
Where is the third ventricle located in the brain?
The third ventricle is a narrow funnel-shaped cavity of the brain. It is located in the midline, comprising the central part of the ventricular system of the brain. As such, the third ventricle directly communicates with other ventricles: It communicates with each lateral ventricle via the foramen of Monro,
How does the third ventricle communicate with other ventricles?
It is located in the midline, comprising the central part of the ventricular system of the brain. As such, the third ventricle directly communicates with other ventricles: It communicates with each lateral ventricle via the foramen of Monro, It communicates with the fourth ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius).
What are the cerebral ventricles of the brain?
The cerebral ventricles consist of the lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle. The third ventricle is one of four brain ventricles. It is a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid located between the two hemispheres of the diencephalon of the forebrain. The third ventricle helps to protect the brain from trauma and injury.
What is the floor of the third ventricle made of?
The floor of the third ventricle is formed by a number of structures including the hypothalamus, subthalamus, mammilary bodies, infundibulum (pituitary stalk), and the tectum of the midbrain. The lateral walls of the third ventricle are formed by the walls of the left and right thalamus.

Is the third ventricle part of the midbrain structure?
The third ventricle is a narrow funnel-shaped cavity of the brain. It is located in the midline, comprising the central part of the ventricular system of the brain....Third ventricle.StructureFour walls (anterior, posterior, two lateral), roof and floorTela choroidea and choroid plexusLocated on the roof of the ventricle1 more row
Which ventricle is in the midbrain?
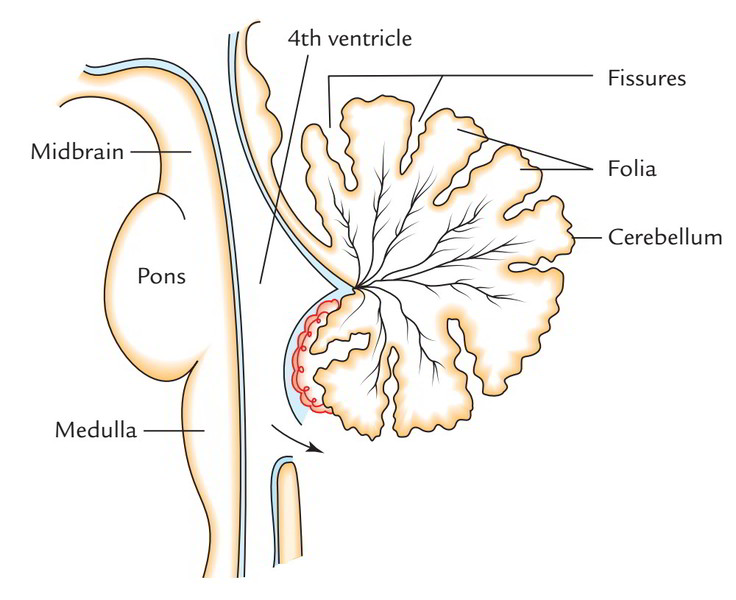
The third ventricle is continuous caudally with the cerebral aqueduct, which runs though the midbrain. At its caudal end, the aqueduct opens into the fourth ventricle, a larger space in the dorsal pons and medulla. The fourth ventricle narrows caudally to form the central canal of the spinal cord.
Is the third ventricle in the forebrain?
The third ventricle is a narrow funnel-shaped cavity of the brain that is located in the midline between the two hemispheres of the diencephalon of the forebrain.
Is 4th ventricle in midbrain?
The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the pons or in the upper part of the medulla oblongata.
What is the 3rd ventricle of the brain?
The third ventricle is one of the four ventricles in the brain that communicate with one another. As with the other ventricles of the brain, it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which helps to protect the brain from injury and transport nutrients and waste.
What is the third ventricle called?
Hence, the correct answer is 'Diacoel'
Is the third ventricle in the hindbrain?
The third ventricle is a narrow cavity located between the two hemispheres of the diencephalon of the forebrain.
What is the midbrain?
The midbrain is the topmost part of the brainstem, the connection central between the brain and the spinal cord. There are three main parts of the midbrain - the colliculi, the tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles.
Where is the 3rd ventricle located?
the brainThe third ventricle is a narrow, funnel-shaped structure that lies in the center of the brain. It lies below the corpus callosum and body of the lateral ventricles, between the two thalami and walls of hypothalamus, and above the pituitary and midbrain (Fig.
Should the fourth ventricle be midline?
The fourth ventricle is a midline, CSF-filled cavity located posterior to the pons and rostral medulla, and anterior to the cerebellum.
Is the fourth ventricle in the brainstem?
The fourth ventricle is a diamond-shaped cavity located in the brainstem. It has two lateral extensions, the lateral recesses of the fourth ventricle and a median one, the median aperture (not shown on this perspective). This ventricle is the most inferior and extends into the central canal of the spinal cord.
Where is the third ventricle located quizlet?
Where is the 3rd Ventricle? The 3rd ventricle is located between the corpus callosum and diencephalon. The cerebral aqueduct connects the third and fourth ventricles.
