
What are xylene xylenes?
Xylenes are produced mainly as part of the BTX aromatics ( benzene, toluene, and xylenes) extracted from the product of catalytic reforming known as reformate . Several million tons are produced annually. In 2011, a global consortium began construction of one of the world's largest xylene plants in Singapore.
What is the ratio of isomers of xylene?
Commercial or laboratory-grade xylene produced usually contains about 40-65% of m -xylene and up to 20% each of o -xylene, p -xylene and ethylbenzene. The ratio of isomers can be shifted to favor the highly valued p -xylene via the patented UOP- Isomar process or by transalkylation of xylene with itself or trimethylbenzene.
Does xylene dissolve wax?
Also, does xylene dissolve wax? Wax is composed of heavy, long-chain alkanes. And as "Like dissolves like" try to dissolve your wax in toluene or in xylene.
What is the boiling point of xylenes?
Xylenes form azeotropes with water and a variety of alcohols. With water the azeotrope consists of 60% xylenes and boils at 94.5 °C. As with many alkylbenzene compounds, xylenes form complexes with various halocarbons.
What's the difference between xylol and xylene?
As nouns the difference between xylene and xylol is that xylene is xylene (di-methyl-benzene) while xylol is xylene.
What is xylene also known as?
Xylene is also known as xylol or dimethylbenzene. Xylene is primarily a synthetic chemical.
Is xylene and xylene the same?
The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical empirical formulas C 8H 10. Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods.
Is xylol the same as acetone?
Acetone and xylene are both flammable substances that have a distinctive odor. Acetone and xylene also both work well as solvents to remove lacquers and paints. Acetone is a smaller molecule than xylene and it contains an oxygen atom in the molecular structure. Xylene has a sweet smell and is toxic to humans.
What can I use instead of xylene?
Carrot oil, Olive oil, Pine oil, Rose oil, are not only bio friendly and economical but can also be used as clearing agent instead of xylene.
What can you use xylene for?
Xylene is commonly used as a paint solvent because it's excellent at removing old paint on a variety of surfaces. It's also effective at removing greasy stains, resins, enamels, and glue. As a paint thinner, this chemical has some advantages over other paint thinning agents like toluene.
What is xylol thinner?
Technical Specs. Sunnyside xylol solvent is used to thin specified oil-based paint, lacquer, varnish, epoxy, adhesives, anti-rust, porch and deck paints and synthetic enamels. Will also remove some adhesives, and is an excellent solvent for cleaning tools and equipment immediately after use.
Is paint thinner and xylene the same?
They include mineral spirits (informally referred to as “paint thinner”), naphtha, toluene, xylene and some “turpentine substitutes” such as turpatine and T.R.P.S. Their primary use in wood finishing is for thinning waxes, oils, and varnishes, including polyurethane varnish, and for cleaning brushes.
What is xylene used for in painting?
Crown Xylol (also known as Xylene) is used for thinning paints, enamels, varnishes and alkyd resins. Often specified as a thinner for specialty paints and coatings. Similar to Toluene, but the evaporation rate is about five times slower.
What is better xylene or acetone?
The key difference between xylene and acetone is that xylene is a cheap and less toxic solvent, whereas acetone is an expensive and more toxic solvent. Both xylene and acetone are important as solvents in chemistry laboratories.
Is xylene the same as MEK?
Xylene and Toluene are very similar solvents. MEK – Very aggressive solvent for cleaning; may damage plastics or paints. Good for cleanup of tools and equipment. May not be available in areas with strict VOC regulations.
Is xylene good for paint prep?
Xylene can be used to thin specified oil-based paint, lacquer, varnish, epoxy, adhesives, anti-rust, porch & deck paints and synthetic enamels. Xylene will also remove certain adhesives, and is an excellent solvent for cleaning tools and equipment immediately after use.
What products contain xylene?
Xylene has been found in many types of foods at levels ranging from 1 to 100 ppb. You may also come in contact with xylene from a variety of consumer products, including gasoline, paint, varnish, shellac, rust preventives, and cigarette smoke.
