
Should my patella move? As long as your kneecap (patella) stays in its groove in the knee, you can walk, run, sit, stand, and move easily. When the kneecap slips out of the groove, problems and pain often result.
Full Answer
What happens when the patella is dislocated?
A network of tendons and ligaments secure the kneecap within the groove, flexing as it moves. When the patella dislocates, it’s forced outside of the trochlear groove and can no longer move up and down. This locks the knee and pulls the ligaments out of place, often tearing them.
How can I Fix my patella problem?
It can be helpful to place a towel roll under your knee in order to bend the knee slightly. This helps to gain more access to the patella, however it will tighten the structures that restrict patellar motion a bit. I find that a slight bend allows for a better mobilization in this direction.
What causes the patella to move?
Normally the patella moves along a path controlled by the quadriceps muscle. If the inside of this muscle group is weak, a muscle imbalance occurs, and the patella can move from its normal path. In time this abnormal movement can cause wear and tear to the cartilage.
Should I mobilize my patella or tendon?
These are reasons NOT to mobilize (unless it has been cleared by your doctor or physical therapist) Patella and tendon mobilizations are done to discourage adhesions from limiting motion (post-surgical) or to mobilize adhesions that have already formed to promote better mobility (post or non-surgical).
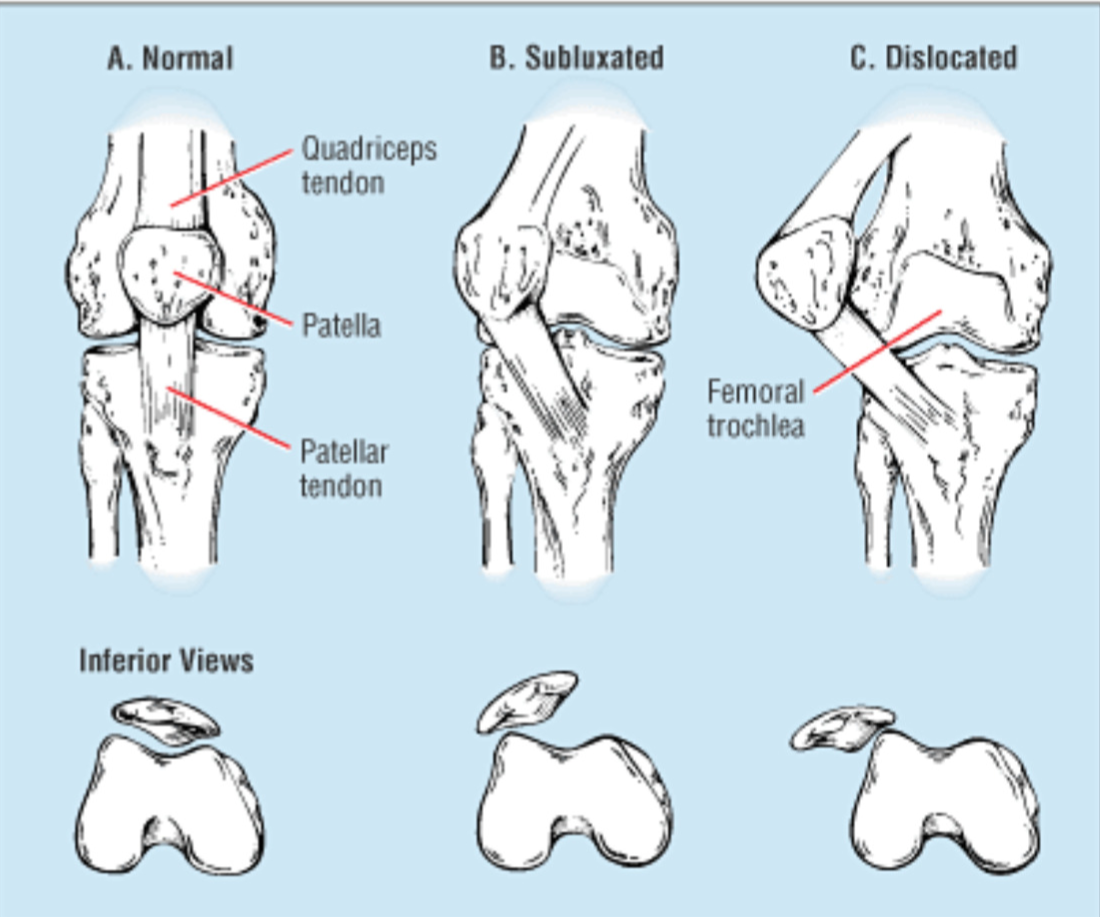
Is it normal for my kneecap to move?
