
Why do we use polar solvents in TLC?
this is for increasing the elution factor. the more polar the TLC solvent which is polar by itself, the better it expels the nonpolar molecules to give higher rf value. So remember, in TLC, we have a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The stationary phase we usually see is made up of silica gel or alumina which are very polar.
What is the principle of TLC?
In TLC, we use a stationary phase (most frequently silica gel) which is deposited over a glass or aluminum support. We then can spot mixtures of compounds over the same line. Then we elute the TLC with an organic solvent, and the different compounds will move upwards at different rates, allowing the separation of the different components.
What are the two phases of TLC?
TLC has two phases. A thin layer of silica or alumina on inert support acting as a solid stationary phase. The second one is a developing solvent that acts as a mobile phase.
What is TLC (thin-layer chromatography)?
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose.
What is TLC in chemistry?
Why is TLC important?
How to spot TLC?
How high is a thin layer chromatography plate?
What is preparative TLC?
What is the stationary phase of TLC?
Can you do thin layer chromatography if you have never been in a chemistry lab before?
See 2 more
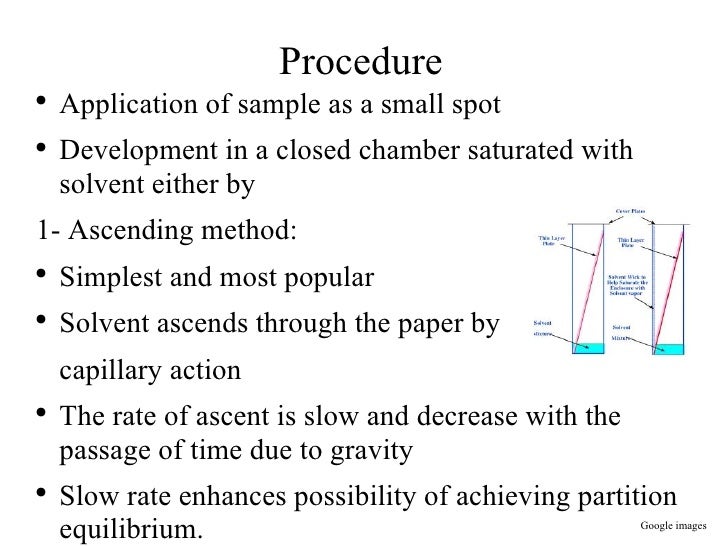
Which TLC plate is most polar?
Answer: Alumina is more polar than is silica (see the first paragraph under “The Adsorbent” in the TLC section). Therefore, each of the compounds would travel slower on an alumina TLC plate than on a silica TLC plate, and the Rf values for each of the compounds would be smaller.
What type of chromatography is TLC?
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is an affinity-based method used to separate compounds in a mixture. TLC is a highly versatile separation method that is widely used for both qualitative and quantitative sample analysis.
Which phase is polar in TLC?
The silica gel of the stationary phase is very polar, which will ultimately affect the rates at which the components of the mixture separate. The mobile phase is a suitable liquid solvent or mixture of solvents. The polarity of the mobile phase can be adjusted from very polar to very nonpolar (and anywhere in between).
How does TLC work polarity?
The stronger a compound is bound to the adsorbent , the slower it moves up the TLC plate. Non-polar compounds move up the plate most rapidly (higher Rf value), whereas polar substances travel up the TLC plate slowly or not at all (lower Rf value).
How does polarity affect TLC?
The more polar the compound, the more it will adhere to the adsorbent and the smaller the distance it will travel from the baseline, and the lower its Rf value.
Does higher Rf mean more polar?
The more polar spot travels slower, and the less polar spot travels faster. Rf values, on the other hand, are directly related to the rate of movement. The fastest moving spot has the highest Rf value. polar (fastest moving), and the spot with the lowest Rf value is the most polar (slowest moving).
How does polarity affect chromatography?
Polarity of the solvent affects the speed of the chromatography process. So, we can say that, if we increase the polarity of the solvent all the other components present in the mixture move faster during the chromatography experiment.
Why is silica a polar stationary phase?
