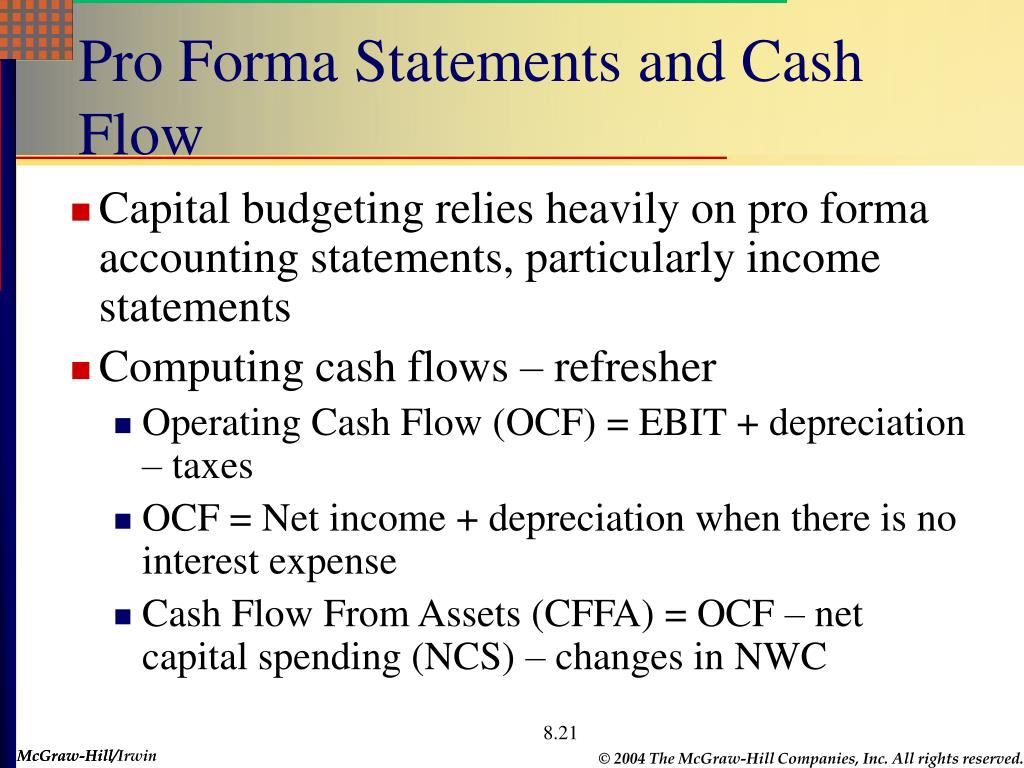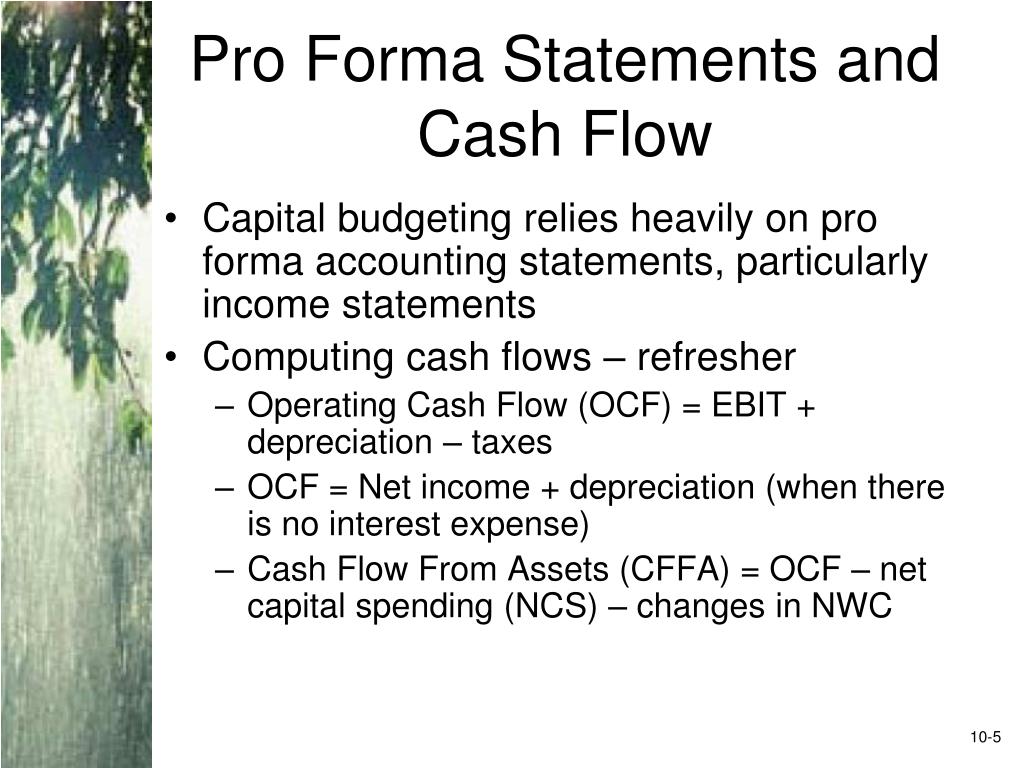
Financing costs are reflected in the required rate of return from an investment project, so cash flows are not adjusted for these costs. The costs are typically congruent with the company’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), which represents the cost the company incurs to run its current capital structure.