Where is the 4th ventricle located?
The fourth ventricle is a diamond-shaped cavity located posterior to the pons and upper medulla oblongata and anterior-inferior to the cerebellum. The superior cerebellar peduncles and the anterior and posterior medullary vela form the roof of the fourth ventricle.
What is located in the midbrain?
There are three main parts of the midbrain - the colliculi, the tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Of the 12 cranial nerves, two thread directly from the midbrain - the oculomotor and trochlear nerves, responsible for eye and eyelid movement.
Where is the third ventricle located?
the brainThe third ventricle is a narrow, funnel-shaped structure that lies in the center of the brain. It lies below the corpus callosum and body of the lateral ventricles, between the two thalami and walls of hypothalamus, and above the pituitary and midbrain (Fig.
What are the 4 ventricles of brain?
There are four ventricles of the brain: the 2 lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle. The ventricles are lined with a specialised membrane called the choroid plexus, which is made up of ependymal cells.
What are the structures that make up the third ventricle?
The floor of the third ventricle is formed by a number of structures including the hypothalamus, subthalamus, mammilary bodies, infundibulum (pituitary stalk), and the tectum of the midbrain. The lateral walls of the third ventricle are formed by the walls of the left and right thalamus.
What is the third ventricle?
Key Takeaways. The third ventricle is one of four brain ventricles. It is a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid located between the two hemispheres of the diencephalon of the forebrain. The third ventricle helps to protect the brain from trauma and injury. The third ventricle is also involved in the transport of both nutrients and waste from ...
How many components are there in the third ventricle?
The third ventricle can be described as having six components: a roof, a floor, and four walls. The roof of the third ventricle is formed by a part of the choroid plexus known as the tela chorioidea. The tela chorioidea is a dense network of capillaries that is surrounded by ependymal cells. These cells produce cerebrospinal fluid.
What causes a dilated third ventricle?
Third ventricle issues and abnormalities can occur in a variety of conditions like stroke, meningitis and hydrocephalus. A relatively common cause of an abnormality of the third ventricle occurs with congenital hydrocephalus (abnormal contour with a dilated third ventricle).
Where is the third ventricle located?
Updated July 05, 2019. The third ventricle is a narrow cavity located between the two hemispheres of the diencephalon of the forebrain. The third ventricle is part of a network of linked cavities (cerebral ventricles) in the brain that extend to form the central canal of the spinal cord.
Which ventricle is connected to the third ventricle?
These channels allow cerebrospinal fluid to flow from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle. The cerebral aqueduct connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle. The third ventricle also has small indentations known as recesses.
How many ventricles are there in the ventricular system?
The ventricular system consists of two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle.
What is the floor of the third ventricle?
The floor of the third ventricle extends from the optic chiasm anteriorly to the aqueduct of Sylvius posteriorly. The anterior portion of the floor is formed by the hypothalamus , while the posterior portion is formed by the midbrain (mesencephalon). Going from the anterior to posterior, the structures that comprise the floor of the third ventricle are the:
How many walls does the third ventricle have?
The third ventricle has four walls in total; anterior, posterior, and two lateral walls.
What is the vascular pia matter that is closely connected to the ependymal lining of the?
Tela choroidea is the vascular pia matter which is closely connected to the ependymal lining of the ventricles. In the third ventricle, the tela choroidea is, in fact, embedded in the multi-layered roof of the ventricle. The tela choroidea gives rise to the choroid plexus.
What is the only structure visible from the posterior aspect of the brain?
The only structure visible from the posterior aspect of the brain is the pineal gland . Inferior to the posterior commissure the ventricle is continuous with the cerebral aqueduct of the midbrain (of Sylvius).
How does the third ventricle communicate with the fourth ventricle?
As such, the third ventricle directly communicates with other ventricles: It communicates with the fourth ventricle via the aqueduct of Sylvius. The third ventricle can be described as a cuboid structure that has a roof, floor and four walls (anterior, posterior, and two lateral).
What is the purpose of a tracing method for a ventricular system?
Ventriculography is a tracing method used to study the ventricular system in living subjects. In this procedure, radiographs are taken after injecting a radio-opaque dye into the ventricular system. Parts of the ventricles can also be seen using computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Hydrocephalus is one of the well known clinical conditions associated with the ventricular system malformations and can be observed using ventriculography.
Which plexus is responsible for the blood-CSF barrier?
The choroid plexus is a collection of capillaries that produce and secrete the CSF into the ventricular system of the brain. The epithelium of the choroid plexus constitutes the blood–CSF barrier.
What is the third ventricle?
The third ventricle is a brain cavity that is slender and in the shape of a funnel. It is situated in the centre line and suggestively forms the central component of the brain’s ventricular system.
How many sides does the third ventricle have?
The third ventricle has four sides: posterior, anterior, and two lateral walls.
What is the choroid plexus?
