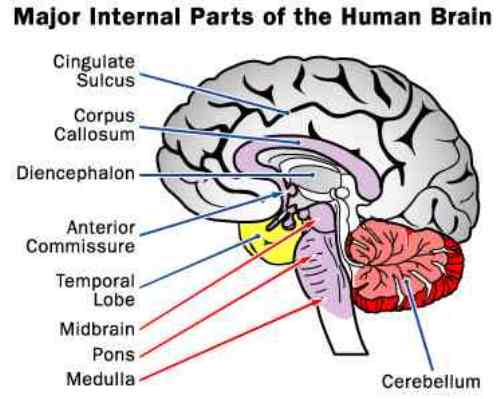
What are the functions of the thalamus?
There are three specific nuclei associated with the thalamic role of motor control:
- Ventrolateral: coordination and cadence of movement
- Ventroanterior: planning and initiation of movement
- Ventrointermedial: coordination of movement
Where is the thalamus located in the brain?
- The thalamus [Thalamus] takes up the space dorsal of the hypothalamus (see ► Chap. ...
- By contrast to the human brain, the left and right parts of the murine thalamus are in close contact, not mostly divided by the third ventricle.
- As a rule of thumb, the thalamus mediates input from the spinal cord (► Chap. ...
What is the thalamus responsible for?
The thalamus plays a major role in regulating arousal, the level of awareness, and activity. Damage to the thalamus can lead to permanent coma. The role of the thalamus in the more anterior pallidal and nigral territories in the basal ganglia system disturbances is recognized but still poorly understood.
What are the main functions of the thalamus and hypothalamus?
Summary of Thalamus and Hypothalamus
- Both the thalamus and the hypothalamus are parts of the brain segment called the diencephalon
- Although they both serve the purpose of connecting different parts of the body, they are fundamentally different
- The thalamus connects the cerebral cortex with the midbrain, while the hypothalamus connects the nervous and endocrine systems
See more
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-696552686-2e1fcb00a0174f6eac151ba160c4e534.jpg)
What are the parts of brain stem?
AnatomyMidbrain: The top part of the brainstem is crucial for regulating eye movements.Pons: The middle portion of the brainstem coordinates facial movements, hearing and balance.Medulla oblongata: The bottom part of the brainstem helps regulate your breathing, heart rhythms, blood pressure and swallowing.
What are the three parts of the brain stem?
Brainstem. The brainstem (middle of brain) connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
Which is not part of the brain stem?
The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain. It contains the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons and the medulla oblongata. Brainstem does not include cerebellum which is part of the hindbrain.
Where is the thalamus located?
the brainThe thalamus is a paired gray matter structure of the diencephalon located near the center of the brain. It is above the midbrain or mesencephalon, allowing for nerve fiber connections to the cerebral cortex in all directions — each thalamus connects to the other via the interthalamic adhesion.
What is the brain stem called?
The brainstem is divided into three sections in humans: the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons (metencephalon), and the medulla oblongata (myelencephalon).
Where is the thalamus located?
Location of the thalamus~ The brain is comprised of ventricles or fluid-filled spaces. The thalamus surrounds the third ventricle. It is a subdivision of part of the brain called the diencephalon and is one of the largest structures derived from the diencephalon during embr
What is the thalamus?
The thalamus is the “sensory sieve” in the brain.
What is the brain stem?
In human brain, mid brain, pons varolli and medulla oblongata forms the base of the brain which is often referred as Brain stem which later form the spinal cord. Brain stem is said to be a very important part of brain as it contains control centres of vital physiological processes such as metabolism, heartbeat, breathing, vasodilation, vasoconstriction, blood pressure, gut peristalsis, gland secretion and certain other involuntary activities. It also serves as a passage for impulses between spinal cord and rest of the brain.
What is the function of the thalamus?
The original and primary function is to make immediate judgements about survival needs and inform action centers to respond appropriately. The thalamus is located just above the brain stem, indicating its primordial connection with survival.
Why is it necessary to provide a brief overview of the thalamus?
I will provide a brief overview of the thalamus because understanding its overall nature makes explaining its relation to vision clearer.
Which part of the brain is responsible for determining what information is selected to focus?
The thalamus also has a specialized she'll called the Reticular Nucleus which acts as an attentions like spotlight determining what information is selected to focus. It is also the gate in sensory motor gating, opening and closing the doors of awareness.
Which part of the brain decides whether the information it's recieving is useful enough to relay to the?
The thalamus decides whether the information it's recieving (every sensory information along with senses like taste, vision, hearing, but NOT smell) is useful enough to relay to the higher centres of consciousness.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus lies at the top of the brain stem near the center of the brain, from where nerve fibers project out towards the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is divided into two prominent bulb-shaped masses of around 5.7 cm in length and positioned symmetrically on each side of the third ventricle. The thalamus is supplied with blood by four branches ...