What is incremental cash flow and why is it important?
Incremental cash flow looks into future costs; accountants need to make sure that sunk costs are not included in the computation. This is especially true if the sunk cost happened before any investment decision was made. 2. Opportunity costs From the term itself, opportunity costs refer to a business’ missed chance for revenues from its assets.
What are the challenges in preparing incremental cash flow?
Here are some of the challenges: 1. Sunk costs Sunk costs are also known as past costs that have already been incurred. Incremental cash flow looks into future costs; accountants need to make sure that sunk costs are not included in the computation. This is especially true if the sunk cost happened before any investment decision was made. 2.
What are the differences between incremental cash flow and allocated costs?
4. Allocated costs These are some costs that must be allocated to a specific department or project and there may not be a rational way to do it (i.e. rent expense).. Incremental cash flow and total cash flow both deal with a business’ or project’s cash flow. However, they are notably different from each other.
Are sunk costs included in incremental cash flow?
1. Sunk costs Sunk costs are also known as past costs that have already been incurred. Incremental cash flow looks into future costs; accountants need to make sure that sunk costs are not included in the computation. This is especially true if the sunk cost happened before any investment decision was made. 2. Opportunity costs
What should be included in incremental cash flow?
There are several components that must be identified when looking at incremental cash flows: the initial outlay, cash flows from taking on the project, terminal cost or value, and the scale and timing of the project.
What is not included in incremental cash flow?
Anything that has occurred in the past is referred to as a sunk cost and should be excluded from relevant cash flows. Only cash flows that arise because of the decision being made should be included; any cash flow that would have arisen anyway, sometimes referred to as a committed cost, should be excluded.
What should not be included as an incremental cash flow for a proposed project?
Incremental cash flow FAQ It only includes the money made and spent on a specific project. It also does not include sunk costs, opportunity costs, and cannibalization.
Why are financing costs excluded from project cash flows?
Financing costs are ignored from the calculations of operating cash flows. Financing costs are reflected in the required rate of return from an investment project, so cash flows are not adjusted for these costs.
Which of the following are examples of incremental cash flow?
Examples of incremental cash flow includes increase in accounts payable, decrease in net working capital, increase in taxes, and decrease in cost of goods sold.
Which one of the following should be excluded from the cash flows of a project?
Interest payments are excluded from the generally accepted definition of free cash flow.
What are the major problems you can identify for determining incremental cash flow?
Difficulties in Determining Incremental Cash FlowSunk costs. Sunk costs are also known as past costs that have already been incurred. ... Opportunity costs. From the term itself, opportunity costs refer to a business' missed chance for revenues from its assets. ... Cannibalization. ... Allocated costs.
How can you determine if a cash flow is incremental to a project?
Follow these steps to calculate incremental cash flow:Identify a company's revenue. ... Note the company's expenses. ... List the initial cost of the project. ... Subtract revenue by expenses. ... Subtract the total in step four by the initial cost. ... Compare the totals.
What is an incremental cash flow for a project?
In simple terms, it is the net impact of the organization's cash inflow and cash outflow for a particular period, say monthly, quarterly, annually, as may be required. read more (cash inflow – cash outflow) over a specific time between two or more projects.
Do you include financing costs in NPV?
Note: As mentioned earlier, financing costs such as interest payments and dividends should NOT be included as part of the incremental cash flows in the calculation of the NPV of the project.
Should you include sunk costs in the cash flow forecasts of a project?
We should not include sunk costs in the cash flows of a project because sunk costs must be paid regardless of whether or not the firm decides to proceed with the project. Sunk costs are not incremental with respect to the current decision.
