What is WPW syndrome?
WPW syndrome (Wolf Parkinson White syndrome) Usually the heart rhythm is controlled by a small pacemaker situated in the right upper chamber of the heart known as the sinus node (SA node).
Is WPW atrioventricular tachycardia?
Because of the accessory pathway, WPW can also present as an atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT). Orthodromic AVRT is a regular narrow complex tachycardia, whereas antidromic AVRT is a regular wide complex tachycardia.
Is there a pre-excitation in concealed WPW syndrome?
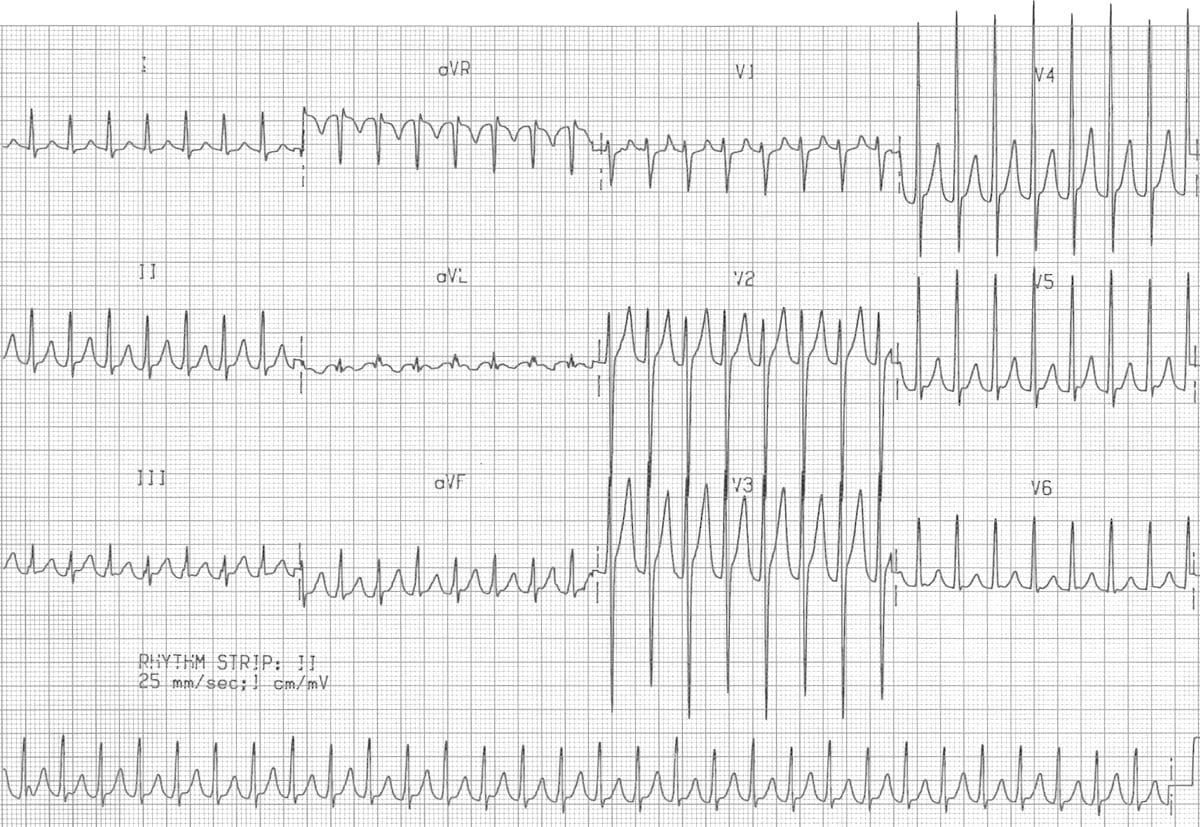
In these cases, there can not be pre-excitation, but there is a risk of antidromic AVRT. This condition is referred to as concealed WPW syndrome (because the delta wave is not visible). Figure 3 displayed the characteristics of orthodromic and antidromic AVRT. Being able to locate the accessory pathway is a task relevant only to cardiologists.
