip cortex?
The brain's parietal lobe is located immediately behind the frontal lobe, and is involved in processing information from the body's senses. It contains the somatosensory cortex, which is essential for processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
What is the motor strip in the brain and what does it do?
The area towards the back of the frontal lobe, called the motor strip, helps to control movement. In the left hemisphere, the motor strip controls movement of the right side of the body; in the right hemisphere, it controls movement of the left side of the body.
What are the 4 motor areas of the cerebral cortex?
The most intensively studied motor areas, the premotor area (PMA), supplementary motor area (SMA), and primary motor cortex (MI), appear to have different roles in movement. PMA is involved in coupling arbitrary cues to motor acts, whereas SMA appears to participate more in internal guidance or planning of movement.
What are the frontal lobes?
The frontal lobes are one of the four main lobes or regions of the cerebral cortex. They are positioned at the front-most region of the cerebral cortex and are involved in movement, decision-making, problem-solving, and planning. The frontal lobes can be subdivided into two main areas: the prefrontal cortex and the motor cortex.
What are the functions of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobes are the largest brain lobes and are involved in several functions of the body including: 1 Motor Functions 2 Higher-Order Functions 3 Planning 4 Reasoning 5 Judgment 6 Impulse Control 7 Memory 8 Language and Speech
What are the effects of frontal lobe damage?
Damage to the frontal lobes can result in a number of difficulties such as a loss of fine motor function, speech, and language processing difficulties, thinking difficulties, an inability to comprehend humor, a lack of facial expression, and changes in personality. Frontal lobe damage can also result in dementia, memory disorders, ...
Which lobes process visual information?
The occipital lobes process visual information. Temporal Lobes: These lobes are located directly inferior to the parietal lobes and posterior to the frontal lobes. The temporal lobes are involved in a multitude of functions including speech, auditory processing, language comprehension, and emotional responses.
Which lobe of the brain controls speech?
Language and Speech. The right frontal lobe controls activity on the left side of the body and the left frontal lobe controls activity on the right side. An area of the brain involved in language and speech production, known as Broca's area, is located in the left frontal lobe. The prefrontal cortex is the front portion ...
Where is the somatosensory cortex located?
The somatosensory cortex is found within the parietal lobes and is positioned directly posterior to the motor cortex of the frontal lobes. The parietal lobes are involved in receiving and processing sensory information. Occipital Lobes: These lobes are positioned at the back of the skull, inferior to the parietal lobes.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for personality expression?
The motor cortex contains the premotor cortex and primary motor cortex. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for personality expression and the planning of complex cognitive behaviors. The premotor and primary motor areas of the motor cortex contain nerves that control the execution of voluntary muscle movement.
What is the Broca area?
Finally, Broca’s area encompasses the pars opercularis and pars triangularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. It is mainly responsible for expressive motor speech, which involves verbal fluency, phonological processing, grammar processing and attention during speech. Although Broca’s area is mainly associated with language production, it also plays a significant role in language comprehension. Studies have shown that it’s especially important in providing the ability to use syntactic information to determine the meaning of complex and ambiguous sentences.
What is the superior frontal gyrus?
The superior frontal gyrus makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It extends from the rectus gyrus anteriorly to the precentral sulcus posteriorly, which separates it from the precentral gyrus. The superior frontal gyrus is also extended onto the medial surface of the frontal lobe up until the cingulate sulcus, which separates it from the anterior cingulate gyrus . Laterally, it is bounded by the superior frontal sulcus, which also separates it from the middle frontal gyrus.
What are the functions of the frontal lobe?
It is associated with higher cognitive functions, such as decision making, motivation, problem-solving, planning and attention. These functions are carried out mainly by the prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe. It also contains the motor cortex, which is responsible for planning and coordinating voluntary movements. Lastly, the frontal lobe contains the Broca’s area, which is essential for producing the motor component of speech.
What are the cells in the primary motor cortex?
The primary motor cortex contains pyramidal cells, which are types of multipolar neurons found in several other areas of the brain. A portion of the primary motor cortex contains characteristic giant pyramidal cells called Betz cells, whose axons form the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts . The Betz cells and their axons are referred to as the upper motor neurons in these tracts. The pyramidal neurons and the Betz cells are arranged somatotopically, which means that, depending on where in the precentral gyrus they originate, they will supply different regions of the body.
Which lobe extends down to the cingulate sulcus?
On the medial (interhemispheric) surface, the frontal lobe extends down to the cingulate sulcus. From posteriorly to anteriorly, it consists mainly of the paracentral lobule (an extension of the precentral and postcentral gyri), and the medial extension of the superior frontal gyrus.
Which lobe has three cortical surfaces?