What costs should be included in NPV?
The general rule is that an NPV model should include all costs and benefits that would be affected by the decision to be taken. These are referred to as being the relevant costs and benefits. Irrelevant costs and benefits should be excluded on the grounds that that they could alter the decision for spurious reasons.
What is an incremental cash flow quizlet?
Incremental cash flow from operations is the cash flow from a project that is expected to be generated after all operating expenses and taxes have been paid.
What is an incremental cash flow for a project?
In simple terms, it is the net impact of the organization's cash inflow and cash outflow for a particular period, say monthly, quarterly, annually, as may be required. read more (cash inflow – cash outflow) over a specific time between two or more projects.
Which of the following is not used in capital budgeting?
9. Which of the following is not followed in capital budgeting? Post-tax Principle.
What is incremental cash flow?
Incremental cash flow looks into future costs; accountants need to make sure that sunk costs are not included in the computation. This is especially true if the sunk cost happened before any investment decision was made. 2. Opportunity costs. From the term itself, opportunity costs.
Why is incremental cash flow important?
Incremental cash flows are helpful, especially in determining if a company should take on a new project or not. However, accountants also encounter certain difficulties when estimating incremental cash flow. Here are some of the challenges:
What is a CFI?
CFI is the official provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)®. Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today!
Why is total cash flow analysis important?
Total cash flow analysis determines the total cumulative cash that’s been generated from doing a project or evaluating a business.
What is it called when a product is reduced in cash flow?
In the event that a reduction in the cash flow of another aspect or product is the result of taking on a new project, then it is called cannibalization. Incremental cash flow is important in capital budgeting.
Why is capital intensive work important?
Such capital-intensive projects could be anything from opening a new factory to a significant workforce expansion, entering a new market, or the research and development of new products. because it helps predict cash flow in the future and determine a project’s profitability.
What is opportunity cost?
From the term itself, opportunity costs#N#Opportunity Cost Opportunity cost is one of the key concepts in the study of economics and is prevalent throughout various decision-making processes. The#N#refer to a business’ missed chance for revenues from its assets. They are often forgotten by accountants, as they do not include opportunity costs in the computation of incremental cash flow.
What is Incremental Cash Flow?
Incremental cash flow is the additional operating cash flow that an organization receives from taking on a new project. A positive incremental cash flow means that the company's cash flow will increase with the acceptance of the project. A positive incremental cash flow is a good indication that an organization should invest in a project.
What are the components of incremental cash flows?
There are several components that must be identified when looking at incremental cash flows: the initial outlay, cash flows from taking on the project, terminal cost or value, and the scale and timing of the project. Incremental cash flow is the net cash flow from all cash inflows and outflows over a specific time and between two or more business choices.
Is incremental cash flow difficult to project?
The simple example above explains the idea, but in practice, incremental cash flows are extremely difficult to project. Besides the potential variables within a business that could affect incremental cash flows, many external variables are difficult or impossible to project. Market conditions, regulatory policies, and legal policies may impact incremental cash flow in unpredictable and unexpected ways. Another challenge is distinguishing between cash flows from the project and cash flows from other business operations. Without proper distinction, project selection can be made based on inaccurate or flawed data.
Is incremental cash flow a good tool?
Incremental cash flow can be a good tool to assess whether to invest in a new project or asset, but it should not be the only resource for assessing the new venture. 1:15.
When are incremental cash flows relevant?
Only incremental cash flows, which are the cash flows that would result if a project is accepted, are relevant when making accept/reject decisions.
What happens if equipment is sold for more than its book value at the end of a project?
If equipment is expected to be sold for more than its book value at the end of a project's life, this will result in a profit. In this case, despite taxes on the profit, the end-of-project cash flow will be greater than if the asset had been sold at book value, other things held constant.
What is simulation analysis?
Simulation analysis is a computerized version of scenario analysis where input variables are selected randomly on the basis of their probability distributions.
Which has more market risk, Project X or Project Y?
Project X has more market risk than Project Y. Currently, Powell Products has a beta of 1.0, and its sales and profits are positively correlated with the overall economy. The company estimates that a proposed new project would have a higher standard deviation and coefficient of variation than an average company project.
Can you deduct interest expense in estimating cash flows?
In calculating the project's operating cash flows, the firm should not deduct financing costs such as interest expense, because financing costs are accounted for by discounting at the WACC. If interest were deducted when estimating cash flows, this would, in effect, "double count" it.