What is the pathophysiology of Parkinson White syndrome (WPW)?
Wolff Parkinson White (WPW) syndrome is due to an accessory atrioventricular pathway which bypasses the normal atrioventricular (AV) nodal delay. ECG (electrocardiogram) manifests a short PR interval and a delta wave.

How common is atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is very common among people with pre-excitation. Up to 30% may develop atrial fibrillation. Some individuals with pre-excitation display multiple accessory pathways, which increase the risk of of atrial fibrillation and complicates treatment.
What is the only communication between the atria and the ventricles?
Pre-excitation. The atrioventricular node and bundle of His are normally the only communication between the atria and the ventricles. The atrial impulse must pass through the atrioventricular node, which delays the impulse due to its slow conduction, before the impulse may reach the ventricles.
What is the Delta wave?
Delta wave: depolarization of ventricular myocardium will start where the accessory pathway inserts into the ventricle, and the impulse will spread slowly because it will propagate outside of the conduction system. This is reflected on the ECG as a slow start of the QRS complex and this part of the QRS complex is referred to as a delta wave.
What is the WPW syndrome?
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome. An individual with evidence of pre-excitation on resting ECG who also has recurring tachyarrhythmias is said to have Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. This is actually a rather common condition and some studies suggest that the prevalence is 1–2 in 1000 in the population.
Where does the reentry impulse travel?
The re-entry impulse travels in retrograde direction through the atrioventricular node in antidromic AVRT. This variant arises when a premature atrial impulse is discharged near the atrioventricular node when it is refractory. The premature atrial impulse will then travel from the atria to the ventricles via the accessory pathway and subsequently back to the atria via the atrioventricular node.
Which pathway is capable of conducting impulses in both directions?
If the accessory pathway is capable of conducting the impulse in both directions (atria to ventricles as well as ventricles to atria) the individual will display pre-excitation during sinus rhythm and also be at risk of antidromic and orthodromic AVRT.
What happens to the ventricles during pre-excitation?
As mentioned in Chapter 1, pre-excitation causes secondary ST-T changes. This is due to the fact that pre-excitation leads to abnormal depolarization of the ventricles and this leads to abnormal repolarization as well.
What is the treatment for WPW with antidromic AVRT?
Since it is virtually indistinguishable, it should be treated with procainamide, amiodarone, or electrical cardioversion in the case of an unstable patient. 1.
What is the rate of atrial impulses in AF with WPW?
First, because of the accessory pathway, the rate is >200 bpm and at times approaches 300 bpm. Second, because of simultaneous conduction through both the accessory pathway and the His-Purkinje system, the QRS complex is wide (>0.12 seconds) and has varying bizarre morphologies. Finally, the axis is stable and not undulating, which differentiates it from PVT. 1
How does an AVRT impulse travel?
In orthodromic AVRT, an impulse leaves the SA node, travels normally through the AV node, and then back to the atria through the accessory pathway. In antidromic AVRT, the impulse travels from the SA node to the accessory path first, and then travels back to the atria via the AV node.
How do we know AF with WPW?
How do we know this is AF with WPW? In normal physiological cardiac conduction, an impulse is generated at the sinus node and travels to the AV node, resulting in atrial contraction (P wave). A conduction delay at the AV node (PR interval) allows the ventricles to fill. Finally, the ventricles are depolarized via the His-Purkinje system (QRS complex), and the ventricles simultaneously contract. In WPW, initial depolarization of the ventricle results via an accessory pathway known as the bundle of Kent. The early activation of the ventricle results in a shortened PR interval and a slow initial upstroke of the QRS complex. This occurs while the rest of the signal propagates normally through the AV node. Thus, a shortened PR interval, a widened QRS, and a delta wave make up the classic triad seen in WPW. 2
What is the differential diagnosis for irregular wide complex tachycardia?