How xylene is produced?
Xylenes are produced by the methylation of toluene and benzene. The ratio of isomers can be shifted to favor the highly valued p-xylene via the patented UOP-Isomar process or by transalkylation of xylene with itself or trimethylbenzene. These conversions are catalyzed by zeolites.
What does xylene do?
It is primarily used as a solvent (a liquid that can dissolve other substances) in the printing, rubber, and leather industries. Along with other solvents, xylene is also widely used as a cleaning agent, a thinner for paint, and in varnishes.
What does xylene smell like?
When pure, xylene is a clear, colorless liquid with a sweet odor. It burns readily. Xylene is obtained from crude petroleum and is used widely in many products such as paints, glues, and pesticides.
What is xylene substitute?
General: This EMS Xylene Substitute solution is specially designed for use in processing and staining histological/cytological specimens. It can be substituted for xylene and can be used with almost all tissue processors and automated slide stainers.
Does xylene remove rust?
Xylene can be used to thin specified oil-based paint, lacquer, varnish, epoxy, adhesives, anti-rust, porch & deck paints and synthetic enamels. Xylene will also remove certain adhesives, and is an excellent solvent for cleaning tools and equipment immediately after use.
Can xylene be stored in plastic?
Oxygenated solvents will stay in anything without diffusing through the plastic too quickly in summer. I would not store xylene/toluene, methylene chloride, or lacquer thinner in any plastic bottle that is not specifically made for solvents.
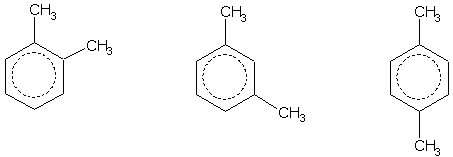
How many isomers does xylene have?
Xylene exists in three isomeric forms. The isomers can be distinguished by the designations ortho - ( o -), meta - ( m -) and para - ( p -), which specify to which carbon atoms (of the benzene ring) the two methyl groups are attached. By counting the carbon atoms around the ring starting from one of the ring carbons bonded to a methyl group, and counting towards the second methyl group, the o -isomer has the IUPAC name of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, the m -isomer is 1,3-dimethylbenzene and the p -isomer is 1,4-dimethylbenzene. Of the three isomers, the p -isomer is the most industrially sought after since it can be oxidized to terephthalic acid.
What is xylene made of?
Small quantities occur in gasoline and aircraft fuels . Xylenes are produced mainly as part of the BTX aromatics ( benzene, toluene, and xylenes) extracted from the product of catalytic reforming known as reformate. The xylene mixture is a slightly greasy, colorless liquid commonly encountered as a solvent .
What are the effects of inhaling xylene vapor?
The main effect of inhaling xylene vapor is depression of the central nervous system (CNS), with symptoms such as headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. At an exposure of 100 ppm, one may experience nausea or a headache.
How much Xylene is toxic to animals?
Xylene is flammable but of modest acute toxicity, with LD 50 ranges from 200 to 5000 mg/kg for animals. Oral LD 50 for rats is 4300 mg/kg. The principal mechanism of detoxification is oxidation to methylbenzoic acid and hydroxylation to hydroxylene.
How are xylenes produced?
Occurrence and production. Xylenes are an important petrochemical produced by catalytic reforming and also by coal carbonisation in the manufacture of coke fuel. They also occur in crude oil in concentrations of about 0.5–1%, depending on the source. Small quantities occur in gasoline and aircraft fuels .
What is p xylene?
p -Xylene is the principal precursor to terephthalic acid and dimethyl terephthalate, both monomers used in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bottles and polyester clothing . 98% of p -xylene production, and half of all xylenes produced is consumed in this manner. o -Xylene is an important precursor to phthalic anhydride. The demand for isophthalic acid is relatively modest so m -xylene is rarely sought (and hence the utility of its conversion to the o - and p -isomers).
What are the side effects of xylene?
