Mean and variance is a measure of central dispersion. Mean is the average of given set of numbers. The average of the squared difference from the mean is the variance.
Full Answer
How do you calculate median?
- Order the data points from lowest to highest, which in this example would be from slow to fast.
- Determine whether you have an even or odd number of data points.
- If you have an odd number, use the (n + 1) / 2 equation to find the median. ...
What is the formula for finding median?
Median Formula
- First, arrange the given data set in ascending order. Say the data set you have is 4, 2, 8, and 1. ...
- Here, n is the number of items in the given data set. ...
- Just apply the variable value n in the formula to get the median. i.e. Median = (n + 1) / 2
How do you find the median of set of numbers?
Median of an Even Set of Numbers
- To find the median, put the numbers in order and then find the number in the middle.
- First we arrange the numbers in ascending order Starting with the smallest number and getting larger. ...
- We cross off the same amount of numbers at each end of the list until two numbers remain in the middle.
What is a median calculation used for?
median formula in statistics refers to the formula which is used in order to determine the middle number in the given data set which is arranged in the ascending order and according to the formula count of the number of the items in data set is added with one and then results will be divided by two to derive at the place of the median value i.e, …

Is median the variance?
Standard deviation and variance is a measure that tells how spread out the numbers is. While variance gives you a rough idea of spread, the standard deviation is more concrete, giving you exact distances from the mean. Mean, median and mode are the measure of central tendency of data (either grouped or ungrouped).
Is variance mean or median?
VARIANCE measures how far the values of the data set are from the mean, on average.
How do you calculate median and variance?
6:2914:45Mean, Median, Variance, Standard Deviation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMiddle points and average them so we take the n over two point and the n plus one over two point andMoreMiddle points and average them so we take the n over two point and the n plus one over two point and add them and then divide by two and that will be the median. Variance and standard deviation.
What is the difference between the median variance and standard deviation?
The variance measures the average degree to which each point differs from the mean. While standard deviation is the square root of the variance, variance is the average of all data points within a group. The two concepts are useful and significant for traders, who use them to measure market volatility.
How do I calculate variance?
Steps for calculating the varianceStep 1: Find the mean.Step 2: Find each score's deviation from the mean.Step 3: Square each deviation from the mean.Step 4: Find the sum of squares.Step 5: Divide the sum of squares by n – 1 or N.
What is variance in statistics?
Unlike range and interquartile range, variance is a measure of dispersion that takes into account the spread of all data points in a data set. It's the measure of dispersion the most often used, along with the standard deviation, which is simply the square root of the variance.
How do I calculate the median?
To find the median, you take these steps:Step 1: Arrange the scores in numerical order.Step 2: Count how many scores you have.Step 3: Divide the total scores by 2.Step 4: If you have an odd number of total scores, round up to get the position of the median number.
What is the variance of the sample mean?
“That is, the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean is the population variance divided by N, the sample size (the number of scores used to compute a mean). Thus, the larger the sample size, the smaller the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean.
How do I find the median?
To find the median, put all numbers into ascending order and work into the middle by crossing off numbers at each end. If there are a lot of items of data, add 1 to the number of items of data and then divide by 2 to find which item of data will be the median.
Is variance and mean the same?
The variance of a data set measures the mathematical dispersion of the data relative to the mean.
Does standard deviation use mean or median?
Standard deviation (SD) is a widely used measurement of variability used in statistics. It shows how much variation there is from the average (mean). A low SD indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean, whereas a high SD indicates that the data are spread out over a large range of values.
Is standard deviation from the mean or median?
Standard deviation (SD) is a widely used measurement of variability used in statistics. It shows how much variation there is from the average (mean).
What is the variance of the sample mean?
“That is, the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean is the population variance divided by N, the sample size (the number of scores used to compute a mean). Thus, the larger the sample size, the smaller the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean.
