Common Causes
The symptoms of chronic urinary retention may include:
- Passing urine more frequently (urinary frequency).
- Difficulty passing urine (dysuria).
- A weak or an interrupted urine stream.
- An urgent need to pass urine with little success.
- Constantly feeling the need to pass more urine, even after just passing urine.
- Mild and constant discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Related Conditions
Which medicine is best for urine problem?
- Oxybutynin (Ditropan XL, Oxytrol)
- Tolterodine (Detrol)
- Darifenacin (Enablex)
- Solifenacin (Vesicare)
- Trospium.
- Fesoterodine (Toviaz)
What are the signs of urine retention?
Symptoms of urinary retention may include: Difficulty starting to urinate. Difficulty fully emptying the bladder. Weak dribble or stream of urine. Loss of small amounts of urine during the day. Inability to feel when bladder is full. Increased abdominal pressure. Lack of urge to urinate.
What is the treatment for urinary retention?
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream.
What are the symptoms of urinary retention?
What is considered urinary retention?

What is the diagnosis of urinary retention?
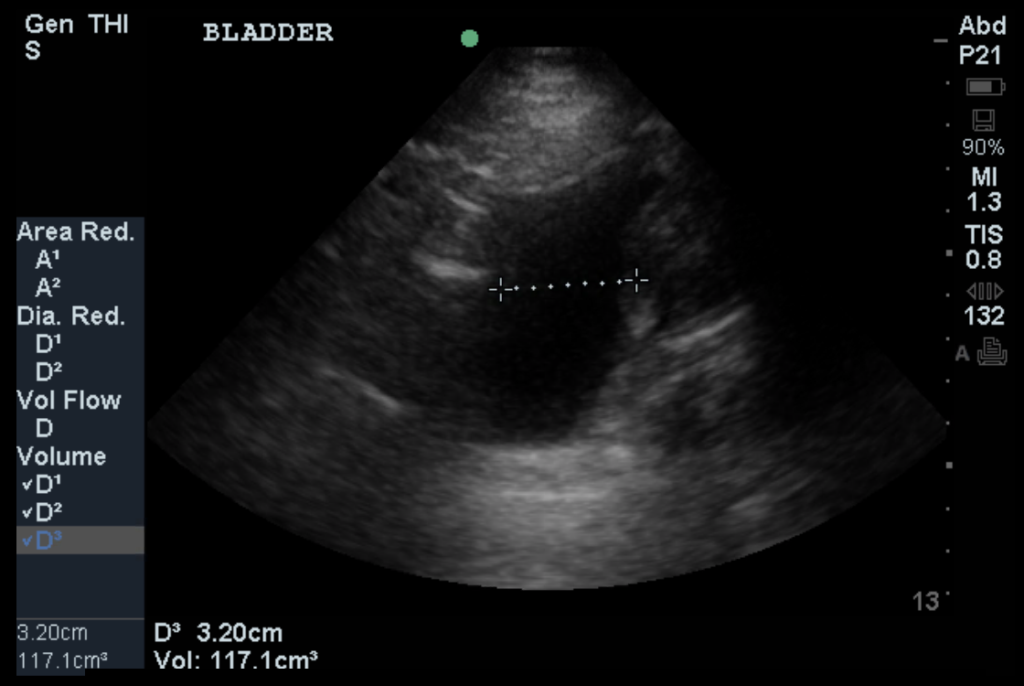
Urodynamic testing Your health care professional may use the following urodynamic tests to help diagnose urinary retention. Uroflowmetry measures the amount of urine released from your body and how quickly the urine comes out. Pressure flow studies measure the pressure in your bladder and the flow rate as you urinate.
Is urinary retention a medical emergency?
Acute urinary retention, a potentially life-threatening medical condition, requires immediate emergency treatment. Acute urinary retention can cause great discomfort or pain. Chronic urinary retention can be a long- lasting medical condition.
What can urinary retention be related to?
The most common cause of urinary retention is benign prostatic hyperplasia. Other common causes include prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis, and vulvovaginitis; receiving medications in the anticholinergic and alpha-adrenergic agonist classes; and cortical, spinal, or peripheral nerve lesions.
Is urinary retention serious?
Acute urinary retention can be life threatening. If you have any of the other symptoms of urinary retention, such as trouble urinating, frequent urination, or leaking urine, talk with your health care professional about your symptoms and possible treatments. Chronic urinary retention can cause serious health problems.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary retention?
ICD-10 code R33. 9 for Retention of urine, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What does a urologist do for urinary retention?
The most common surgery is transurethral resection of the prostate. In this procedure, the urologist uses a tiny tool, inserted through a catheter, to remove a section of the prostate. This treatment is used frequently for urinary retention caused by BPH. Internal urethrotomy.
Can urinary retention be cured?
Urinary retention is treatable, and there is no need to feel embarrassed or ashamed. A doctor can often diagnose the problem. However, in some cases, a person may need a referral to a urologist, proctologist, or pelvic floor specialist for further testing and treatment.
