In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel or seed) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells , have no nuclei , and a few others including osteoclasts have many .
What are membrane bound organelles and defining characteristics of eukaryotes?
Topic: Membrane Bound Organelles And Defining Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. The nucleus of living cells contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell.
Which type of cell has membrane bound organelles?
A eukaryotic cell is the type of cell that has membrane bound organelles because it is defined by the presence of membrane-bound organelles, whereas a prokaryotic cell is defined by the absence of such organelles. The functions of membrane bound organelles are categorized as either single or double membrane-bound organelles.
What does the nucleus do in a cell?
Nucleus A nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's chromosomes. Pores in the nuclear membrane allow for the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus. The nucleus is one of the most obvious parts of the cell when you look at a picture of the cell.
What is the difference between organelle and membrane-bound organelle?
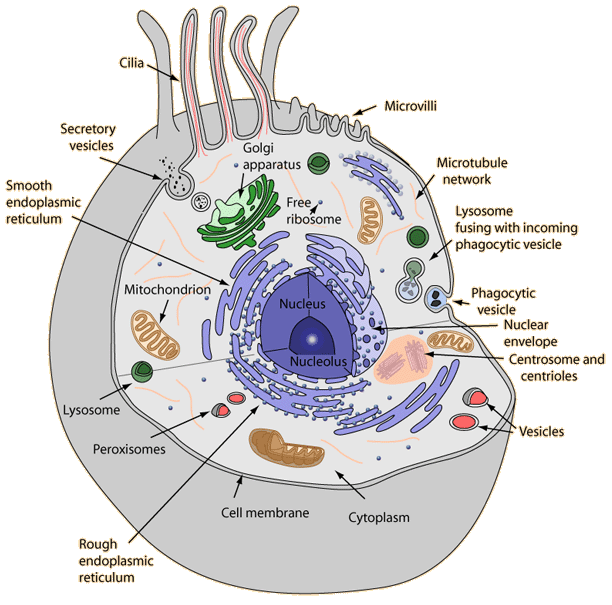
Organelles are structures within a cell that have specific functions; membrane-bound organelles are organelles protected by a single or double plasma membrane. Mitochondria, lysosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are examples of membrane-bound organelles.

Which is a membrane bound organelle?
Examples of membrane-bound organelles are nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, plastids, lysosomes, and vacuoles.
Which is not a membrane bound organelle?
Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound organelles.
What has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles?
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as well as most algae.
Is nucleus membranous or Nonmembranous?
membranous organellesNucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, plastids, and lysosomes are membranous organelles. Membranous organelles are fluid-filled, and are separated from the cytoplasm.
Is nucleolus membrane bound?
Nucleolus, ribosomes and centrioles are not bounded by a membrane.
What is a membrane-bound nucleus?
A membrane-bound nucleus, a central cavity surrounded by membrane that houses the cell's genetic material.
What's a membrane-bound nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell's DNA. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. The nucleus of living cells contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell. The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope.
What has no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages.
Which of the following is not a membrane bound organelle quizlet?
No, some examples of non-membrane bound organelles are ribosomes, the cell wall, and the cytoskeleton.
Which is a non membrane bound organelle quizlet?
Which non-membrane-bound organelle functions primarily in digestion within the cell? The proteasome does.
What is the nucleus?
Nucleus. =. A nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's chromosomes. Pores in the nuclear membrane allow for the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
What is the nucleus? What is its function?
The nucleus is one of the most obvious parts of the cell when you look at a picture of the cell. It's in the middle of the cell, and the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes, which encode the genetic material. So this is really an important part of the cell to protect. The nucleus has a membrane around it that keeps all the chromosomes inside and makes the distinction between the chromosomes being inside the nucleus and the other organelles and components of the cell staying outside. Sometimes things like RNA need to traffic between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and so there are pores in this nuclear membrane that allow molecules to go in and out of the nucleus. It used to be thought that the nuclear membrane only allowed molecules to go out, but now it's realized that there is an active process also for bringing molecules into the nucleus.
Why is the nucleus important?
So this is really an important part of the cell to protect. The nucleus has a membrane around it that keeps all the chromosomes inside and makes the distinction between the chromosomes being inside the nucleus and the other organelles and components of the cell staying outside.
What are the membrane bound organelles of eukaryotic cells?
Topic: Membrane Bound Organelles And Defining Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells. Eukaryoticcells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell’s DNA. The nucleusis the control center of the cell. The nucleus of living cells contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell.
Which cell contains membrane bound nuclei that house the cell's DNA?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is the control…. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is the control….