What are the two parts of the thalamus?
Distinct groups of neurons make up other parts such as the periventricular, the nucleus limitans, and the intralaminar elements collectively called the allothalamus.
What are the two regions of the brain?
Brain regions. Also located in the diencephalon are the epithalamus and the perithalamus, which contain regions called the zona incerta and the reticulate nucleus. These are distinct from the thalamus proper.
Which artery supplies the thalamus with blood?
The thalamus is supplied with blood by four branches of the posterior cerebral artery, namely the polar artery, paramedian thalamic-subthalamic arteries, thalamogeniculate arteries and the posterior choroidal arteries. Within the thalamus lie myelinated nerve fibers called lamellae that separate the structure into individual parts.
What is the function of the thalamus?
The primary function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex.
Which part of the brain surrounds the third ventricle?
The thalamus surrounds the third ventricle. It is a subdivision of part of the brain called the diencephalon and is one of the largest structures derived from the diencephalon during embryonic development.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is located deep within the brain in the cerebral cortex, adjacent to the hypothalamus. It is a symmetrical structure, situated on top of the brain stem and on either side of the third cortex. The two halves are bulb-shaped and are about 5.5 to 6.0 centimeters in length in the average adult.
What is the function of the thalamus?
Its chief function is processing information going to and from the spinal cord and cerebrum. It also regulates sleep cycles, consciousness, and alertness. The thalamus receives information from nearly every sensory system, apart from the olfactory system, which it then sends to the relevant cortical area. Research has revealed that the thalamus ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating consciousness?
The thalamus also has strong connections with the cerebral cortex, and together they are involved with regulating consciousness; damage to the thalamus can lead to a permanent coma.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter that is located in the forebrain and is superior to the midbrain. It is also near the center of the brain, where the nerve fibers project out to the cerebral cortex in all directions. The medial surface of the thalamus constitutes the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle ...
What is Thalamus?
The thalamus may be a small structure within the brain located just above the brainstem between the cerebral mantle and therefore the midbrain has extensive nerve connections to both. The main and primary function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral mantle. It also aids in the regulation of sleep, alertness, and wakefulness.
What is the function of the diencephalon?
Thalamus function is to act as a relay centre in between the subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex.
What is the medial surface of the thalamus?
The medial surface of the thalamus constitutes the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle and is connected to the surface that is corresponding to the opposite thalamus by a flattened gray band, the interthalamic adhesion. The lateral part of the thalamus consists of the pulvinar, the lateral nuclei, ...
What is the lateral part of the thalamus?
The lateral part of the thalamus consists of the pulvinar, the lateral nuclei, and the medial and lateral geniculate nuclei. These are the newest part of the thalamus phylogenetically. There are areas of substantia alba within the thalamus including the stratum zonale that covers the dorsal surface, and therefore the external and internal medullary lamina. The external lamina covers the lateral surface and the internal lamina helps to divide the nuclei into anterior, medial, and lateral groups.
What is the brain's function?
It also aids in the regulation of sleep, alertness, and wakefulness. The brain consists of the ventricles or fluid-filled spaces. The thalamus surrounds the third ventricle. It is a subdivision of a part of the brain called the diencephalon and is one of the most important structures derived from the diencephalon during embryonic development.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the sensory information relay?
The thalamus is believed to process both the sensory information as well as a relay of each of the primary sensory relay areas that receive strong feedback connections from the cerebral cortex. Similarly, the medial geniculate nucleus acts as a key auditory relay between the center of the midbrain and therefore the primary auditory area.
What are the parts of the thalamus?
The anterior, mediodorsal, and centromedian nuclei of the thalamus are the primary parts that play a role in this emotional regulation: 1 Anterior: involved in the storage of memory and emotion. 2 Mediodorsal: responsible for motivation, enthusiasm, and emotions related to inspiration. 3 Centromedian: governs the emotional component of pain.
Which structure is located on the superior surface of the thalamus?
The lateral region of the superior surface of the thalamus contains the stria terminalis, a structure that plays a role in the regulation of emotions and behaviors related to stress.
Why is the thalamus important?
The thalamus is extremely important to the regulation of the human nervous system. It is the center of information processing, and is what maintains consciousness, organizes subconscious information and regulates the very survival of the human being. There is still much to be learned about this structure and it poses quite the challenge due to its countless neuronal connections to structures within the central nervous system, limbic system, and more.
How many ends does the thalamus have?
The thalamus has two ends, the anterior and posterior poles, and four surfaces: medial, lateral, superior, and inferior. Nuclei in a given pole or surface regulate specific functions or processing of sensory information and maintain particular connections with parts of the nervous and limbic system. Understanding the anatomy of the thalamus will ...
