
Can reflex control improve walking after incomplete spinal injuries?
Reflex control could improve walking after incomplete spinal injuries. A training regimen to adjust the body’s motor reflexes may help improve mobility for some people with incomplete spinal cord injuries, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health.
Which part of the brain controls reflex action while walking?
Most of the reflex action is conveyed through the spinal cord and the brain also performs reflexes while walking is controlled by the brain. 3. Reflex action cannot be controlled while walking can be changed or modified.
What is the physiology of reflexes?
Physiology of Reflexes Reflex movements are movements initiated by sensory receptors, which, by having synaptic contacts within the spinal cord, are a basic level of regulation of muscles or glands. The Spinal Reflexes are the most basic of all reflexes, but other parts of the central nervous system also contain reflex pathways.
What is the function of spinal cord reflexes?
The Spinal Cord. Topics : Reflex movements are movements initiated by sensory receptors, which, by having synaptic contacts within the spinal cord, are a basic level of regulation of muscles or glands. The Spinal Reflexes are the most basic of all reflexes, but other parts of the central nervous system also contain reflex pathways.
What is the most effective way to learn about spinal reflex?
Why is the inverse stretching reflex protective?
How to test monosynaptic stretching reflexes?
How many neurons are involved in monosynaptic reflexes?
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Which neuron sends the signal that causes the stretched muscle to contract?
What is the perception that the somatosensory cortex gets after receiving all of this information?
See 4 more
About this website
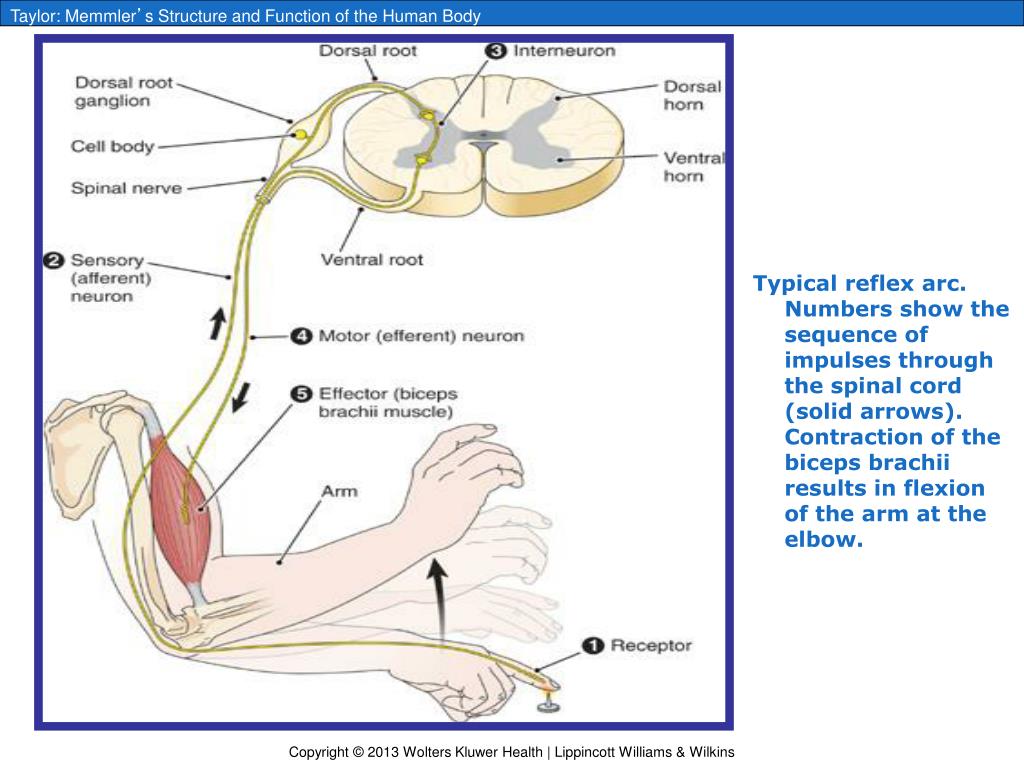
What is an example of a spinal reflex?
