The epidermis is a thinner portion of the skin, which is composed of epithelial tissue. While the epidermis is avascular, the dermis is vascular. For this reason, if you cut the epidermis there is no bleeding, but if the cut penetrates to the dermis there is bleeding. The epidermis is composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
What is the layer between the dermis and epidermis?
What tissues make up the skin?
- The epidermis is the epithelial tissue layer of skin.
- The dermis is the connective tissue layer of skin.
- Beneath the skin lies the hypodermis — connective tissue which may be adipose or fibrous, depending on location.
What are the five layers of the epidermis?
- (1) Keratinocyte
- (2) Melanocyte
- (3) Langerhans cells
- (4) Merkel cell
What are the seven layers of skin?
Understanding The 7 Layers Of The Skin
- 15 feet of blood vessels
- 4 yards of nerves
- 650 sweat glands
- 100 oil glands
What is the function of epidermis?
The epidermis serves several functions: it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds, and (especially in roots) absorbs water and mineral nutrients. what is the upper and lower epidermis of a leaf? The epidermis consists of the upper and lower epidermis; it aids in the regulation of gas exchange via stomata.
Is epithelial tissue in the dermis?
The dermis is made of connective tissue and is covered on its surface by a thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium that we call the epidermis. The dermis is a highly vascularized tissue, while the epidermis – – like any other type of epithelial tissue – – is avascular.
What tissue is found in the dermis?
The dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, elastic tissue, and other extracellular components that includes vasculature, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands.
Where are epithelial tissues found?
Some examples of epithelial tissue include: The outer layer of your skin (epidermis). The lining of your intestines. The lining of your respiratory tract.
What part of the skin is an epithelial tissue?
What Is Epithelial Tissue? Epithelial tissue or epithelium forms the outer covering of the skin and also lines the body cavity. It forms the lining of respiratory, digestive, reproductive and excretory tracts.
How many types of tissue are in the dermis?
three typesTissue Composition The dermis is composed of three types of tissues that are present throughout the dermis rather than in layers: Collagen. Elastic tissue. Reticular fibers.
Which type of tissue is found in the dermis quizlet?
The dermis has connective tissue, smooth muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
Which of the following is NOT epithelial tissue?
Answer and Explanation: The correct answer is (c) Skull. Epithelial tissue consists of a thin layer of cells which adhere to the basement membrane and form a barrier around an organ or part of the body.
Which layer of the dermis is dense?
Reticular layer of Dermis. The deeper reticular dermis, which accounts for about 80% of the thickness of the dermis, is dense irregular connective tissue. Its extracellular matrix contains thick bundles of interlacing collagen and elastic fibers that run in many different planes. However, most run parallel to the skin surface.
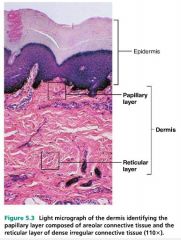
What is the papillary layer of the dermis?
Papillary layer of Dermis. The papillary dermis, the superficial 20% of the dermis, is areolar connective tissue containing very thin collagen and elastic fibers. It includes the dermal papillae (“nipples”), fingerlike projections that extend into the overlying epidermis. These projections of the dermal papillae into the epidermis increase ...
What is the effect of dermal papillae on the epidermis?
These projections of the dermal papillae into the epidermis increase the surface area for exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products between these layers. Recall that the epidermis is avascular and depends on the diffusion of these materials from the underlying dermis. The inter-digitation of these layers also strengthens ...
How many layers of the epidermis are there?
Where exposure to friction is greatest, such as in the fingertips, palms, and soles, the epidermis has five layers—stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and a thick stratum corneum. This is called thick skin.
Where are the dermal papillae located?
On the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet, the dermal papillae lie atop larger mounds called dermal ridges. These elevate the overlying epidermis into epidermal ridges or friction ridges, which create fingerprints, palm-prints, and footprints. Epidermal ridges increase friction and enhance the gripping ability of the hands and feet.
What is the name of the layer of the skin that runs parallel to the skin surface?
However, most run parallel to the skin surface. The reticular layer is named for its networks of collagen fibers (reticulum = network); the name does not imply any special abundance of reticular fibers. Separations or less dense regions between the collagen bundles form the cleavage lines or tension lines of the skin.
Where are the accessory structures of the skin located?
