
Does the taiga have good soil?
The soil quality of a taiga biome is very poor. This poor quality is due to the fact that the taiga has such low temperatures for such a long period of time. Fallen leaves and moss can remain on the floor for a long time without decomposing due to the cold, moist climate. This limits their organic contribution to the soil, creating spodosol.
Does the taiga have fertility soil?
Floodplains throughout the taiga biome are free of permafrost, high in soil fertility, and repeatedly disturbed in ways that renew the early, rapid growth stages of forest succession. Fertile soils, known as loess, resulted, on which highly productive upland forests are found today.
What soil characteristics does the taiga have?
This taiga region was completely glaciated, or covered by glacier s, during the last ice age. The soil beneath the taiga often contains permafrost —a layer of permanently frozen soil. In other areas, a layer of bedrock lies just beneath the soil. Both permafrost and rock prevent water from draining from the top layers of soil.
Does taiga have lot of trees?
taiga - taiga - Trees: Scotch pine is the most widely distributed pine species in the world, growing from northern Scotland to the Russian Pacific shore. The relatively humid and productive taiga of northern Europe and south-central Siberia is dominated by this species. Forest management has greatly favoured this species in Scandinavia and Finland.
Does taiga have good soil?
The soil in the taiga is thin, acidic and not very nutrient rich. It also is rocky. Due to these factors, plants in the taiga have different adaptations than the plants we find around Santa Barbara. The< name, evergreen, describes an important adaptation of conifers.
What is the soil like in taiga?
Soils are shallow due to lack of decomposition and weathering caused by the cold. They are acidic due to leaching from rainfall and they are also poor in nutrients. The litter layer is thick with needles due to slow decomposition.
Does the taiga have poor soil?
Types of Taiga: Light and Dark The light taiga is found more often in regions where the soil is too nutrient-poor to support as many trees.
Is the soil fertile in the boreal forest?
In fact the undergrowth of boreal forests is almost non-existent. The species present are able to get their nutrient requirements from the very shallow layer of soil above the permafrost. The trees present have a notable climatic tolerance and survive on rather infertile soils.
How do plants survive in the taiga?
Plant Adaptations in the Taiga Biome Needles will retain moisture and shed snow. The waxy coating on the tree needles prevents evaporation. The darkness of the needles helps to attract more sun. Many of the branches on evergreen trees droop down allowing the shedding of snow.
What are 5 facts about taiga?
Taiga Biome: Taiga comes from a Russian word for the marshy pine forest. Biome means the area dense with flora and fauna, which is why the Taiga forest is the world's largest land biome. Taiga has a cold climate and low precipitation (rain and snow) rate. It is believed that the Taiga forest existed 12,000 years ago.
How acidic is taiga soil?
Taiga conifer litter is highly acidic. Soils of the more humid and southern taiga are highly leached spodosols, which are characterized by the leaching of iron, aluminum, and organic matter from the chemically and biologically distinct surface layer—horizon A—to the next layer—horizon B.
Is the taiga wet or dry?
Telling taiga from tundra In contrast, the taiga sees precipitation, mostly in the form of snowfall, which can total over 80 inches a year. This means that the taiga is a wet biome with plenty of available moisture; in some places, even boggy. In contrast, the tundra is desertlike; the soil stays frozen and dry.
Why do taiga trees grow fast?
Most of the forest-tundra is within the continuous permafrost zone. Forest productivity in the middle and northern taiga zones is directly related to soil temperature. Warmer soils decompose organic matter more quickly, releasing nutrients for new plant growth and creating a more productive site.
Which forest type has the most fertile soil?
Deciduous forests have soils called Alfisols. These soils do not have a bleached E horizon, but do have clays that accumulate in the subsoils. Alfisols are very common in the Midwestern region, and are the most fertile type of forest soils.
Which part of forest soil are highly fertile?