At an exposure between 200 and 500 ppm, symptoms can include feeling "high", dizziness, weakness, irritability, vomiting, and slowed reaction time. The side effects of exposure to low concentrations of xylene ( < 200 ppm) are reversible and do not cause permanent damage.
What is xylene used for?
It is primarily used as a solvent (a liquid that can dissolve other substances) in the printing, rubber, and leather industries. Along with other solvents, xylene is also widely used as a cleaning agent, a thinner for paint, and in varnishes. Beside above, does xylene dissolve wax?
Can LDPE be dissolved?
Chemical compatibility charts claim the plastic will weaken, but it won't dissolve.
Is xylene a solvent?
Xylene is a colorless mixture of chemically-related hydrocarbons that often finds use as a solvent for paints and printing inks. It's very good at dissolving compounds that dissolve poorly in water, which is why it is so useful. Its ability to do so stems from its properties and its chemical structure.
Is wax soluble in water?
Wax is composed of heavy, long-chain alkanes. And as "Like dissolves like" try to dissolve your wax in toluene or in xylene. In this way, is xylene soluble in water? Xylene is a colorless liquid and vapor. Xylene is not soluble in water and will float on top of denser water if combined.

Overview
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (from Greek ξύλον (xylon) 'wood'; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H4. They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly gr…
Occurrence and production
Xylenes are an important petrochemical produced by catalytic reforming and also by coal carbonisation in the manufacture of coke fuel. They also occur in crude oil in concentrations of about 0.5–1%, depending on the source. Small quantities occur in gasoline and aircraft fuels.
Xylenes are produced mainly as part of the BTX aromatics (benzene, toluene, and xylenes) extracted from the product of catalytic reforming known as reformate.
History
Xylene was first isolated and named in 1850 by the French chemist Auguste Cahours (1813–1891), having been discovered as a constituent of wood tar.
Industrial production
Xylenes are produced by the methylation of toluene and benzene. Commercial or laboratory-grade xylene produced usually contains about 40–65% of m-xylene and up to 20% each of o-xylene, p-xylene and ethylbenzene. The ratio of isomers can be shifted to favor the highly valued p-xylene via the patented UOP-Isomar process or by transalkylation of xylene with itself or trimethylbenzene. These conversions are catalyzed by zeolites.
Properties
The physical properties of the isomers of xylene differ slightly. The melting point ranges from −47.87 °C (−54.17 °F) (m-xylene) to 13.26 °C (55.87 °F) (p-xylene)—as usual, the para isomer's melting point is much higher because it packs more readily in the crystal structure. The boiling point for each isomer is around 140 °C (284 °F). The density of each isomer is around 0.87 g/mL (7.26 lb/U.S. gallon or 8.72 lb/imp gallon) and thus is less dense than water. The odor of xylene i…
Applications
p-Xylene is the principal precursor to terephthalic acid and dimethyl terephthalate, both monomers used in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bottles and polyester clothing. 98% of p-xylene production, and half of all xylenes produced is consumed in this manner. o-Xylene is an important precursor to phthalic anhydride. The demand for isophthalic acid is relatively modest, so m-xylene is rarely sought (and hence the utility of its conversion to the o- and p-isom…
Chemical properties
Generally, two kinds of reactions occur with xylenes: those involving the methyl groups and those involving the ring C–H bonds. Being benzylic and hence weakened, the C–H bonds of the methyl groups are susceptible to free-radical reactions, including halogenation to the corresponding xylene dichlorides (bis(chloromethyl)benzenes), while mono-bromination yields xylyl bromide, a tear gas agent. Oxidation and ammoxidation also target the methyl groups, affording dicarboxylic acid…
Health and safety
Xylene is flammable but of modest acute toxicity, with LD50 ranges from 200 to 5000 mg/kg for animals. Oral LD50 for rats is 4300 mg/kg. The principal mechanism of detoxification is oxidation to methylbenzoic acid and hydroxylation to hydroxylene.
The main effect of inhaling xylene vapor is depression of the central nervous system (CNS), with symptoms such as headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. At an exposure of 100 ppm, one …