The dermis is also the site where all the accessory structures of the skin – your hair, nails, and a variety of multicellular exocrine glands originate. These structures are located in the dermis and protrude through the epidermis to the surface. The dermis has two regions: the Papillary Dermis and. the Reticular Dermis.
What is the epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is one of the four tissue types. It is found lining the inner and outer body surfaces and comprising the parenchyma of the glands. It is divided into surface (covering) and glandular (secreting) epithelium. Surface epithelium consists of one or more cell layers, stacked over a thin basement membrane.
What is the epithelium?
Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues. Like all types, it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). ...
What is the cuboidal epithelium?
Simple cuboidal epithelium – a single layer of cube-shaped cells. This type of epithelium offers greater protection than simple squamous due to its increased thickness. It also has secretory, absorptive and excretory functions because of its organelle rich cytoplasm. Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in organs with these functions, such as the ducts of the salivary glands, liver, pancreas and other exocrine glands. It forms thyroid follicles, kidney tubules, seminiferous tubules of male testis, and covers the surface of the ovaries (germinal epithelium).
Why doesn't the epithelium have blood vessels?
This is one reason why epithelia doesn't have blood vessels, as abrasion could result in tearing of the vessel and bleeding. Epithelia specialized for protection, such as the stratified squamous keratinized epithelium of the skin, are multilayered and have a high cell renewal rate. This means that they repair quickly after injury.
What is stratified epithelium?
Stratified epithelium consists of two or more cell layers. Based on the shape of their most apical cell layer, they are further classified into squamous, cuboidal and columnar. There are also two types of specialized stratified epithelium: keratinized and transitional.
What is pseudo-seudostratified epithelium?
Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of simple columnar epithelium. It is termed “pseudo” because, although single, it appears to have multiple layers. All the cells are attached to the basement membrane but not all of them reach the free surface, thus forming a sheet of cells with different heights and irregularly located nuclei.
Which type of epithelium is responsible for detecting smells?
These epithelial receptor cells have apical cilia which detect the chemical signals of incoming odors. They pass that signal to the olfactory nerve (CN I) which transmits the information about the smell to the central nervous system. Other receptor epithelia include stratified columnar epithelia of the retina, taste buds , organ of Corti and ampullae in the inner ear.
What is the dermis in histology?
Histology, Dermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. The dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, elastic tissue, and other extracellular components that includes vasculature, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands.
What are the primary cells of the dermis?
Fibroblasts are the primary cells within the dermis, but histiocytes, mast cells, and adipocytes also play important roles in maintaining the normal structure and function of the dermis. The dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, ...
How does UV damage affect the dermis?
Aging and chronic sun exposure can weaken the dermis. Solar elastosis is due to chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure, resulting in damage to elastic fibers. Histology reveals basophilic degeneration of elastic fibers in the dermis.[29] The reduction of connective tissue in aging, usually with concomitant UV damage, causes actinic purpura (i.e., senile purpura) where the dermis cannot support its vasculature. As a result, minor trauma can lead to extravasation of blood.[30] Similar manifestations may be seen in chronic glucocorticoid users. Glomus tumors can also occur within the dermis and deeper tissues, especially within the digits and palms where glomus bodies are concentrated. [31]
What are the components of the dermis?
Collagen is the principal component of the dermis. Specifically, type I and type III collagen are found in abundance. Elastic fibers also play an important structural role within the dermis. Elastic fibers are composed of elastin and fibrillin microfibrils. In contrast to collagen , the biochemical configuration of elastin allows for gliding, stretching, and recoiling of fibers.[2] The reticular dermis comprises thick elastic fibers. Two subtypes of elastic fibers are worth further discussion: elaunin and oxytalan fibers[3]. Elaunin fibers are horizontally arranged elastic fibers found near the junction of the papillary and reticular dermis. Oxytalan fibers are perpendicular elastic fibers found in the papillary dermis. [4]
How is dermis examined?
The dermis is examined using a standard skin biopsy. The tissue sample should first be fixated with formalin to preserve tissue structure. After fixation, the specimen is dehydrated with an alcohol (e.g., ethanol) to remove water. The alcohol agent is then cleared using xylol.
Which layer of the dermis is composed of loose connective tissue?
The papillary dermis is the superficial layer, lying deep to the epidermis. The papillary dermis is composed of loose connective tissue that is highly vascular. The reticular layer is the deep layer, forming a thick layer of dense connective tissue that constitutes the bulk of the dermis. Collagen is the principal component of the dermis.