Who is at risk for urinary retention?
Those at the greatest risk of suffering from urinary retention include: Men more than women. Young, sexually active men. People over the age of 50.
Can urinary retention be caused by stress?
People with anxiety disorders can experience a range of symptoms and side effects, even physical ones. More frequent symptoms include a pounding or rapid heartbeat, unexplained aches and pains, dizziness, and shortness of breath, but anxiety can also cause less common side effects like urinary retention.
How is chronic urinary retention treated?
Medications that can help treat urinary retention include :antibiotics for infections of the prostate, bladder, or urinary tract.medications to relax your prostate or sphincters and help urine flow more freely.medications to reduce the size of your prostate (if you have BPH)
What tests are used to determine if you have urinary retention?
Health care professionals use your medical history, a physical exam, and a postvoid residual urine measurement to diagnose urinary retention. Your health care professional may also order lab and other diagnostic tests to help find the cause of your urinary retention.
What is the best way to find out what is causing urinary retention?
uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to create images of your urinary tract. A health care professional may use urinary tract imaging tests such as an ultrasound, VCUG, MRI, or CT scan to find out what’s causing your urinary retention.
What is the best test for urinary retention?
Imaging tests . Your health care professional may use the following urinary tract imaging tests to diagnose other conditions that may be causing your urinary retention. . Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) uses x-rays to show how urine flows through the bladder and urethra.
What is the purpose of video urodynamics?
Video urodynamics takes pictures and videos of your bladder as it fills and empties. Cystometry measures how much urine your bladder can hold, how much pressure builds up in your bladder as it stores urine, and how full your bladder is when you begin to feel the urge to urinate.
What lab test is used to determine if a kidney is causing urinary retention?
Your health care professional may order the following lab tests to look for signs of certain diseases and conditions that may be causing your urinary retention. Urinalysis. NIH external link. is used to find medical conditions that may be causing urinary retention, such as a urinary tract infection (UTI), a kidney problem, or diabetes.
What are the symptoms of urinary tract infection?
symptoms, also sometimes called lower urinary tract symptoms. current and past medical problems such as operations and use of a catheter. prostate problems. pregnancy and childbirth history. over-the-counter and prescription medicines. eating and drinking habits. bowel habits.
What is a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy is a procedure that uses a cystoscope —a long, thin instrument—to look inside your urethra and bladder. The health care professional will look for swelling, redness, signs of infection, cancer, and structural problems.
What are the symptoms of urinary retention?
If your chronic urinary retention causes symptoms, they may include. the inability to completely empty your bladder when urinating. frequent urination in small amounts. difficulty starting the flow of urine, called hesitancy. a slow urine stream. the urgent need to urinate, but with little success.
How do you know if you have urinary retention?
Symptoms of acute urinary retention may include. the inability to urinate. pain—often severe—in your lower abdomen. the urgent need to urinate. swelling of your lower abdomen.
Why is my bladder underactive?
Causes of underactive bladder include. Neurological problems. Urinary retention can occur when there is a problem with your nervous system. NIH external link. that prevents messages from travelling from your brain to your bladder and urethra. There are many different causes of neurological problems, including.
Why does my bladder keep retaining urine?
The causes of urinary retention are related to either a blockage that partially or fully prevents urine from leaving your bladder or urethra, or your bladder not being able to maintain a strong enough force to expel all the urine.
What does it feel like to pee after a pee?
feeling the need to urinate after finishing urination. leaking urine without any warning or urge. lower abdominal pain or discomfort. The symptoms of acute urinary retention are often severe and can include abdominal pain and the inability to urinate, whereas chronic urinary retention may cause few or no symptoms.
What is enlarged prostate?
enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. bladder outlet obstruction, such as urethral stricture or scar tissue in the bladder neck. pelvic organ prolapse, including cystocele and rectocele. urinary tract stones, also called calculi. constipation.
Why is my bladder weak?
Bladder muscles that are weak may not contract with enough strength or force to empty the bladder completely. Causes of weakness can include. age-related loss of bladder muscle strength. overdistention—a bladder that has been stretched such that the muscles are damaged. pregnancy and childbirth.

Diagnosis
Inability to voluntarily empty the bladder (pass urine) completely or partially.
Causes
Clinical significance
Risks
- The acute form is an emergency. You need to see a doctor right away. The chronic form occurs most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
Treatment
- There is more than one cause. It can happen when something blocks the free flow of urine through the bladder and urethra. The urethra is the tube that takes urine from the bladder out of the body. The problem can also be caused by using drugs such as antihistamines (like Benadryl®), antispasmodics (like Detrol®), and tricyclic antidepressants (like Elavil®) that can c…
Symptoms
- Infection and swelling. In men, an infection of the prostate can cause it to swell. This causes it to press on the urethra to block the flow of urine. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can cause swelling of the urethra to cause this problem. Diseases spread by having sex (called STDs) can also cause swelling and lead to retention.