Key Takeaways
- Expensing a purchase allows you to claim the entire cost in the first year, whereas depreciating the expense means claiming the cost over a period of years.
- The IRS has numerous rules for which business purchases can fall into either category.
- Depreciable expenses typically involve the purchase of long-term assets that require a significant investment.
Is the depreciation a loss or an expense?
Depreciation is a type of expense that represents an item that a business purchases that loses value over time. Businesses include these on an annual tax report for deduction. The IRS requires depreciation costs to be reported on annual tax returns and detail the item purchased, the amount paid for the item and the period of time you it will ...
Can I capitalize an asset without depreciation?
You can have your machines capitalized without depreciation because paragraph 16.55 of IAS 16 states that depreciation of an asset begins when it is available for use as intended by the management. Until the accessories are purchased, the machines need not be depreciated.
Is depreciation expense an asset or liability?
Depreciation is neither an asset nor a liability. It is a contra-asset account, meaning it reduces the accounting value of an asset. For example, you bought a car at $10,000, and you decide to depreciate the vehicle over five years using the straight-line method. That’s a depreciation amount of $2,000 ($10,000 / 5) each year to book.
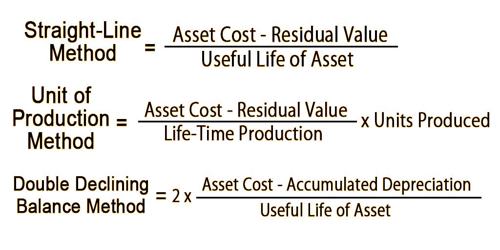
How do I calculate depreciation expense?
The straight line calculation steps are:
- Determine the cost of the asset.
- Subtract the estimated salvage value of the asset from the cost of the asset to get the total depreciable amount.
- Determine the useful life of the asset.
When should I depreciate an asset?
If you have an asset that will be used in your business for longer than the current year, you are generally not allowed to deduct its full cost in the year you bought it. Instead, you need to depreciate it over time. This rule applies whether you use cash or accrual-based accounting.
Should I depreciate my rental?
In short, you are not legally required to depreciate rental property. However, choosing not to depreciate rental property is a massive financial mistake. It's the equivalent of pouring a percentage of your rental property profits down the drain.
What is the difference between expense and depreciation?
The IRS defines expenses as strictly operational costs of items that are used on a daily basis and do not lose value over time. Depreciation deductions are capital assets—large purchases made by a company or business for work-related tasks that lose value due to continued, long-term use.
Why is depreciation Good for taxes?
A company's depreciation expense reduces the amount of earnings on which taxes are based, thus reducing the amount of taxes owed. The larger the depreciation expense, the lower the taxable income, and the lower a company's tax bill.
What if I never took depreciation on my rental property?
You should have claimed depreciation on your rental property since putting it on the rental market. If you did not, when you sell your rental home, the IRS requires that you recapture all allowable depreciation to be taxed (i.e. including the depreciation you did not deduct).
Can I choose not to take depreciation?
Depreciation is a deduction that allows the investor to recoup the cost of assets (in this case, the rental property) used as a source of income. Whether or not you choose to take depreciation doesn't matter to the IRS.
Should I expense or depreciate equipment?
It's generally better to expense an item rather than depreciate it because money has a time value. You get the deduction in the current tax year when you expense it. You can use the money that the expense deduction has freed from taxes in the current year.
Is it better to capitalize or expense?
When a cost that is incurred will have been used, consumed or expired in a year or less, it is typically considered an expense. Conversely, if a cost or purchase will last beyond a year and will continue to have economic value in the future, then it is typically capitalized.
What happens when you fully depreciate an asset?
If the fully depreciated asset is disposed of, the asset's value and accumulated depreciation will be written off from the balance sheet. In such a scenario, the effect on the income statement will be the same as if no depreciation expense happened.
How much depreciation can you write off?
Section 179 asset deductions The IRS allows businesses to write off the entire cost of an eligible asset in the first year. Any asset written off under Section 179 must be used more than 50 percent in a trade or business, and only the business percentage is written off.
How much can I claim on depreciation?
Claiming a deduction for depreciation own the asset for less than one year. only partly use the asset for business purposes. For example, if you use it for 60% business purposes and 40% private purposes, you can only claim 60% of its total depreciation. own the asset for some time before you start the business.
What assets Cannot be depreciated?
Land can never be depreciated. Since land cannot be depreciated, you need to allocate the original purchase price between land and building. You can use the property tax assessor's values to compute a ratio of the value of the land to the building.
Which depreciation method is best for rental property?
The standard method of depreciation in the United States is called the modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS). Under this system, the capitalized cost basis of property is recovered over a specified life by annual deductions for depreciation.
Do you have to pay back depreciation on rental property?
If you decide to sell your rental property for more than its current depreciated value, you will be required to pay what is referred to as the depreciation recapture tax. Essentially, this amounts to a 25 percent tax on the amount above depreciation value that your property sells for.
Can I claim depreciation on my rental property?
If you receive rental income from the rental of a dwelling unit, there are certain rental expenses you may deduct on your tax return. These expenses may include mortgage interest, property tax, operating expenses, depreciation, and repairs.
How do you avoid depreciation recapture on rental property?
Investors may avoid paying tax on depreciation recapture by turning a rental property into a primary residence or conducting a 1031 tax deferred exchange. When an investor passes away and rental property is inherited, the property basis is stepped-up and the heirs pay no tax on depreciation recapture or capital gains.