What is the dermis?
The dermis is a connective tissue layer of mesenchymal origin located deep to the epidermis and superficial to the subcutaneous fat layer .[1] . The composition of the dermis is mainly fibrous, consisting of both collagen and elastic fibers. Between the fibrous components lies an amorphous extracellular "ground substance" containing ...
What are the layers of the dermis?
The dermis has two layers: 1 papillary dermis – made up of loosely woven connective tissue fibers embedded in a jelly-like substance known as ground substance. This layer conforms exactly to the contours of the stratum basale of the epidermis. Together with the basement membrane, which acts as a selective filter for substances moving between the two layers, the papillary dermis helps to protect the appendages of the epidermis and provides structure and support to the epidermis. 2 reticular dermis – thicker and deeper and is made up of dense connective tissue that is irregularly arranged, providing additional support.
What is the dermis made of?
The dermis has two layers: papillary dermis – made up of loosely woven connective tissue fibers embedded in a jelly-like substance known as ground substance . This layer conforms exactly to the contours of the stratum basale of the epidermis.
What is the function of the papillary dermis?
Together with the basement membrane, which acts as a selective filter for substances moving between the two layers, the papillary dermis helps to protect the appendages of the epidermis and provides structure and support to the epidermis.
What are the subcutaneous tissues?
Subcutaneous Tissues. The subcutaneous tissues support the skin and are composed of adipose tissue and fascia. Adipose tissue houses our body’s fat and is made up of loose connective tissue. It also stores fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K).
Why is the dermis important?
Although the dermis has fewer layers that are much less well defined, it is equally important. The dermis is quite elastic and pliable and is very vascular, owing to the presence of numerous capillary beds that provide nutrition to both layers.
What is the function of the dermis?
The dermis also contains sensory fibers which provide the brain with information on temperature, pressure, vibration and touch. The dermis serves many functions. In addition to nourishing both layers, it houses the appendages of the epidermis, plays an active role in controlling infection, provides sensation and assists in control ...
What are the deep tissues of the body?
Deeper tissues include bone, the joint capsules, muscle, ligaments and tendons. Each of these structures has a characteristic appearance. It is important to be able to distinguish between these structures when working with deep wounds that extend into or expose these deeper tissues, particularly if debridement is to be part of your job description.
How thick is the epidermis?
The epidermis has no blood supply and it is nourished by diffused oxygen from surrounding air. The thickness of the epidermis is approximately 0.1mm. It acts as a protective layer as it protects the entering of pathogens.
Which layer of the epidermis is the most superficial?
The stratum corneum is the most superficial layer of the epidermis and is the layer exposed to the outside environment. The increased keratinization of the cells in this layer gives it its name. There are usually 15 to 30 layers of cells in the stratum corneum.
Why is the stratum granulosum grainy?
The stratum granulosum has a grainy appearance due to further changes to the keratinocytes as they are pushed from the stratum spinosum.
What is the papillary layer?
Papillary layer. The papillary layer is made of loose, areolar connective tissue, which means the collagen and elastin fibers of this layer form a loose mesh. This superficial layer of the dermis projects into the stratum basale of the epidermis to form finger-like dermal papillae. Within the papillary layer are fibroblasts, ...
What is the structure of the skin?
Structure of skin – A Creature of Epidermis, Dermis and Hypodermis. Epidermis – It is made up of closely packed epithelial cells. Dermis – It is made up of dense, irregular connective tissue that includes blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Hypodermis – It is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.
What is the difference between the hypodermis and the dermis?
Dermis – It is made up of dense, irregular connective tissue that includes blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Hypodermis – It is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.
Where is the stratum lucidum located?
The stratum lucidum is a smooth, seemingly translucent layer of the epidermis located just above the stratum granulosum and below the stratum corneum. This thin layer of cells is found only in the thick skin of the palms, soles, and digits. The keratinocytes that compose the stratum lucidum are dead and flattened.
What is the outermost layer of the epidermis?
Stratum corneum: This is the outermost or top layer of the epidermis. It's made of dead, flat keratinocytes that shed approximately every two weeks. The epidermis contains three specialized cells: Langerhans cells that act as the first line of defense in the skin's immune system.
What are the two layers of the dermis?