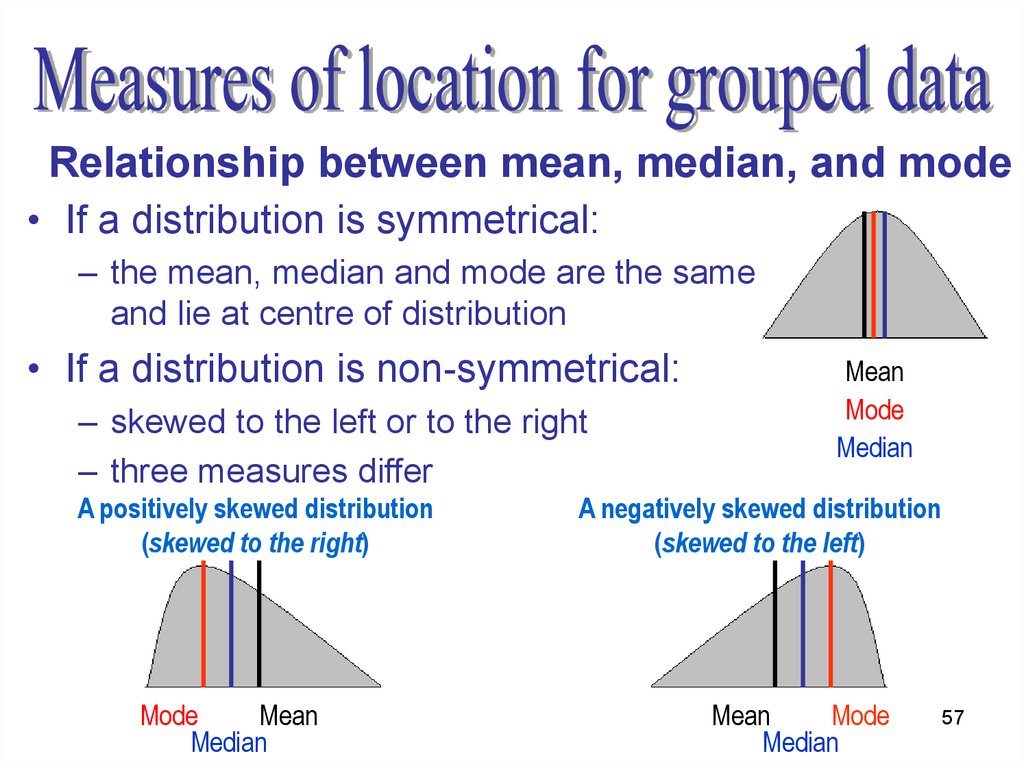
What is median in statistics?
The median is the middle number in a sorted, ascending or descending list of numbers and can be more descriptive of that data set than the average. It is the point above and below which half (50%) the observed data falls, and so represents the midpoint of the data.
When should mean median mode and standard deviation be used?
The mean, median and mode are all estimates of where the "middle" of a set of data is. These values are useful when creating groups or bins to organize larger sets of data. The standard deviation is the average distance between the actual data and the mean.
What is variance in statistics?
Published on September 24, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on October 12, 2020. The variance is a measure of variability. It is calculated by taking the average of squared deviations from the mean. Variance tells you the degree of spread in your data set.
What does variance tell you?
Variance tells you the degree of spread in your data set. The more spread the data, the larger the variance is in relation to the mean.
What is the difference between standard deviation and variance?
Variance is the average squared deviations from the mean, while standard deviation is the square root of this number. Both measures reflect variability in a distribution, but their units differ:
What is the term for a test that requires equal or similar variances?
These tests require equal or similar variances, also called homogeneity of variance or homoscedasticity, when comparing different samples. Uneven variances between samples result in biased and skewed test results. If you have uneven variances across samples, non-parametric tests are more appropriate.
What is the purpose of variance testing?
Statistical tests like variance tests or the analysis of variance (ANOVA) use sample variance to assess group differences. They use the variances of the samples to assess whether the populations they come from differ from each other.
What is standard deviation derived from?
The standard deviation is derived from variance and tells you, on average, how far each value lies from the mean. It’s the square root of variance.
Why is standard deviation used as a measure of variability?
Since the units of variance are much larger than those of a typical value of a data set, it’s harder to interpret the variance number intuitively. That’s why standard deviation is often preferred as a main measure of variability.
What is variance in statistics?