What is the limbic system?
Limbic System. Miscellaneous Functions of the Thalamus. The thalamus, or the dorsal and ventral thalamus collectively, are two oval structures made up of gray matter at the base of the cerebrum. This structure’s primary function is as a relay center through which sensory nerves transmit signals from the spinal cord and brainstem on the way to ...
What is the role of the thalamus in the body?
The thalamus also plays a significant role in sensory perception and movement. Certain areas of the thalamus are dedicated to specific parts of the body and where the sensations are meant to travel toward the cerebral cortex.
What is the lateral surface of the thalamus?
The lateral surface of the thalamus is covered by a layer of myelinated fibers called the external medullary lamina which separates the lateral surface from the reticular nuclei.
What is the brainstem?
Anatomy. The brainstem is a stem shaped structure, extending down from the posterior (back) part of the brain to the spinal cord. It is protected by the meninges, which are composed of three layers of sheet-like connective tissue that envelop the brain and spinal cord. Outside the meninges, the brainstem is shielded by the lower part of the skull.
What is the brainstem composed of?
Medulla: Cranial nerves nine through 12. The deeper portion of the brainstem is composed of grey matter, and the remaining nerve pathways of the brainstem are primarily are composed of white matter, which is more heavily myelinated (protected by a type of fat that insulates nerves). In an average size adult, the brainstem measures approximately 3 ...
Where are the cranial nerves located?
Cranial nerve roots are located in the brainstem , and each pair of the 12 cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem. The cranial nerve levels are: Cerebrum: Cranial nerves one and two. Midbrain: Cranial nerves three and four. Pons : Cranial nerves five through eight. Medulla: Cranial nerves nine through 12.
How does the brainstem work?
Some of the structures located in the brainstem work by coordinating with neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) and structures in other parts of the brain and throughout the body to control complex functions.
What is the fluid that flows between the brain and the meninges?
Outside the meninges, the brainstem is shielded by the lower part of the skull. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows between the meninges and the brainstem, providing nourishment and protection.
What is the function of the brainstem?
Function. The brainstem contains nerves and tracts (nerve pathways) that provide motor and sensory functions throughout the body. Nerve tracts are composed of a sequence of nerves that rapidly send messages along a specific route. Major nerve pathways in the brainstem include: Spinothalamic: This tract runs at the outer portion of the brainstem, ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for controlling the heart and breathing?
Associated Conditions. Tests. The brainstem is the part of the brain that directly connects with the spinal cord. It contains regions that modulate breathing and heart function, as well as pathways for communication between the brain and the spinal cord. The cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem—controlling movement and sensation in ...
Where does the brainstem begin?
The brainstem begins at the level of the cerebral peduncles (anteriorly) and the corpora quadrigemina or quadrigeminal plate (posteriorly) or tectal plate. It continues along a slight posteroinferior course until it ends at the decussation of the pyramids (at the level of the foramen magnum of the skull ).
What part of the brain is connected to the rest of the body?
Similarly, the majority of brain tissue is connected to the rest of the body via the brainstem . The brainstem is a stalk-like projection extending caudally from the base of the cerebrum.
What is the narrowest part of the brain?
The medulla ob longata or medulla is the narrowest and most caudal part of the brainstem. It is a funnel-like structure that extends from the decussation of the great pyramids, passes through the foramen magnum (which is the largest of all the foramina and fissures of the skull ), to the inferior pontine sulcus ( pontomedullary groove ). As the medulla continues upward in the posterior cranial fossa, it terminates at the inferior pontine sulcus (anteriorly) and the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle (posteriorly).
What is the division of the midbrain?
Most textbooks divide the midbrain into tectum and tegmentum, but the division is actually extended caudally into other brainstem segments. The tectum (Latin word for roof) and tegmentum (Latin word for covering) are used in relation to the developing central cavity of the neural tube .
What are the parts of the brain?
The brainstem is widest at its proximal end and becomes narrower toward the distal end. There are three parts of the brainstem: 1 the medulla oblongata is the narrowest and most distal part 2 the pons lies anteriorly and in the middle segment of the brainstem 3 and the midbrain is the widest and most superior segment.
Where does the medulla end?
As the medulla continues upward in the posterior cranial fossa, it terminates at the inferior pontine sulcus (anteriorly) and the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle (posteriorly). At the upper posterior surface of the medulla, there is the fourth ventricle, the floor of which is called rhomboid fossa.
Why is the brainstem important?
All of these brainstem functions are enabled because of its unique anatomy ; since the brainstem houses cranial nerve nuclei and is a passageway for many important neural pathways.