Soils that formed under deciduous forests are very fertile and productive agricultural lands because of the decomposing leaves at the soil surface. However, soils formed under pine trees are usually more acidic and sandy, and are less suited to growing crops.
Does boreal forest have rich soil?
Soils in the boreal forest are typically podzols (from the Russian word for “ash”), gray soils that are thin, acidic, and poor in nutrients.
Is the soil in a taiga biome acidic?
Soils. Taiga conifer litter is highly acidic. Soils of the more humid and southern taiga are highly leached spodosols, which are characterized by the leaching of iron, aluminum, and organic matter from the chemically and biologically distinct surface layer—horizon A—to the next layer—horizon B.
What type of soil is in a boreal forest?
Soils in the boreal forest are typically podzols (from the Russian word for “ash”), gray soils that are thin, acidic, and poor in nutrients.
What type of soil is in the tundra?
The soil in the Arctic is largely permafrost or soil that remains frozen year-round, leaving only a thin surface layer of thawed soil in summer for plant roots to grow in. Tundra soil is also scarce in many of the nutrients that plants need to grow.
What type of soil is in the temperate forest?
Typical soils in the temperate rainforest include Andisols, soil formed from deposits of volcanic ash; Spodosols, soils dominated by sand; and Alfisols, soils with a clay-enriched B horizon.
Why is taiga acidic?
Spodosol, which is found in much of the southern boreal forests, is highly acidic due to needles from conifer trees.
What is the most important soil for nutrient leaching?
Most important nutrients leach through spodosol so il and into the ground below. Histosol develops in wetlands that form as a result of water being unable to drain due to surrounding topography, permafrost or rivers. This soil is characterized by its high peat content and occurs over a large portion of the bare taiga.
What is inceptisol soil?
Inceptisol is a very poorly developed type of soil that is characterized by very little or no clear layering. This usually occurs as a result of continuous waterlogging and/or the weather-resistant bedrock that lies just underneath most taiga.
Does Taiga have gelisol?
Some areas of taiga may also contain gelisol, a well-layered soil characterized by the presence of permafrost, but this is usually found further towards the pole in the tundra. ADVERTISEMENT.
What are the factors that contribute to the climate of a taiga biome?
Several factors—namely, the solar elevation angle, day length, and snow cover —conspire to produce this cold climate. In the taiga biome the Sun is never directly overhead (90°) as it can be in the tropics.
Why is the Taiga important?
The taiga actually mitigates this cooling because it roughens and darkens what would otherwise be a smooth, snow-covered, energy-reflecting surface for much of the year. It has been estimated that Earth would be significantly colder without the taiga.
What is the northern limit of the Taiga?
Mean annual temperatures in the taiga range from a few degrees Celsius above freezing to −10 °C (14 °F) or more. Areas with a mean annual temperature below freezing are susceptible to the formation of permafrost soils (frozen ground; see below Soils ).
Why are trees so cool in Alaska?
On the North American side, in western Alaska, summers are too cool for trees to grow, because of cold air masses moving off the Bering Sea. The growing season in the taiga is generally cool. The mean temperature of the warmest month, July, is generally between 15 and 20 °C (59 and 68 °F).
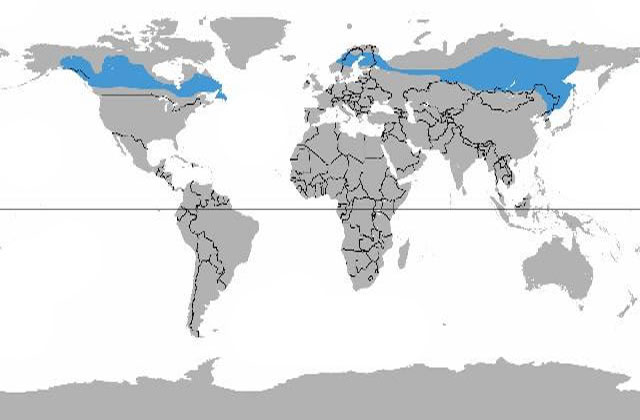
Where is the Taiga located?