Normally, when you bend and straighten your leg, the kneecap slides up and down inside a vertical groove between the bottom end of the thighbone and the upper end of the shinbone (the trochlear groove). A network of tendons and ligaments secure the kneecap within the groove, flexing as it moves.
How much should the patella move?
The patella glides inferiorly with knee flexion and superiorly with knee extension (Figure 11). With a quadriceps set the patella should migrate approximately 10 mm superiorly.
Why does my knee cap move side to side?
Injuries from sports, overuse, or trauma can cause the patella to move slightly off and not track properly in the trochlear groove. In most cases, the kneecap shifts to the outside of the leg, but it can also move towards the inside.
What happens when your patella moves?
When you have misalignment, or a patellar tracking issue, your kneecap can push to one side of the trochlear groove when you bend your knee. That irritates the area, causing pain. Tracking problems could come from overall alignment issues between your leg and hip. Weak thigh muscles can also be part of the problem.
How do you know if your patella is tracking?
Symptoms of patellar tracking disorder The most common symptom of patellar tracking disorder is pain (in the front of the knee) when going down stairs, jumping, squatting or kneeling. Other symptoms of patellar tracking disorder: Popping or grinding in the kneecap when you bend or straighten the leg.
Why does my kneecap feel loose?
The feeling of a loose knee cap is most commonly caused by an injury that has sprained or tore ligaments. A meniscal or anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury can also cause knee instability and pain.
How do you keep the patella in place?
The thigh muscles (quadriceps) help keep the kneecap (patella) stable and in place. Weak quadriceps increase the risk of patellar tracking disorder. Ligaments and tendons also help stabilize the patella.
How do you test for patellar instability?
Diagnostic Procedures. Patellar instability is normally diagnosed through a comprehensive history of the patient's symptoms and functional objective assessment of the knee. Further scans such as MRI's and Ultrasound imaging can be performed to rule out any structural deficits.
How do I fix my patella tracking?
Most patellar tracking problems can be treated effectively without surgery. Nonsurgical treatment may include rest, regular stretching and strengthening exercises, taping or bracing the knee, using ice, and short-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) .
How do you fix patellar instability?
Management and TreatmentKnee brace to immobilize the knee and keep the kneecap in place. ... Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), rest, elevation and ice packs to ease pain and swelling.Physical therapy to strengthen muscles that hold the kneecap in place and improve range of motion.
Can patellar subluxation be cured?
Treating patellar subluxation can require surgery, but it depends on the cause and severity. Non-surgical treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications, several weeks of rest, and physical therapy.
What does patellar subluxation feel like?
pain at the front of the knee that worsens after activity. popping or cracking in the knee. stiffness or swelling of the knee.
How do you tighten your patella?
Tighten the muscles on top of your thigh by pressing the back of your knee flat down to the floor. (If you feel discomfort under your kneecap, place a small towel roll under your knee.) Hold for about 6 seconds, then rest up to 10 seconds. Do this for 8 to 12 repetitions several times a day.
How do you know if your knee cap is misaligned?
What are the symptoms?Pain in the front of the knee, especially when you squat, jump, kneel, or use stairs (most often when going down stairs).A feeling of popping, grinding, slipping, or catching in your kneecap when you bend or straighten your leg.More items...
What is high riding patella?
Patella alta or high-riding patella refers to an abnormally high patella in relation to the femur. The patella sits high on the femur where the groove is very shallow. Here, the sides of the femoral groove provide only a small barrier to keep the high-riding patella in place.
How can I improve my patella mobility?