The dermis is split into two parts—the papillary dermis, which is the thin, upper layer, and the reticular dermis, which is the thick, lower layer. 5
What is the middle layer of the skin?
The dermis is the middle layer of the three layers of skin. It's located between the epidermis and the subcutaneous tissue. It contains connective tissue, blood capillaries, oil and sweat glands, nerve endings, and hair follicles.
What are the three types of cells in the epidermis?
The epidermis contains three specialized cells: 1 Melanocytes that produce pigment (melanin) 2 Langerhans cells that act as the first line of defense in the skin's immune system 3 Merkel cells that have a function that is not yet fully understood. 4
How many layers of the epidermis are there?
There are five layers of the epidermis: 2 . Stratum basale: This bottom layer, which is also known as the basal cell layer, has column-shaped basal cells that divide and push older cells toward the surface of the skin. As the cells move up through the skin, they flatten and eventually die and shed. Stratum spinosum: This layer, which is also known ...
What is the role of subcutaneous tissue in body temperature?
It also acts as a cushion, so if you ever fall or hit something with your body, it protects your insides and makes the injury hurt less.
How many layers of skin are there?
There are three main layers of skin.
What are the layers of the dermis?
The dermis contains two layers : the outermost papillary layer and the deeper reticular layer. The thin papillary layer is composed of loose connective tissue and connects to the epidermis with papillae. Papillae may nourish the epidermis or act as touch receptors.
Which layer of the skin contains sweat glands?
The reticular layer contains hair follicles, sweat glands, Pacinian corpuscles, which sense pressure, lymph vessels and smooth muscle. To read about the skin in more detail, check out this link. Answer link.
What are the two layers of skin?
Our skin has two principal layers : epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is composed of epithelial tissue, and the dermis is connective tissue. The dermis supports the epidermis and binds it to the subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis), the loose connective tissue directly under the skin. Diagram of different layers of skin :
What is the thick reticular layer made of?
And the thick reticular layer is made of dense connective tissue with irregular bundles of collagen fibers ( dense irregular connective tissue ).

Anatomy and Structure
Tissue Composition
- The dermis is composed of three types of tissues that are present throughout the dermis rather than in layers: 1. Collagen 2. Elastic tissue 3. Reticular fibers The papillary layer, the upper layer of the dermis, contains a thin arrangement of collagen fibers. The lower layer, known as the reticular layer, is thicker and made of thick collagen fibe...
Roles It Plays
- The dermis is the thickest layer of skin and arguably the most important. It plays several key roles, including: 1. Producing sweat and regulating the body's temperature: Within the dermis are sweat glands that produce sweat that comes out of the pores. The body sweats as a way to cool itself off, regulate temperature and flush out toxins. There are more than 2.5 million sweat glands in th…
Interactions with The Epidermis
- Not only does the dermis have complex functions, but it is in constant contact and communication with the epidermis, regulating important bodily processes. Cells in the epidermis influence the dermis, which in turn influence the turnover of cells in the epidermis (via activities of cells such as mast cells, which secrete cytokines). It is the interaction of these two layers that is, in fact, most …
Aging Process
- Many people wonder about what causes the skin to wrinkle and age. There are several important changes in all three layers of our skin as we age. The dermal layer becomes thinner with age as less collagen is produced.6Elastin wears out—becoming less elastic just as the elastic waistband in a pair of shorts may lose its elasticity. This is what leads to wrinkling and sagging. The sebace…
Tumors
- Just as abnormal growths in the epidermis give rise to the all-too-common skin cancers, tumors can arise from the dermal layer of the skin as well. One type of tumor which begins in the dermis is called a dermatofibroma (or benign fibrous histiocytoma.)8These fairly common tumors often occur on the legs of middle-aged women. It's not known what exactly causes these tumors, but t…
Protection
- Just as it's important to protect your epidermis from too much sun, it's important to protect your dermis as well. Sun exposure damages collagen (and causes changes in elastin), which can result in premature wrinkling.6
Causes
Structure
Functions
Genetics
Clinical significance
Symptoms
Variations
Physical characteristics
Overview
- Tactile epithelial cells, or Merkel cells, are the least numerous of the epidermal cells. They are located in the deepest layer of the epidermis, where they contact the flattened process of a sensory neuron (nerve cell), a structure called a tactile disc or Merkel disc. Tactile epithelial cells and their associated tactile discs detect touch sensat...