The variance in statistics is the average squared distance between the data points and the mean. Because it uses squared units rather than the natural data units, the interpretation is less intuitive. Higher values indicate greater variability, but there is no intuitive interpretation for specific values. Despite this drawback, some statistical hypothesis tests use it in their calculations. For example, read about the F-test and ANOVA.
Why is variance always greater than or equal to zero?
It is almost always a positive value because only datasets containing one repeated value (e.g., all values equal 15) have a value of zero.
What is the measure of variability?
Variance is a measure of variability in statistics. It assesses the average squared difference between data values and the mean. Unlike some other statistical measures of variability, it incorporates all data points in its calculations by contrasting each value to the mean.
How to find variance of a population?
To find the variance, take a data point, subtract the population mean, and square that difference. Repeat this process for all data points. Then, sum all of those squared values and divide by the number of observations. Hence, it’s the average squared difference.
How to calculate the difference in statistics?
To calculate the statistic, take each data value (1) and subtract the mean (2) to calculate the difference (3) , and then square the difference (4).
How many formulas are there for variance?
There are two formulas for the variance. The correct formula depends on whether you are working with the entire population or using a sample to estimate the population value. In other words, decide which formula to use depending on whether you are performing descriptive or inferential statistics.
When to use sample variance formula?
Use the sample variance formula when you’re using a sample to estimate the value for a population. For example, if you have taken a random sample of statistics students, recorded their test scores, and need to use the sample as an estimate for the population of statistics students, use the sample variance formula.
What is variance in statistics?
The variance measures the average degree to which each point differs from the mean—the average of all data points.
How to find variance of a number?
The variance is the average of the squared differences from the mean. To figure out the variance, first calculate the difference between each point and the mean; then, square and average the results. For example, if a group of numbers ranges from 1 to 10, it will have a mean of 5.5. If you square the differences between each number and the mean, ...
What Does Standard Deviation Mean?
Standard deviation measures how data is dispersed relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of its variance. The further the data points are, the higher the deviation. Closer data points mean a lower deviation. In finance, standard deviation calculates risk so riskier assets have a higher deviation while safer bets come with a lower standard deviation.
What Is Variance Used for in Finance and Investing?
Investors use variance to assess the risk or volatility associated with assets by comparing their performance within a portfolio to the mean. For instance, you can use the variance in your portfolio to measure the returns of your stocks. This is done by calculating the standard deviation of individual assets within your portfolio as well as the correlation of the securities you hold.
How are standard deviation and variance determined?
Standard deviation and variance are both determined by using the mean of a group of numbers in question. The mean is the average of a group of numbers, and the variance measures the average degree to which each number is different from the mean. The extent of the variance correlates to the size of the overall range of numbers—meaning the variance is greater when there is a wider range of numbers in the group, and the variance is less when there is a narrower range of numbers.
Why do we take the root of variance?
Taking the root of the variance means the standard deviation is restored to the original unit of measure and therefore much easier to interpret.
Why do we use squares in standard deviation?
The calculation of variance uses squares because it weighs outliers more heavily than data closer to the mean. This calculation also prevents differences above the mean from canceling out those below, which would result in a variance of zero.
What is the median absolute deviation?
In statistics, the median absolute deviation ( MAD) is a robust measure of the variability of a univariate sample of quantitative data. It can also refer to the population parameter that is estimated by the MAD calculated from a sample.
Why is MAD better than standard deviation?
Because the MAD is a more robust estimator of scale than the sample variance or standard deviation, it works better with distributions without a mean or variance, such as the Cauchy distribution .
What is MAD in statistics?
that is, starting with the residuals (deviations) from the data's median, the MAD is the median of their absolute values .
Variance vs Standard Deviation
Population vs Sample Variance
- Different formulas are used for calculating variance depending on whether you have data from a whole population or a sample.
Steps For Calculating The Variance
- The variance is usually calculated automatically by whichever software you use for your statistical analysis. But you can also calculate it by hand to better understand how the formula works. There are five main steps for finding the variance by hand. We’ll use a small data set of 6 scores to walk through the steps.
Why Does Variance Matter?
- Variance matters for two main reasons: 1. Parametric statistical tests are sensitive to variance. 2. Comparing the variance of samples helps you assess group differences.