What kind of boundary makes up the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is the transform plate boundary where a thin sliver of western California, as part of the Pacific Plate, slides north-northwestward past the rest of North America.
What are two plates border the San Andreas Fault?
The vast majority of the San Andreas fault is occupied by the North American (NA) plate to the East, and the Pacific plate to the West. Keep in mind that in many places it is not a single linear feature. Rather, the San Andreas is a system of faults accommodating the strain of the overall system.
What type of stress caused the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas fault was formed by the movement of the North American and Pacific tectonic plates sliding past each other in opposite directions. This movement causes displacement of objects on each side of the fault as stress from the movement builds up. Because of its horizontal direction of movement, the San Andreas fault is categorized as ...
What is inside the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is known as a transform fault, which is where two of the earth's plates meet. In this case, it's where the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate come together. Geologists divide the San Andreas Fault into three parts: the Southern San Andreas Fault, the Central San Andreas Fault, and the North San Andreas Fault.

What type of plate boundary is the San Andreas Fault?
transform plate boundaryThe San Andreas Fault is part of a transform plate boundary that disrupts the topography of an ancient subduction zone.
Is San Andreas Fault line on conservative plate boundary?
The most famous example of a conservative plate margin is the San Andreas Fault on the west coast of North America.
What plates are at a conservative boundary?
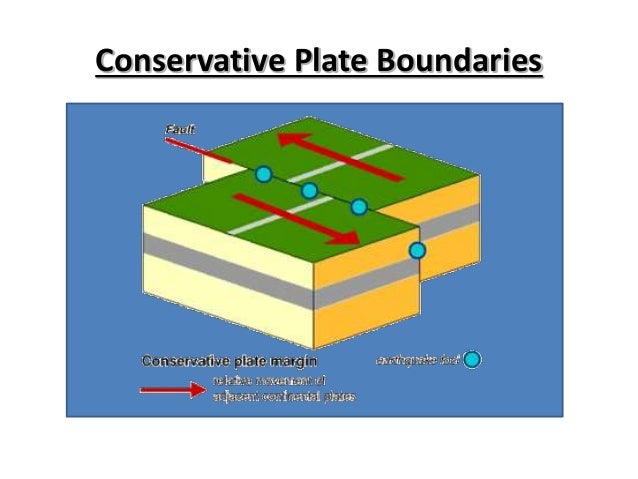
A conservative plate boundary, sometimes called a transform plate margin, occurs where plates slide past each other in opposite directions, or in the same direction but at different speeds. Friction is eventually overcome and the plates slip past in a sudden movement. The shockwaves created produce an earthquake .
Are there earthquakes at conservative plate boundaries?
At conservative plate margins, tectonic plates slide past each other. There is no volcanic activity associated with conservative plates, though earthquakes can often occur. This is because plates do not pass each other smoothly; friction causes resistance.
What type of plate boundary is California?
Notice at the northern part of California, we have a divergent plate boundary or an offshore seafloor spreading center where new oceanic crust forms and then is pushed away.
Why is it called conservative plate boundary?
5.4. 1 Introduction. Transform plate boundaries, also known as conservative plate boundaries, occur where lithospheric plates slide past each other and where the crust is neither destroyed nor formed.
Why is transform fault plate boundary also known as conservative plate margin?
Nomenclature. Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface.
Why do earthquakes occur conservative plate boundary?
At a conservative plate margin , the plates move past each other or are side by side moving at different speeds. As the plates move, friction occurs and plates become stuck. Pressure builds up because the plates are still trying to move.
What plate boundary causes earthquakes?
convergent boundariesAbout 80% of earthquakes occur where plates are pushed together, called convergent boundaries. Another form of convergent boundary is a collision where two continental plates meet head-on.
What are constructive destructive and conservative plate boundaries?
These are constructive, destructive, conservative and collision margins. A constructive plate boundary occurs when two plates move away from each other. Find out more about constructive plate margins. A destructive plate boundary occurs when an oceanic plate is forced under (or subducts) a continental plate.
What hazards happen at a conservative plate boundary?
The main effects of a conservative plate boundary are earthquakes, which can be fairly violent and frequent. Two plates slide past each other, without creating or destroying any land. As they move past each other they often get stuck, building up great pressure until finally they jolt past each other.