The choroid plexus is a network of capillaries that produces and secretes Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the brain’s ventricular system. The blood–Cerebrospinal fluid border is made up of the choroid plexus epithelial tissue. The anterior choroidal division of the internal carotid artery and choroidal divisions of the posterior cerebral artery supplies the majority of blood to the choroid plexus. A solitary choroidal vein drains the venous blood. The choroid plexuses of the lateral and third ventricles are uninterrupted when examined in the sagittal segment.
What percentage of brain tumors are third ventricles?
Third ventricle tumours are rare, accounting for approximately 0.6 to 0.9 per cent of all brain tumours. Primary tumours (such as colloid cysts, choroid plexus papillomas, and ependymomas) and secondary tumours can be distinguished (e.g., craniopharyngiomas, optic nerve gliomas, pineal tumours, and meningiomas).
What is the hollow in the diencephalon called?
Figure 1 Between the thalami of each cerebral hemisphere, there is a hollow in the diencephalon, called the third ventricle (in red colour). The interventricular foramen connects the third ventricle to the lateral ventricles, and the cerebral aqueduct connects it to the fourth ventricle.
Which ventricle floor is the anterior segment of the base layer?
The third ventricle floor stretches from the optic chiasm in the anterior region to the Sylvius aqueduct in the posterior area. The hypothalamus forms the anterior segment of the base layer, whereas the midbrain forms the posterior part (mesencephalon).
What are the lateral walls of the third ventricle?
Lateral Walls: The medial sides of the thalamus and hypothalamus, divided by the hypothalamic sulcus, create the lateral walls of the third ventricle. When seen from the side, the shapes of the lateral walls resemble the profile of the head of a bird who has its beaks all opened up. The medial portion of the thalamus makes up the major portion of the lateral wall.
What is the floor of the third ventricle?
The floor of the third ventricle is formed by hypothalamic structures and this can be opened surgically between the mamillary bodies and the pituitary gland in a procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy. An endoscopic third ventriculostomy can be performed in order to release extra fluid caused by hydrocephalus .
Where does the third ventricle originate?
The third ventricle, like other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develops from the neural canal of the neural tube. Specifically, it originates from the most rostral portion of the neural tube which initially expands to become the prosencephalon. The lamina terminalis is the rostral termination of the neural tube.
What is the lateral side of the ventricle?
The lateral side of the ventricle is marked by a sulcus – the hypothalamic sulcus – from the inferior side of the interventricular foramina to the anterior side of the cerebral aqueduct. The lateral border posterior/superior of the sulcus constitutes the thalamus, while anterior/inferior of the sulcus it constitutes the hypothalamus. The interthalamic adhesion usually tunnels through the thalamic portion of the ventricle, joining together the left and right halves of the thalamus, although it is sometimes absent, or split into more than one tunnel through the ventricle; it is currently unknown whether any nerve fibres pass between the left and right thalamus via the adhesion (it has more resemblance to a herniation than a commissure ).
What is the slit in the diencephalon?
It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami.
Which part of the ventricle is responsible for sleep?
The superior part of the posterior border constitutes the habenular commissure, while more centrally it the pineal gland, which regulates sleep and reacts to light levels.
What is a rare tumor that can arise in the third ventricle?
A chordoid glioma is a rare tumour that can arise in the third ventricle.
Why do they do endoscopic third ventriculostomy?
An endoscopic third ventriculostomy can be performed in order to release extra fluid caused by hydrocephalus . Several studies have found evidence of ventricular enlargement to be associated with major depression, particularly enlargement of the third ventricle.
What is the third ventricle?
The third ventricle is a narrow, four-sided, . irregularly shaped opening in the middle of . the brain that provides a pathway for . cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid is . the cushiony fluid that protects the brain . and spine from trauma. In addition to the . third ventricle, there is a fourth ventricle .
What is the narrow roof of the third ventricle?
ROOF: The narrow roof of the third ventricle is formed by a thin membrane known as the tela choroidea.
What is the wall in the back of the ventricle called?
The wall in the back is known as the posterior wall. The wall in the front is known as the . anterior wall. The walls on the side are known as the lateral walls. "Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™. On each side of the third ventricle is a thalamus and the .
Which ventricle is connected to each of the lateral ventricles and to the fourth ventricle?
The third ventricle is connected to each of the lateral ventricles and to the fourth ventricle. The area that
How many ventricles are there on the right side of the body?
the right. There is one lateral ventricle on
Where is the midbrain tegmentum located?
The midbrain tegmentum is a term for the major part of the midbrain. The midbrain tegmentum is located in the top part of the midbrain. Below is a picture of the midbrain and the rest of the brainstem (pons and medulla). You can see how the top of the midbrain forms part of the floor of the third ventricle.
What is the pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is an area in the brain that . secretes (forms and gives off) chemicals known as . hormones, such as those that are important for growth. Hormones are natural chemicals produced by the body . and released into the blood that have a specific effect . on tissues in the body.
Overview
- There are several variations of the third ventricle.3The most common variations are: 1. Masses: Deformities of the different segments of the floor can be caused by tumors of the posterior fossa and hydrocephalus. 2. Longstanding hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pr…
Structure
Development
Clinical significance
See also
External links
The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius) at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner o…