The frontal lobe exhibits three cortical surfaces: lateral, medial and inferior surfaces. The convexity of the lateral surface presents four important convolutions (gyri), which are the precentral gyrus, superior frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus and inferior frontal gyrus.
Which lobe is inferior to the frontal lobe?
Posterior and inferior to the frontal lobe is the temporal lobe, separated from it by the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The central sulcus demarcates the posterior border of the frontal lobe, while the Sylvian fissure demarcates its inferior border.
Why do neuronal systems contribute to threat detection?
And just because the amygdala contributes to threat detection does not mean that threat detection is the only function to which it contributes.
What are the two hemispheres of the brain?
Forebrain Structures. The two hemispheres of the. cerebral cortex. are part of the (Figure 1), which is the largest part of the brain. The forebrain contains the cerebral cortex and a number of other structures that lie beneath the cortex (called subcortical structures): thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ...
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language?
The. frontal lobe. is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central . The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language. It contains the. motor cortex. , which is involved in planning and coordinating movement; the. prefrontal cortex.
Where did the rod go in Phineas Gage?
The rod entered Gage’s face on the left side, passed behind his eye, and exited through the top of his skull, before landing about 80 feet away. (credit a: modification of work by Jack and Beverly Wilgus. Probably the most famous case of frontal lobe damage is that of a man by the name of Phineas Gage.
What is the strip on the side of the brain?
This strip running along the side of the brain is in charge of voluntary movements like waving goodbye, wiggling your eyebrows, and kissing. It is an excellent example of the way that the various regions of the brain are highly specialized.
What are some examples of damage to the Broca's area?
People who suffer damage to Broca’s area have great difficulty producing language of any form. For example, Padma was an electrical engineer who was socially active and a caring, involved mother. About twenty years ago, she was in a car accident and suffered damage to her Broca’s area.
How many lobes are there in the cerebral hemisphere?
Each cerebral hemisphere can be subdivided into four lobes, each associated with different functions. Figure 1. The brain and its parts can be divided into three main categories: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
What Happens if the Motor Cortex is Damaged?
Besides causing general problems with movement, there are some specific signs that indicate damage to the primary motor cortex. These are known collectively as upper motor neuron syndrome.
What is the term for the involuntary reaction of a muscle when passively stretched by a tendon?
Overactive reflexes. Deep tendon reflexes, also known as ‘muscle stretch reflexes’ are the involuntary reactions of a muscle when passively stretched by a tendon. These reflexes are often exaggerated in individuals with upper motor neuron syndrome, and can present as clonus or spasticity.
How does damage to the motor cortex affect the body?
The effects of damage to the primary motor cortex are serious. Fortunately, some of them can be reversed by activating neuroplasticity through exercise.
How to overcome primary motor cortex damage?
Therefore, the best way to overcome primary motor cortex damage is to engage neuroplasticity through exercise.
What part of the brain is responsible for leg movements?
For example, a significant portion of the motor cortex is devoted to finger movements and facial expressions, while a smaller portion of the brain is responsible for leg motions. This fact explains why many brain injury ...
What is the purpose of the motor cortex?
These purposeful movements include everything from moving your hands, arms, and legs to controlling facial expressions and even swallowing motions. Signals from the primary motor cortex cross over the body’s midline to activate muscles on the opposite side of the body. This means that the movements on the right side of your body are controlled by ...
Why do stroke patients have difficulty with fine motor control?
Because those movements are controlled by a larger portion of the motor cortex, they have a much higher likelihood of becoming damaged during an injury.
What is the motor homunculus?
The motor homunculus is a representation of the body parts along the primary motor cortex, or precentral gyrus. Each part of the body that is able to move is represented along this gyrus in an anatomical fashion, representing the contralateral side of the body.
What are the two areas of the nonprimary motor cortex?
The nonprimary motor cortex is further divided into two areas: the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor cortex. The premotor cortex is thought to be involved in planning and executing motor movements.
What causes the motor cortex to be damaged?
Damage to this area may result in dysfunctions associated with the pyramidal neurons, a condition known as upper motor neuron disease.
What is the motor cortex?
The motor cortex is an area within the cerebral cortex of the brain that is involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. The motor cortex can be divided into the primary motor cortex and the nonprimary motor cortex.
What is the role of the supplementary motor cortex in the movement of a person?
The supplementary motor cortex is thought to be critical to the execution of sequences of movement, the execution of motor skills, and the control of movement. This can involve taking a role in making a decision to change to a different movement based on sensory input.
What is the primary motor cortex?
The primary motor cortex is a region of the motor cortex which is important for initiating motor movements. The areas of the primary motor cortex correspond precisely to specific body parts.
Why is the homunculus distorted?
Therefore, the reason for the distorted representations of the homunculus is not due to how large in size the parts of the body are but is due to how richly supplied those parts are by the motor cortex.