Silica gel, the most commonly used stationary phase, has the empirical formula SiO2. However, at the surface of the silica gel particles, the dangling oxygen atoms are bound to protons. The presence of these hydroxyl groups renders the surface of silica gel highly polar.
Is TLC adsorption chromatography?
TLC is an adsorption chromatography technique. In this process a sheet of glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with silica gel, aluminium oxide or cellulose acts as a stationary phase and a single solvent or a mixture of solvent like ethanol and chloroform act as mobile phase.
Why is TLC superior to paper chromatography?
TLC tends to produce more useful chromatograms than paper chromatography, which show greater separation of the components in the mixture - and are therefore easier to analyse. The distance a sample travels can depend on the size or the polarity of the molecules involved.
What is TLC chromatography used for?
The technique of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is normally used as an analytical method to follow the progress of a reaction, to analyse mixtures or to establish conditions for a preparative separation of compounds using column chromatography.
What is the principle of TLC chromatography?
What is the principle of TLC? TCL is based on the principle of separation through adsorption type. The separation relies on the relative empathy of compounds towards the mobile phase and stationary phase.
What happens when you can no longer see any A by TLC?
As B is in excess what you are really looking for is loss of A. When you can no longer see any A by TLC, the reaction can be worked up. The groups that make for low running are those that interact strongly with the silica surface: basic amines, acids, alcohols.
What makes a molecule low running?
The groups that make for low running are those that interact strongly with the silica surface: basic amines, acids, alcohols. This is a general rule of thumb, but in my experience trying to guess where a multi-functioned molecule is going to run is quite a lottery. I do not believe that it is a safe assumption that a product similar to C would always run below a SM similar to B.
Is alcohol a polar group?
The alcohol is a polar group and will also pull it down thus the sum of these effects is that it runs lower. This missing information is the eluent. From what what is given in the question it is clear that the eluent is something like DCM/MeOH/NH3 (that would be my first attempt to separate such basic components).
Does silica run on TLC?
I am assuming this is TLC run on silica. Silica is a mildly acidic surface so basic compounds such as amines do not come off the baseline unless you use a very polar eluent with added base (e.g. ammonia/triethylamine). Starting material B is a basic amine. Starting material A is an epoxide and fairly non-polar (kinda similar to an ether) and will run high in most systems, certainly any system where B comes off the baseline. Your product C is more basic (tertiary v secondary), this is the strongest effect. The second non-polar aromatic group raises the likelihood that it will run above B, but this is a weak effect. The alcohol is a polar group and will also pull it down thus the sum of these effects is that it runs lower
What is TLC in chemistry?
TLC is a time saving technique as compared to paper chromatography.
Which is better HPLC or TLC?
HPLC is far faster, more reliable for quantitative analysis, and gives greater resolution than TLC and CC.
What is the difference between paper chromatography and thin layer chromatography?
The difference between paper chromatography and thin layer chromatography is the type of stationary phase used. In TLC, the stationary phase is a thin layer of solid adsorbent on an inert support. The adsorbent often used is silica gel. While in paper chromatography, the water content present in cellulose or paper will act as a stationary phase.
What are the phases of TLC?
A thin layer of silica or alumina on inert support acting as a solid stationary phase. The second one is a developing solvent that acts as a mobile phase.
Why is TLC better than paper chromatography?
TLC is preferred over paper chromatography as it is time saving, more sensitive, non-destructive, and temperature resistant technique. Furthermore, TLC is more precise and accurate than paper chromatography.
Why is 2D TLC used?
Thus, a 2D TLC is used in which two mobile phases separate analyte against a stationary phase in two steps.
What temperature to use for activation of TLC plate?
When we intend to remove the water content or moisture from the TLC plate, silica gel is heated at 100 -110°C for activation. Silica gel is preferred as it is stable at high temperatures and does not interact with any mobile phase.
Why do researchers use TLC?
Researchers may employ TLC as a tool to monitor the progress of a reaction, to purify small amounts of compounds, or even to select effective solvent systems for other chromatographic procedures. Because of its simplicity, cost effectiveness, and efficiency, TLC functions as one of the most widely used analytical analyses in the chemistry world.