The differential diagnosis for an irregular wide complex tachycardia (WCT) includes polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (PVT); AF with aberrant conduction (bundle branch block or non-specific intraventricular conduction delay); and AF with pre-excitation (WPW). 1
What is the normal heart rate for a 28 year old male?
Vital signs are within normal limits except for a recorded heart rate of 220 bpm. An ECG is obtained (Figure 1).
Is WPW orthodromic or antidromic?
WPW with orthodromic AVRT looks identical to run-of-the-mill paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and can be treated as such. Vagal maneuvers or AV nodal blocking agents are the treatment of choice, as they slow conduction through the AV node and disrupt the re-entrant circuit. On the other hand, WPW with antidromic AVRT will look identical to ventricular tachycardia (VT). Since it is virtually indistinguishable, it should be treated with procainamide, amiodarone, or electrical cardioversion in the case of an unstable patient. 1
How is tachyarrhythmia facilitated?
Tachyarrhythmias can be facilitated by: Formation of a reentry circuit involving the accessory pathway, termed atrioventricular reentry tachycardias (AVRT) Direct conduction from the atria to the ventricles via the accessory pathway, bypassing the AV node, seen with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in conjunction with WPW.
Why are QRS complexes narrow?
The QRS complexes are narrow because impulses are being transmitted in an orthodromic direction (A -> V) via the AV node
What is WPW syndrome?
Refers to the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias. Incidence is 0.1 – 3.0 per 1000. Associated with a small risk of sudden cardiac death.
How fast is LBBB?
However, the morphology is not typical of LBBB, the rate is too rapid (up to 300 bpm in places, i.e. too rapid to be conducted via the AV node) and there is a subtle beat-to-beat variation in the QRS width which is more typical of WPW (LBBB usually has fixed width QRS complexes)
What is Delta wave?
Delta wave: slurring slow rise of initial portion of the QRS
Where does anterograde conduction occur?
In orthodromic AVRT, anterograde conduction occurs via the AV node, with retrograde conduction occurring via the accessory pathway. This can occur in patients with a concealed pathway.
What is the pathophysiology of pre-excitation and accessory pathways?
Pathophysiology of pre-excitation and accessory pathways. Pre-excitation refers to early activation of the ventricles due to impulses bypassing the AV node via an accessory pathway. Accessory pathways, also known as bypass tracts, are abnormal conduction pathways formed during cardiac development and can exist in a variety ...
Management Of Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Preexcitation
Blomström-Lundqvist, C, Scheinman, MM, Aliot, EM. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular ArrhythmiasExecutive Summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines .
Atrial Fibrillation And Wpw
Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome have an accessory pathway or a bypass tract that connects the electrical system of the atria directly to the ventricles, thereby allowing conduction to avoid passing through the AV node.
Antidromic Svt In Wpw
In antidromic SVT, the action potential conducts to the ventricle initially via the accessory pathway, then wanders shambolically around the ventricles producing a weird wide QRS, and then propagates up the AV node in an unnatural retrograde manner.
Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
How Can We Tell The Location Of The Ap Based On The Superficial 12
The ECG hallmark of an antegradely conducting AP is the delta wave along with a shorter than usual PR interval and a widened QRS complex. Conversely, the presence of retrograde conduction only in an AP will not be apparent on a surface ECG during sinus rhythm .
Which Drugs Are Used To Treat Wolff
Class Ic drugs are typically used with an AV nodal blocking agent in low doses to avoid atrial flutter with a 1:1 conduction. class III drugs are also reasonable choices, although these agents are less effective for altering accessory pathway conduction properties. Class Ic drugs should not be given if the patient has structural heart disease .
What Are Wpw And Avrt
Preexcitation describes the situation in which impulses from the SA node or atrium reach the ventricle through an accessory pathway in addition to the AV node. WPW is a type of preexcitation syndrome in which there are ECG findings of an atrial-ventricular bypass tract and the patient demonstrates related tachydysrhythmias.