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons recommend the following exercises to help strengthen the muscles around the knee and increase the range of motion....Knee stretchesQuadriceps stretch. Stand upright with feet flat on the floor. ... Calf stretch. ... Hip abduction. ... Squat. ... Wall slide. ... Lateral hip and thigh stretch.
Where is the patella located?
Location. The patella sits between the femur and tibia , not only protecting the knee joint but connecting muscles in the front of the femur to the tibia. Under the patella and the at the end of the femur is articular cartilage, which makes it possible for the patella and femur bones to move alongside each other.
What is the name of the area where the patella grows larger than it should be for the space it lives in?
Hyperplastic properties, where the patella grows larger than it should be for the space it lives in (known as patella magna). Hunter’s cap patella, where the lateral side of the patella takes up the anterior surface of the bone.
What is the apex of the patella?
The apex, or point, of the patella points downward towards the shin while the base of the bone sits upward towards the thigh. The base is also what attaches to the quadriceps tendon. The back of the patella forms a joint with the femur, otherwise known as the thighbone. This makes the femur become a joint facet, ...
What muscle is in the middle of the knee?
Muscles in the thigh, parts of the femur, and a tendon in the knee, referred to as medial patellar retinaculum and that crosses the knee joint in the middle of the patella, all work together to keep the patella stabilized.
What connects the tibia to the patella?
From the apex of the patella comes the patellar ligament, which connects to the front of the tibia (shin bone). The middle of the patella consists of openings for arteries to supply blood to the kneecap. Muscles in the thigh, parts of the femur, and a tendon in the knee, referred to as medial patellar retinaculum and that crosses the knee joint in the middle of the patella, all work together to keep the patella stabilized.
How to treat patellar tendonitis?
Depending on the severity of the pain and tendonitis options range from over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen to physical therapy to help stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons surrounding the patella.
How old is the patella bone?
The patella bone goes through the process of ossifying (turning into bone) between the ages of three and six years old. In its whole, complete form the patella is a flat, triangular-shaped bone that is fairly dense. The apex, or point, of the patella points downward towards the shin while the base of the bone sits upward towards the thigh.
Why not mobilize patella?
These are reasons NOT to mobilize (unless it has been cleared by your doctor or physical therapist) Patella and tendon mobilizations are done to discourage adhesions from limiting motion (post-surgical) or to mobilize adhesions that have already formed to promote better mobility (post or non-surgical).
How to assess patella?
Assessment of the patella should be done by shifting or gliding the patella in different directions. Our assessment includes: 1 Medial glide - gliding the patellar toward the centerline of the body 2 Lateral glide - gliding the patella away from the centerline of the body 3 Superior glide - gliding the patella to the top of body 4 Inferior glide - gliding the patella toward the feet 5 Patellar Tendon - assessing the amount of movement of the patellar tendon medially and laterally 6 Suprapatellar region - assessing the amount of movement of the region above the patella
How long should you mobilize your quad muscles?
Our protocol recommends doing the mobilizations for 5-15 minutes, 3-4 times per day.
How to check if you have quad muscles?
This is a way to check if you are on the right structure. Place one finger lateral to the tendon and the other medial. Push the tendon side to side (lateral to medial) to its maximal excursion.
Where is the patellar tendon located?
To find the patella tendon, locate the medial and lateral border of the patella and follow it to downward to the lower portion of the patella. When you can not feel the bone of the patella anymore, feel for a soft, cord-like structure.
Why do you put a towel under your knee?
It can be helpful to place a towel roll under your knee in order to bend the knee slightly. This helps to gain more access to the patella, however it will tighten the structures that restrict patellar motion a bit. I find that a slight bend allows for a better mobilization in this direction.
Where is the suprapatellar pouch?
It lies over the suprapatellar pouch, which is an extension of the knee joint capsule. This is an area where swelling usually appears first. To mobilize these structures, place your fingers above the patella and move the tissue side-to-side, as if you are massaging the muscle just above the patella.
Why Does My Patella Dislocate Laterally?
Most commonly, your patella will dislocate laterally after a bad blow to your knee or strange twisting motion of your knee.
What side of knee is the patella pulled?