What is the most important parameter in TLC?
Choosing an appropriate solvent system , or mobile phase, is viewed as the most important parameter of an efficient, effective TLC process. To select a good solvent system, scientists consider their solution’s solubility in the system as well as its different affinities with the mobile and stationary phases on the plate.
What is the chemical formula for TLC plates?
TLC plates are coated in silica gel, a solid substance containing silicon dioxide with alternating silicon and oxygen atoms. At the surface of the silica gel lie polar hydroxyl groups with the chemical formula: -OH. The components of a given compound interact with these polar compounds in different ways according to the varying polarities of their functional groups. These interactions directly impact the speed at which they migrate up a TLC plate once it is placed in a solvent system, as shown above. This facilitates the separation of different “dots” of compound components. TLC analyses allow scientists to obtain well defined, separated spots that denote the different components of a mixture.
How does a solvent move up a TLC plate?
The solvent, or mobile phase, should rise up the TLC plate, or stationary phase, via capillary action. As the components of your solution travel up the plate, they will interact with the silica hydroxyl groups in various ways, depending on their respective functional groups.
What is a strong polar net dipole?
A substance containing polar functional groups, or a strong polar net dipole, interacts “significantly” with the stationary phase. This means that the substance is strongly absorbed to the stationary phase. It should move slowly up the TLC plate, “sticking” to the silica gel.
What is the process of spotting a TLC plate with a compound?
The TLC process involves spotting a TLC plate with a compound in order to isolate and identify its constituents and check reaction progress.
How to examine a TLC plate?
To examine the developed plate, use a UV light source to illuminate the locations of each dot. Trace everything you see–this includes splotches, dots, lines, and streaks. You may also utilize a staining agent, such as iodine, to complete this step. Staining agents react with particular functional groups, rendering their spots more visible; submerging your TLC plate in a staining agent, then placing it on a hot plate to dry, will accomplish this.
What is TLC in chemistry?
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose.
Why is TLC used in chemical reactions?
Because of its simplicity and speed, TLC is often used for monitoring chemical reactions and for the qualitative analysis of reaction products.
What is HPTLC in quantitative analysis?
A number of enhancements can be made to the original method to automate the different steps, to increase the resolution achieved with TLC and to allow more accurate quantitative analysis. This method is referred to as HPTLC, or "high-performance TLC". HPTLC typically uses thinner layers of stationary phase and smaller sample volumes, thus reducing the loss of resolution due to diffusion .
Why do compounds travel at different rates?
Different compounds in the sample mixture travel at different rates due to the differences in their attraction to the stationary phase and because of differences in solubility in the solvent. By changing the solvent, or perhaps using a mixture, the separation of components (measured by the Rf value) can be adjusted. Also, the separation achieved with a TLC plate can be used to estimate the separation of a flash chromatography column. (A compound elutes from a column when the amount of solvent collected is equal to 1/R f .) Chemists often use TLC to develop a protocol for separation by chromatography and use TLC to determine which fractions contain the desired compounds.
What is the mobile phase of a TLC plate?
Because different analytes ascend the TLC plate at different rates, separation is achieved. The mobile phase has different properties from the stationary phase. For example, with silica gel, a very polar substance, non-polar mobile phases such as heptane are used. The mobile phase may be a mixture, allowing chemists to fine-tune the bulk properties of the mobile phase.
How are TLC plates made?
They are prepared by mixing the adsorbent, such as silica gel, with a small amount of inert binder like calcium sulfate (gypsum) and water. This mixture is spread as a thick slurry on an unreactive carrier sheet, usually glass, thick aluminum foil, or plastic. The resultant plate is dried and activated by heating in an oven for thirty minutes at 110 °C. The thickness of the absorbent layer is typically around 0.1–0.25 mm for analytical purposes and around 0.5–2.0 mm for preparative TLC.
What is added to the adsorbent layer to allow for the visualization of spots under UV-C light?