The perfect example of the monosynaptic reflex is the knee-jerk or the patellar reflex. In this reflex, neuron I has its peripheral ending within the tendons of the quadriceps muscle....Monosynaptic reflex.Biceps brachiiC5, C6Triceps surae (Achilles tendon)S1, S23 more rows
What are the 4 types of spinal reflexes?
Spinal reflexes include the stretch reflex, the Golgi tendon reflex, the crossed extensor reflex, and the withdrawal reflex.
What are spinal level reflexes?
Spinal Reflex/The Reflex Arc The reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought as it occurs through a reflex arc. Reflex arcs act on an impulse before that impulse reaches the brain. Relex arcs can be. Monosynaptic ie contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron ...
Does the spinal cord control walking?
When we are moving, motor circuits in the spinal cord are constantly being barraged by information from sensory receptors in the skin and muscles, telling these circuits what our limbs are doing or what the ground underfoot feels like. This information is critical for actions like walking or standing still.
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Reflex action is a sudden involuntary action that is taken in response to a stimulus whereas walking is a voluntary action taken by the body not necessarily in response to a stimulus.
How many spinal reflexes are there?
4 Types4 Types of Spinal Reflexes.
Is knee jerk a spinal reflex?
The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord.
What are two types of reflexes in spinal cord?
There are two types: autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs) and somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles). Autonomic reflexes sometimes involve the spinal cord and some somatic reflexes are mediated more by the brain than the spinal cord.
What is the difference between spinal reflex and cranial reflex?
During a spinal reflex, information may be transmitted to the brain, but it is the spinal cord, not the brain, that is responsible for the integration of sensory information and a response transmitted to motor neurons. Some reflexes are cranial reflexes with pathways through cranial nerves and the brainstem.
What part of your spine controls your walking?
Lumbar region Nerve roots coming from the spinal cord in the lumbar spine control the legs.
What part of the nervous system is responsible for walking?
Neurons in the motor cortex, the region of the brain that controls voluntary movement, send their axons through the corticospinal tract to connect with motor neurons in the spinal cord.
What nerve is responsible for walking?
The sciatic nerveThe sciatic nerve originates in the lower spine and is responsible for motor and sensory functions of the lower body. The mixed (sensory and motor) sciatic nerve provides the majority of the functions in the lower limbs and makes actions such as walking, running, climbing, lifting weights, and standing possible.
What are two types of reflexes in spinal cord?
There are two types: autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs) and somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles). Autonomic reflexes sometimes involve the spinal cord and some somatic reflexes are mediated more by the brain than the spinal cord.
What are the 4 plexuses of spinal nerves?
Spinal PlexusesCervical Plexus—Serves the Head, Neck and Shoulders. ... Brachial Plexus—Serves the Chest, Shoulders, Arms and Hands. ... Lumbar Plexus—Serves the Back, Abdomen, Groin, Thighs, Knees, and Calves. ... Sacral Plexus—Serves the Pelvis, Buttocks, Genitals, Thighs, Calves, and Feet.More items...•
What is spinal cord and somatic reflexes?
Somatic Reflex Arc. These are neural pathways that are responsible for the automatic response between a sensory and motor neuron. The sensory input generates a specific motor output. The simplest spinal reflex is mediated by a single synaptic process called the monosynaptic reflex.
What is the importance of spinal reflex?
Spinal reflex control allows your body to react automatically without the effort of thought. The reflex arc is a nerve pathway involved in a reflex action. In your vertebrae, most sensory neurons do not pass straight to the brain but synapse in the spinal cord.
What is a good example of a spinal reflex? - Quora
Answer: The definition of a spinal reflex is a sensory-motor nerve pathway that occurs completely independent of the brain. In other words some sensory stimulus triggers a nerve. The nerve impulse flows into the spinal cord. Inside the cord interneurons connect with motor fibers and that impulse...