If you experience a patellar subluxation or patellar dislocation, your kneecap is likely being pulled towards the outside (lateral side) or inside (medial side) of your knee.
What happens when your kneecap is dislocated?
If your kneecap becomes partially dislocated from your patellofemoral groove, you are experiencing a patellar subluxation. Dislocations. When your kneecap moves all the way out, usually to the outside of your leg (lateral side), it has been dislocated.
Why does my kneecap move freely?
Unlike most of your other bones, the reason your kneecap (patella) moves freely is that it is not actually attached to another bone in your body. Your kneecap is the largest sesamoid bone in your body and is kept in place by a couple tendons, your quadriceps tendon and patellar tendon.
What happens if you hit your knee?
Injury of the Knee. Similar to lateral patellar dislocation, medial patellar subluxation can also occur if there is a direct hit to your knee. This means that there was some type of accident that caused your patella to shift medially. Usually, a ligament is torn when this happens.
What is medial tracking of kneecap?
Medial Patellar dislocation and subluxation are possible, but it is very rare! Medial tracking of your kneecap occurs when your patella shifts towards the inside of your leg.
What is the Q angle of the knee?
The Q angle of your knee is a measurement of the angle between your quadriceps muscles and your patella tendon. The angle is formed by drawing one line from your pelvis anterior superior iliac spine to the middle of your patella, and a second line drawn from the middle of your patella to your tibial tubercle.
Why does the patella move off the inside of my leg?
Injuries from sports, overuse, or trauma can cause the patella to move slightly off and not track properly in the trochlear groove. In most cases, the kneecap shifts to the outside of the leg, but it can also move towards the inside.
How to treat patellar tracking?
Home remedies include: over-the counter pain relievers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen, aspirin), if you tolerate them well. The RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) is a good place to start your home treatments.
How to tell if patellar tracking disorder is dislocated?
To determine if you have a patellar tracking disorder your doctor will do a physical examination, flexing and putting the knee in various positions. They may observe you walk, squat, rise from a seated position, and sit down.
What is the medical term for the kneecap?
Patella is the medical term for your kneecap. Patellar tracking disorder (or patellar maltracking) describes movement of your kneecap that isn’t aligned, like your kneecap moving sideways. It can usually be relieved with exercises and physical therapy. The kneecap is a separate bone that’s attached to your thigh bone ...
What are the symptoms of patellar tracking disorder?
Patellar tracking disorder symptoms. Symptoms of patellar tracking disorder include: pain, and possibly swelling, in the front of the knee, that increases when you squat, jump, kneel, run, or walk downstairs. a popping, grinding, slipping, or catching feeling when you bend your knee. Pain varies depending on the severity of the disorder.
How to get rid of knee pain?
The RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) is a good place to start your home treatments. Rest completely after a painful episode, and only return to activity as you improve. Pull back if you start to feel pain, or you may aggravate things more. Purchase flexible knee braces online.
What is the best way to repair a kneecap?
One commonly recommended surgery is to make a cut in the ligament, the lateral retinaculum, that anchors the outer edge of the patella. Another surgery is repair of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) that attaches to the inner side of the kneecap, and can keep it from slipping outward.
How does the patella track down?
In order for the patella to track up and down normally within the patellofemoral groove (formed by the medial and lateral condyles of the femur), there has to be a balanced pull from both the lateral (outside) and medial (inside) sides of the patella. This balance is achieved by the overall alignment of the leg and the associated soft tissues around the knee. Importantly, a patella that stays centered within the patellofemoral groove throughout the knee’s full range of motion is a well-functioning patella.
Why does my patella dislocate laterally?
Usually this is due to a structural problem with your knee.
What causes patella to slip out of the groove?
This forms the lateral “bunker” of the patello-femoral groove which keeps the patella tracking within the groove. If the femoral condyle is too small , this bunker may be non-existent. Consequently, the patella will have a tendency to slip out of the groove.
How to tell if you have chondromalacia patellae?