Areas of the taiga located in the centre of continents generally receive 30 to 50 cm (12 to 20 inches) of annual precipitation. Precipitation totals are relatively modest in these locations because they are a significant distance from unfrozen oceans that supply moisture. Some taiga regions are semiarid and may even include grasslands interspersed with the forest. These forests are found in regions of Yukon and Alaska that occur on the leeward side of mountains which are sheltered from moisture-bearing winds, as well as in some portions of the interior of the Far East region of Russia. Annual precipitation in low elevations of these regions is 30 cm or less. The highest annual precipitation total in the taiga, which can exceed 100 cm, is in eastern North America and northern Europe. During ancient eras of colder climate, these regions also received relatively abundant precipitation, which resulted in the buildup of glacial ice sheets. Today these once heavily glaciated regions support extensive lakes, streams, and wetlands.
Where are taiga forests found?
Some taiga regions are semiarid and may even include grasslands interspersed with the forest. These forests are found in regions of Yukon and Alaska that occur on the leeward side of mountains which are sheltered from moisture-bearing winds, as well as in some portions of the interior of the Far East region of Russia.
Where is the highest annual precipitation in the Taiga?
The highest annual precipitation total in the taiga, which can exceed 100 cm, is in eastern North America and northern Europe. During ancient eras of colder climate, these regions also received relatively abundant precipitation, which resulted in the buildup of glacial ice sheets.
What is a taiga?
Taiga, also called boreal forest, biome (major life zone) of vegetation composed primarily of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreen trees, found in northern circumpolar forested regions characterized by long winters and moderate to high annual precipitation. The taiga, “land of the little sticks” in Russian, ...
What are the adaptations of the Taiga biome?
Plants and animals in the taiga are adapted to short growing seasons of long days that vary from cool to warm. Winters are long and very cold, the days are short, and a persistent snowpack is the norm. The taiga biomes of North America and Eurasia display a number of similarities, even sharing some plant and animal species.
What is the name of the biome in which evergreen trees grow?
taiga, also called boreal forest, biome(major life zone) of vegetation composed primarily of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreentrees, found in northern circumpolar forested regions characterized by long wintersand moderate to high annual precipitation. The taiga, “land of the little sticks” in Russian, takes its name from the collectiveterm for the northern forestsof Russia, especially Siberia.
What is the name of the tree that grows in the Taiga?
Northward beyond this limit, the taiga merges into the circumpolar tundra. The taiga is characterized predominantly by a limited number of conifer species—i.e., pine ( Pinus ), spruce ( Picea ), larch ( Larix ), fir ( Abies )—and to a lesser degree by some deciduous genera such as birch ( Betula) and poplar ( Populus ).
How did the Taiga move?
As the glaciers began to retreat gradually about 18,000 years ago, species of the taiga began to move northward in Europe and North America. In eastern and central North America the northward movement of the forest was relatively steady and gradual. An exception to this progression occurred about 9,000 years ago in western Canada, when white sprucespread rapidly northward across 2,000 km (1,240 miles) of newly deglaciated land in only 1,000 years. This rapid migration resulted from seed dispersal facilitatedby strong northward winds caused by clockwise atmospheric circulationaround the remnant ice cap of northern Quebec and the western part of Hudson Bay.
What is the name of the biome of the little sticks?
Taiga, biome composed mainly of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreen trees, found in northern circumpolar regions typified by long winters and moderate to high annual precipitation. Taiga, ‘land of the little sticks’ in Russian, is named for the term for Russia’s northern forests, especially Siberia.
What is the most widespread conifer in the Scottish Highlands?
A small, isolated area of boreal forest in the Scottish Highlands lacks some continental species but does contain the most widespread conifer of the Eurasian taiga, Scotch pine ( Pinus sylvestris ). Distribution of boreal forests in the Eastern Hemisphere. Distribution of boreal forests in the Western Hemisphere.