What is a spinal reflex arc? | MyTutor
An unconscious motor response to a sensory stimulus.. Sensory stimulus: An external factor that has stimulated and started an impulse (Action potential) in sensory nerves.. There are lots of different types of sensory nerves in the skin that respond to external signals such as heat, vibration, pressure.
Spinal reflex | definition of spinal reflex by Medical dictionary
spinal reflex: [ re´fleks ] a reflected action or movement; the sum total of any particular automatic response mediated by the nervous system. A reflex is built into the nervous system and does not need the intervention of conscious thought to take effect. The knee jerk is an example of the simplest type of reflex. When the knee is tapped, the ...
Spinal Reflex - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
M.M. Patterson, in International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2001 Spinal reflexes traditionally have been viewed as hard-wired, unchanging neural circuits. Studies of learning-like changes in spinal reflex excitability have shown that spinal reflex circuits are capable of long-lasting alterations under varying stimulus conditions.
Lab Practical #2 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Ipsilateral Reflex, Contralateral Reflex, Consensual Reflex and more.
The role of the spinal cord as a reflex center for the ... - PubMed
Somatic afferent regulation of splenic natural killer (NK) cell activity by hindpaw pinching has been proven, in anesthetized rats, to be a reflex response whose reflex center is in the brain and efferent arc is a splenic sympathetic nerve. Using central nervous system (CNS)-intact and acutely spina …
How to improve mobility after spinal cord injury?
A training regimen to adjust the body’s motor reflexes may help improve mobility for some people with incomplete spinal cord injuries, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. During training, the participants were instructed to suppress a knee jerk-like reflex elicited by a small shock to the leg.
Can H-reflexes help with spinal cord injuries?
H-reflexes are routinely measured for diagnosing nerve disorders and injuries, but this is the first study to examine whether consciously modifying an H-reflex can help people with spinal cord injuries. Participants in the study received electrical stimulation to the soleus (calf muscle) of their weaker leg while standing with support.
Is reflex conditioning a rehabilitation technique?
Dr. Wolpaw said he views reflex training, also known as reflex conditioning, as a complement to current rehabilitation practices. The technique could be tailored to focus on specific reflexes that affect different muscle groups, and in some cases, to increase reflexes instead of decrease them. In its 2006 study, his group found that enhancing soleus H-reflex was beneficial for rats that had spinal cord injuries predominantly characterized by weakness without spasticity.
Does reflex training work on rats?
Wolpaw’s work on reflex training for nearly three decades. Until recently, this work was done mostly on rats, and focused on reflex control in the uninjured spinal cord. Those studies helped demonstrate that spinal reflexes can change with training, defined many of the complex modifications in brain and spinal cord that underlie reflex change, and established reflex training as a model for studying how circuits in the brain change with learning.
Can a spinal cord injury cause spasms?
After an incomplete injury, some reflexes may be weakened while others become exaggerated. These hyperactive reflexes can cause spasticity (muscle stiffness) and abnormal patterns of muscle use during movement.
Is soleus H-reflex good for rats?
In its 2006 study, his group found that enhancing soleus H-reflex was beneficial for rats that had spinal cord injuries predominantly characterized by weakness without spasticity. In the current study, it is not clear why only two-thirds of the patients with spinal cord injury were able to suppress their reflexes and benefit from training.
Can a spinal reflex improve locomotion?
Thompson AK et al. "Operant conditioning of a spinal reflex can improve locomotion after spinal cord injury in humans." Journal of Neuroscience, February 6, 2013.
What is the physiology of reflexes?
Physiology of Reflexes. Reflex movements are movements initiated by sensory receptors, which , by having synaptic contacts within the spinal cord, are a basic level of regulation of muscles or glands. The Spinal Reflexes are the most basic of all reflexes, but other parts of the central nervous system also contain reflex pathways.