Depending on the underlying problem, symptoms vary. For instance, people with chondromalacia patellae may experience vague knee pain that is hard to localize. Pain is commonly associated with walking down stairs or hills, keeping the knee bent for long periods of time (i.e. prolonged sitting), or while kneeling. The knee may even feel as though it wants to gives out on occasion, but this is a reflex response to pain and not an indication of instability in the knee. Finally, you may feel that your knee grinds or pops when squatting or going up and down stairs. This occurs with motion as the normally smooth surfaces of the patella and femur become roughened and rub against one another.
What is the patella of the knee?
The patella, or kneecap, is the circular and more mobile bone that exists on the front of the knee. The patella is part of the extensor mechanism of the leg; a major stabilizer of the knee and the primary extensor of the knee (i.e. straightens the knee). The extensor mechanism is composed of the quadriceps, the quadriceps tendon, patella and patellar tendon, and their associated soft tissues. The patella gives mechanical advantage to the quadriceps muscle and enables it to more powerfully straighten out the knee.
Why does my knee bend?
This happens because of an underlying muscle or structural imbalance around the knee. Normally the patella moves centrally within the patellofemoral groove — a path controlled by the quadriceps muscle and the patellar tendon. Abnormal movement can cause wear and tear to the cartilage.
What is the procedure called when the patella stays centered?
This latter surgery is called a MPFL (medial patello-femoral ligament) reconstruction.
What happens when you flex your knee?
Once your knee is in about 45 degrees of flexion the movement of patella diminishes and is forced downward into the intracondylar groove of the knee joint. This is the area between the medial and lateral femoral condyles of the distal femur. As further flexion of the knee ensues there is less movement of the patella.
Why is the kneecap seperated from the femoratibeal joints?
Also it is possible because posteriorly, the kneecap is seperated from the femoratibeal joints by the infrapatella fat pad which can reduce friction if you are moving your kneecap around.
Why is my knee bump messy?
It's messy because of all the different forces which the quadriceps is collecting and directing. When there is a lot of force on that spot, the bump is much larger.
Why do people have large kneecaps?
So in theory, a person with a large kneecap is a person who uses their quadriceps a lot for some reason, structural or behavioral. The pull affects its size.
What is the kneecap of a human?
The kneecap, patella, is a bone that is completely surrounded by muscles and tendons. It is not anchored to any other bone. (Technically called a sesemoid type of bone).
Can you dislocate your patella?
Skeletal flexibility is a positive thing in itself; however, too loose and you can dislocate your patella
Is it normal to have a bent knee cap?
So essentially it's more of a “free floating” bone and it's perfectly normal. If your legs were bent while your were moving your knee cap around that'd be a concern.
What happens if you let patellar tendonitis progress?
Research shows that the further you let your patellar tendonitis progress, the more cellular damage will have occurred in your tendon and the weaker it will have become. The weaker the tendon becomes the more of its resilience you’ll lose.
Where do you feel patellar tendonitis pain?
You will feel it on the side of your kneecap, in front of your kneecap, and sometimes even behind the kneecap. Most commonly, the pain is felt in the patellar tendon right below the kneecap.
What tendon connects the kneecap to the shinbone?
The patellar tendon connects your patella, the kneecap, to the shinbone. You use this tendon every time you straighten your knee. This tendon can withstand very high forces, but in spite of its durability, the patellar tendon can still wear down over time if it’s frequently overstressed.
What stage of tendonitis does it hurt when you are in stage 2?
This means that activities that didn’t cause you pain when you’re in stage 1 of patellar tendonitis are too stressful for your knee when you’re in stage 2 or 3 and will then cause pain.
How many red flags are there for patellar tendonitis?
This article will show you the symptoms of patellar tendonitis and the three red flags that tell you how serious your patellar tendonitis has become.
What are some exercises that cause knee pain?
This includes climbing stairs, squatting, cycling, and walking downhill. Explosive leg movements, such as jogging, weightlifting, jumping , and sprinting are particularly likely to worsen the pain.
Does resting help patellar tendonitis?
In other words, if you have any of the red flag symptoms for stages two through four, resting will not get you back to 100%. The second set of requirements applies to the chronic stages of patellar tendonitis, when the symptoms have become somewhat constant: Healing Requirements for Stages 2 – 4: Resting will not heal your tendon completely, you ...