What are 4 plate boundaries?
There are four types of boundaries between tectonic plates that are defined by the movement of the plates: divergent and convergent boundaries, transform fault boundaries, and plate boundary zones. Microplates are smaller fragments of tectonic plates that appear in plate boundary zones.
What is conservative plate boundary GCSE?
At conservative plate margins , fault lines will be formed. These are plate boundaries where two plate are either slipping past each other in opposite directions or at different rates in the same direction. The plates do not move past each other smoothly.
What direction do plates move at a conservative plate boundary?
At conservative margins, plates slide past each other, so that the relative movement is horizontal, and classified as either sinistral (to the left) or dextral (to the right).
What is an example of a collision plate boundary?
Examples of continent-continent convergent boundaries are the collision of the India Plate with the Eurasian Plate, creating the Himalaya Mountains, and the collision of the African Plate with the Eurasian Plate, creating the series of ranges extending from the Alps in Europe to the Zagros Mountains in Iran.
What is a scarp in a fault?
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement along faults. They are exhibited either by differential movement and subsequent erosion along an old inactive geologic fault (a sort of old rupture), or by a movement on a recent active fault.
Where is the 1300km boundary?
A 1300km conservative plate boundary in California, where the North American Plate (slower rate of 1cm per year) and Pacific Plate (moving in the same direction but at a faster rate) slide past each other. A Strike-Slip Fault Displacement is lateral along fault.
What is conservative plate margin?
These are plate boundaries where two plate are either slipping past each other in opposite directions or at different rates in the same direction. The plates do not move past each other smoothly.
Where are the plates sliding past each other?
A good example of this is along the San Andreas Fault where the Pacific and the North American plates are sliding past each other.
What is plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics. The Earth's plates move in different directions depending on the type of boundary. Learn about the layers of the Earth's crust and plate boundaries. Part of. Geography. The restless earth. Add to My Bitesize. Share this with. Twitter.

Overview
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1,200 kilometers (750 mi) through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal). The fault divides into three segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The slip rate along th…
Fault zones
The northern segment of the fault runs from Hollister, through the Santa Cruz Mountains, epicenter of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, then up the San Francisco Peninsula, where it was first identified by Professor Lawson in 1895, then offshore at Daly City near Mussel Rock. This is the approximate location of the epicenter of the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. The fault returns onshore at Bolinas …
Plate boundaries
The Pacific Plate, to the west of the fault, is moving in a northwest direction while the North American Plate to the east is moving toward the southwest, but relatively southeast under the influence of plate tectonics. The rate of slippage averages about 33 to 37 millimeters (1.3 to 1.5 in) a year across California.
The southwestward motion of the North American Plate towards the Pacific is creating compres…
Formation
The San Andreas began to form in the mid Cenozoic about 30 Mya (million years ago). At this time, a spreading center between the Pacific Plate and the Farallon Plate (which is now mostly subducted, with remnants including the Juan de Fuca Plate, Rivera Plate, Cocos Plate, and the Nazca Plate) was beginning to reach the subduction zone off the western coast of North America. As the relative motio…
Study
The fault was first identified in Northern California by UC Berkeley geology professor Andrew Lawson in 1895 and named by him after the Laguna de San Andreas, a small lake which lies in a linear valley formed by the fault just south of San Francisco. Eleven years later, Lawson discovered that the San Andreas Fault stretched southward into southern California after reviewing the effects …
Earthquakes
The San Andreas Fault has had some notable earthquakes in historic times:
• 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake: About 350 kilometers (220 mi) were ruptured in central and southern California. Though it is known as the Fort Tejon earthquake, the epicenter is thought to have been located far to the north, just south of Parkfield. Two deaths were reported. Its moment magnitude was 7.9.
See also
• California earthquake forecast
• Central Valley (California) – Flat valley that dominates central California
• Coast Range Geomorphic Province
• Garlock Fault – Fault running along the margins of the Mojave Desert of Southern California,United States
Further reading
• Collier, Michael (December 1, 1999). A Land in Motion. UC Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21897-0.
• Stoffer, Philip W. (2005). The San Andreas Fault In The San Francisco Bay Area, California: A Geology Fieldtrip Guidebook To Selected Stops On Public Lands. USGS. General Interest Publication 16.