Where are reflexes located?
The site of the synapse is generally within the spinal cord , although the enteric nervous system also participates in reflex activity confined to the gut wall.
What is the inverse myotatic reflex?
This is in contrast to the fast-conducting afferents in the stretch and clasp knife reflexes. The flexor withdrawal reflex is sometimes called the 'inverse myotatic reflex'.
What is the reflex that allows a dynamic, fast feedback to occur from the active muscles?
This reflex is called the stretch reflex or knee jerk reflex (and sometimes the myotatic reflex), because it is initiated by stretching the muscle. The reflex is an essential part of the motor control system in the intact nervous system, and allows a dynamic, fast feedback to occur from the active muscles.
What is the flexion reflex?
As the flexion reflex involves afferent activity in nociceptors, the reflex is elicited at the same time as the ascending pathways concerned with pain and nociception. Further consideration of the latter will be covered later. Nociceptors, like all afferents, use glutamate as a primary transmitter.
What is the simplest reflex pathway?
This, the simplest of reflex pathways, is preserved following spinal transection, and is tested by clinicians who use a tendon hammer to apply a small stretch to the muscle.
How many synapses are there in the muscle afferent?
For these, there is only one synapse - between the muscle afferent and the motoneurones - hence the term monosynaptic reflex.
What is the most effective way to learn about spinal reflex?
Interactive anatomy is the most effective way to learn. Find out what it is and how you can use it to learn about the spinal reflex. So, the adequate stimulus is the stretching of the muscle, and the adequate response is its contraction.
Why is the inverse stretching reflex protective?
This reflex is protective because it prevents the potential tearing of the muscle and the tendons during excessive muscle contractions.
How to test monosynaptic stretching reflexes?
Testing the monosynaptic stretching reflexes is examined with a simple pattern and is explained in the patellar reflex . The patient sits with the specific leg relaxed and hanging slightly above the ground. The physician then strikes the patellar tendon with the reflex hammer. This typically causes excitation of muscle spindles in the quadriceps muscle, which will ultimately end with the involuntary contraction of that muscle group. If this reaction lacks, that means that there may be a pathological process in one or more of the structures that participate in the reflex arc.
How many neurons are involved in monosynaptic reflexes?
The monosynaptic reflexes consist of two neurons. The first is located within the spinal ganglion. This is the sensory neuron (afferent) whose peripheral process detects the stimuli from the muscle. Then, the central process of the first neuron conducts this signal to the ventral horn of the spinal cord, where the second neuron is situated. The neuron II is a motor neuron (efferent) that sends the appropriate signal via its axon back to the same muscle in which the sensory neuron had detected the signal. This process occurs after the sensory information is received from neuron I. This means that the entire arc has only one neuronal synapse that is directly between neuron I and neuron II (without the participation of interneurons).#N#To make it simple, let’s recap this through a specific example. The perfect example of the monosynaptic reflex is the knee-jerk or the patellar reflex. In this reflex, neuron I has its peripheral ending within the tendons of the quadriceps muscle. Once the tendon is excessively or suddenly stretched, neuron I detects that and informs neuron II that action is needed to avoid any injury to the tendon. Then, neuron II of the patellar reflex, which is in the lumbar segments of the spinal cord, sends the efferent signal through its axon to the quadriceps muscle to contract.
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Spinal reflex. A major part of the spinal cord function is regulated by the brain. Many functions of the spinal cord are also executed independently from the brain, such as a spinal reflex. The definition of a spinal reflex as well as their components, functions, pathways, and physiology will be described in this article ...
Which neuron sends the signal that causes the stretched muscle to contract?
Then, the alpha motor neuron sends the signal that causes the stretched muscle to contract.
What is the perception that the somatosensory cortex gets after receiving all of this information?
The impression that the somatosensory cortex gets after receiving all of this information is actually the awareness of the body’s position in space, which is called kinesthesia .