What is the control center of an eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei that house the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. The nucleus of living cells contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell.
What is the boundary of a cell?
The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope. It consists of two phospholipid bilayers: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The nucleus is also where we find the nucleolus.
What is the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatinwhere ribosomesynthesis occurs. Nuclear poresallow substances to enter and exit the nucleus. For example, proteins with a nuclear localization signal are recognized by nuclear pores for entry into the nucleus. Practice Questions.
Which cell contains genetic material?
nucleus:membrane-bound control center of the eukaryotic cell, contains genetic material. nuclear envelope: a boundary of the nucleus, made of a phospholipid bilayer. nuclear pores: pores in nuclear envelope that allows substances to go in and out.
Which region of chromatin is a condensed region of chromatin?
nucleolus:a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. eukaryotic: are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes. phospholipid bilayer: consists of two layers of phospholipids, with a hydrophobic, or water-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or water-loving, exterior.
What are organelles?
Organelles are specialized structures within cells that conduct a variety of functions. The word literally translates to “tiny little organs.” Organelles provide specialized functions to keep a cell alive in the same way that organs such as the heart, liver, stomach, and kidneys serve specific roles to keep an organism alive.
List of membrane bound organelles
The above listed are the membrane bound organelles in a cell, some of these organelles are either double or single bounded membrane organelles.
What type of cell has membrane bound organelles?
A eukaryotic cell is the type of cell that has membrane bound organelles because it is defined by the presence of membrane-bound organelles, whereas a prokaryotic cell is defined by the absence of such organelles.
Function of membrane bound organelles
The functions of membrane bound organelles are categorized as either single or double membrane-bound organelles. The functions will be in a tabular form for easy understanding.
FAQ on membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane surrounding them, but no internal membrane-bound organelles within their cytoplasm.
What Is a Cell with a Nucleus?
When you think of your body, consider the ultimate boss of everything. What organ tells your entire body what to do? The answer is your brain! Your brain tells your lungs to breathe, your heart to speed up or slow down, and your digestive system to break down food.All these organs are made of cells.
Examples of Membrane Bound Organelles
We now know that the nucleus is the brain of the cell, holding the DNA. But other organelles inside the nucleus are also important, just like the other organs in our body are.A city is another analogy that works for the cell.
Examples of Eukaryotes & Their Organelles
Let’s take a look now at how some of these organelles function in specific cell types. Different cells have different amounts of each organelle, depending on their job in the body. For example, cardiomyocytes are the cells that make up our heart. Our heart beats all the time, even in our sleep.
Lesson Summary
In summary, cells are the basic units of life. Eukaryotic cells are cells with a nucleus that holds DNA for the cell. Eukaryotic cells also have membrane bound organelles, which are tiny parts of the cell.
What are membrane bound organelles?
What Is a Membrane-Bound Organelle? Organelles are structures within a cell that have specific functions; membrane-bound organelles are organelles protected by a single or double plasma membrane. Mitochondria, lysosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are examples of membrane-bound organelles.
Which organelle contains DNA?
Certain species of bacteria possess primitive protein pockets that fulfill some organelle functions but are not defined structures protected by a membrane. Mitochondria are unique organelles that contain their own DNA. They produce the cell's energy through respiration.
Which part of the reticulum produces lipids?
The endoplasmic reticulum produces lipids and proteins. The rough outer membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes and is responsible for protein synthesis; the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and synthesizes lipids.
What is the powerhouse of the cell?
Because of this, they are also known as the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria are covered by two membranes: a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. Mitochondrial DNA is passed down through the mother and is a useful tool in genetic tests. The endoplasmic reticulum produces lipids and proteins.
Which organelle is double membrane bound?
Double membrane-bound organelles: Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell. Let us learn more in detail about the different cell organelles in brief.
Which organelle is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
They are present both in prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Single membrane-bound organelles: Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell.
Where are ribosomes found?
Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein. They are named as the 70s (found in prokaryotes) or 80s (found in eukaryotes) The letter S refers to the density and the size, known as Svedberg’s Unit. Both 70S and 80S ribosomes are composed of two sub-units. Ribosomes are either encompassed within the endoplasmic reticulum or are freely traced in the cell’s cytoplasm. Ribosomal RNA and Ribosomal proteins are the two components that together constitute ribosomes. The primary function of the ribosomes includes protein synthesis in all living cells that ensure the survival of the cell.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell.#N#There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
What is the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded. These cell organelles contain enzymes, mainly responsible for controlling all metabolic activity taking place within the cell and are the site for most of the chemical reactions within a cell.
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
What is the plasma membrane?
It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