Often a small amount of a fluorescent compound, usually manganese -activated zinc silicate, is added to the adsorbent that allows the visualization of spots under UV-C light (254 nm). The adsorbent layer will thus fluoresce light-green by itself, but spots of analyte quench this fluorescence.
What is the stationary phase of TLC?
So remember, in TLC, we have a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The stationary phase we usually see is made up of silica gel or alumina which are very polar. The mobile phase can range from non-polar to very polar solvents. We pick the solvents based on whatever we know about the compound we are trying to separate.#N#The polar molecules in the compound will be attracted to the silica gel while the more non-polar molecules will stay in the solvent (mobile phase). Let's say if you developed a TLC plate and you saw all the dots very close to the bottom of the plate. This means that the solvent wasn't polar enough to kick off the polar compound off the silica or alumina and move it further up the plate. So in this case, you would have a lower rf value since the molecules did not travel far.#N#We could then increase the polarity of the solvent which would help "elute" the molecules and move them further up the silica plate. This would result in larger rf values.#N#And if you need further clarification:#N#Given two compounds that differ in polarity, the more polar compound has a stronger interaction with the silica and is, therefore, more capable to dispel the mobile phase from the binding places. As a consequence, the less polar compound moves higher up the plate (resulting in a higher R f value). If the mobile phase is changed to a more polar solvent or mixture of solvents, it is more capable of dispelling solutes from the silica binding places, and all compounds on the TLC plate will move higher up the plate.
What does it mean when you see dots on a TLC plate?
This means that the solvent wasn't polar enough to kick off the polar compound off the silica or alumina and move it further up the plate.
What happens when a compound is more polar?
As a consequence, the less polar compound moves higher up the plate (resulting in a higher R f value). If the mobile phase is changed to a more polar solvent or mixture of solvents, it is more capable of dispelling solutes from the silica binding places, and all compounds on the TLC plate will move higher up the plate.
How would increasing the polarity of the solvent help the molecules?
We could then increase the polarity of the solvent which would help "elute" the molecules and move them further up the silica plate. This would result in larger rf values.
What happens if a molecule is nonpolar?
If the molecules are nonpolar (ether, butane, etc) then they won't be as "sticky" and will be allowed to continue up the strip resulting in a higher Rf.
Is silica gel polar or nonpolar?
The silica gel is polar. This means that it'll hold other polar molecules tightly and keep the Rf low. If the molecules are nonpolar (ether, butane, etc) then they won't be as "sticky" and will be allowed to continue up the strip resulting in a higher Rf.
What is TLC in chemistry?
If there is one technique or experiment that every chemist, or student learning chemistry should know, it is Thin Layer Chromatography (or TLC for short). If you want to become a synthetic chemist, or you are planning to ace an experimental course on organic chemistry, TLC is something you really need to master. TLC of black ink.
Why is TLC important?
As you can see, TLC is extremely important for both reaction monitoring and product purification, the two cornerstones of any synthesis laboratory.
How to spot TLC?
Spot the TLC mixtures at the corresponding mark in the line above the bottom of the plate. Then elute the plate and see how many compounds there is in your mixture, and how polar are they, just by checking out the different spots. Try to spot your mixtures as tightly as possible. Make very small spots of sample.
How high is a thin layer chromatography plate?
Usually, a thin layer chromatography plate is around 5–7 cm high, and a line is drawn around 0.5–1.0 cm from the bottom. That is the line in which you will spot your mixtures to separate. It is important that you spot the mixtures above the solvent level on your elution chamber!
What is preparative TLC?
Well, preparative TLC is just a regular thin layer chromatography separation, but with a bigger plate!
What is the stationary phase of TLC?
In TLC, we use a stationary phase (most frequently silica gel ) which is deposited over a glass or aluminum support. We then can spot mixtures of compounds over the same line. Then we elute the TLC with an organic solvent, and the different compounds will move upwards at different rates, allowing the separation of the different components.
Can you do thin layer chromatography if you have never been in a chemistry lab before?
I can tell you that even if you have never been in a chemistry lab before, you will be prepared to do a thin layer chromatography just by continuing to read the first sections.
