What are the causes of acid base imbalance?
There are several different causes of respiratory acidosis including:
- chest deformities or injuries
- chronic lung and airway diseases
- overuse of sedatives
- obesity
Why is potassium given in DKA?
Replacement of potassium in intravenous fluids is the standard of care in treatment of DKA to prevent the potential consequences of hypokalemia including cardiac arrhythmias and respiratory failure.
What is dka in medical terms?
- Diabetes Complications in Dogs and Cats: Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Increases Risk of Acute Renal Failure in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Can DKA cause lactic acidosis?
Lactic acidosis is more common in DKA than traditionally appreciated and is not associated with increased ICU LOS or mortality. The positive correlation of lactate with glucose raises the possibility that lactic acidosis in DKA may be due not only to hypoperfusion but also to altered glucose metabolism.

Is DKA metabolic acidosis or alkalosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is associated with a metabolic alkalosis, which is thought to be due to vomiting. However, alkalosis can occur in DKA without vomiting. We retrospectively reviewed the acid-base disturbances in DKA admissions without vomiting.
Is diabetic ketoacidosis a pH imbalance?
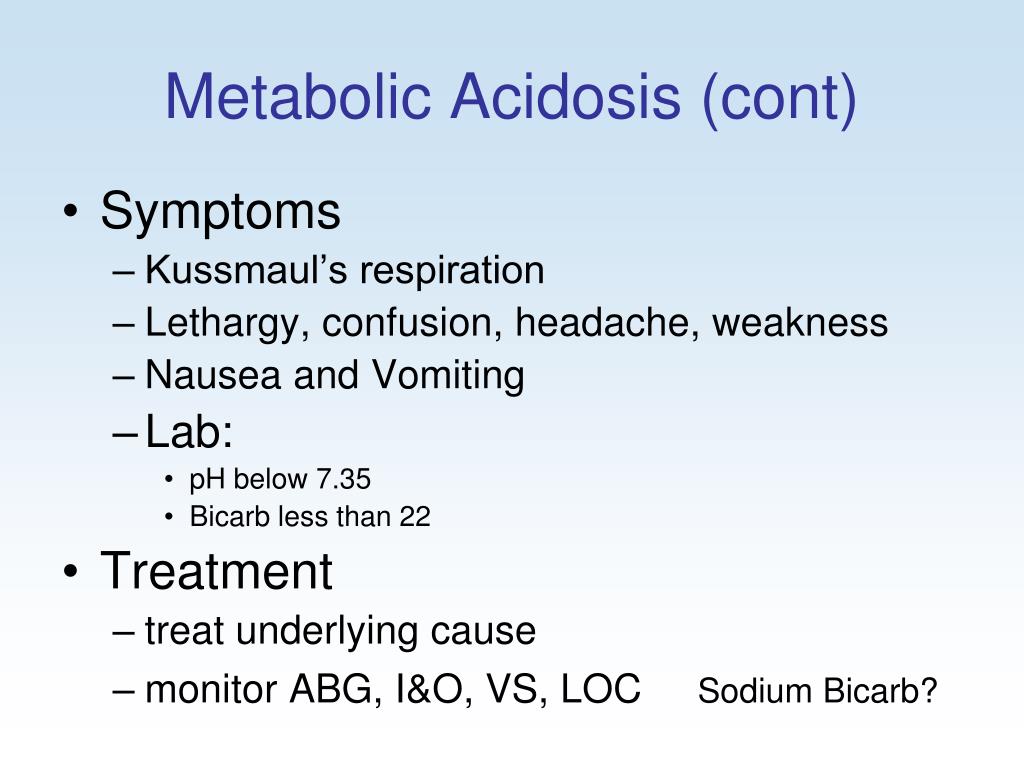
A diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis requires the patient's plasma glucose concentration to be above 250 mg per dL (although it usually is much higher), the pH level to be less than 7.30, and the bicarbonate level to be 18 mEq per L or less.
Does ketoacidosis cause metabolic acidosis?
Ketoacidosis is a common cause of raised anion gap metabolic acidosis with a wide differential diagnosis. It most frequently occurs in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA arises due to a partial or complete deficiency in insulin and raised counter-regulatory hormones (1).
What electrolyte imbalance does DKA cause?
During diabetic ketoacidosis, there may be rapid shifts in the plasma concentration of potassium ions. Although diabetic ketoacidosis leads to a deficit in total-body stores of potassium ion, the plasma concentration is usually normal or elevated, since the acidemia leads to the exit of potassium ions from cells.
Why is pH low in diabetic ketoacidosis?
During DKA, pH is low primarily because the bicarbonate buffer is exhausted, i.e. bicarbonate concentration is reduced.
What is metabolic acidosis and alkalosis?
Normal human physiological pH is 7.35 to 7.45. A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase over this range is alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body's pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process.
How DKA causes respiratory alkalosis?
Detection of primary respiratory alkalosis in a patient with DKA has great importance because it often provides a clue for the presence of sepsis[62] which is the underlying cause of DKA in many instances[37-39], respiratory distress secondary to cerebral edema, and other causes of respiratory alkalosis.
Does DKA cause hypokalemia or hyperkalemia?
DKA is a well-known cause of hypokalemia caused by osmotic diuresis leading to a total body potassium deficiency of 3 to 6 mEq/kg.
What is the most significant basic defect in the development of DKA?
Overall, the most common precipitating factor for developing DKA was insulin non-adherence, seen in 51.2% of the cases.
Which electrolyte is most affected when the patient is in DKA?
Loss of Potassium During Episode of DKA First entity to get disturbed by the lack of insulin is electrolytes among which, potassium is most affected (6, 7).
Why does DKA cause hyponatremia?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) causes a hyperosmolar state driven by the osmotic force of hyperglycemia in the intravascular space. Dilutional hyponatremia is common due to water driven into the intravascular space from inside cells. On rare occasions, hypernatremia is found in DKA.
Why there is hypokalemia in DKA?
Hypokalemia in DKA likely results from a combination of kaliuresis, secondary to prolonged osmotic diuresis, inadequate oral intake, and gastrointestinal losses from diarrhea or vomiting. Kaliuresis is also driven by secondary hyperaldosteronism from profound losses of sodium and extracellular volume.
What are the 3 P's in diabetic ketoacidosis?
The three Ps of DKA: Polydipsia—thirst. Polyuria—urination. Polyphagia—appetite.
What is the most common cause of DKA?
Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens after: An illness. An infection or other illness can cause the body to make higher levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol. These hormones work against the effects of insulin and sometimes cause diabetic ketoacidosis.
Can diabetic ketoacidosis cause electrolyte imbalance?
Electrolyte imbalance is commonly present in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The cause is usually multifactorial, but usually results from insulin deficiency in diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia.
What lab values indicate DKA?
Diabetes-related ketoacidosis is generally diagnosed if you have the following four conditions:Your blood glucose (sugar) level is above 250 mg/dL. ... Your blood pH is less than 7.3 (acidosis).You have ketones in your urine and/or blood.Your serum (blood) bicarbonate level is less than 18 mEq per L.
What acid-base disturbances are commonly seen in DKA?
The most common disturbance was metabolic alkalosis, present in 116 patients (74 in group A, 34 in group B and 8 in group C). Metabolic acidosis was found in 33 patients (7 in group A, 9 in group B and 17 in group C). Respiratory disturbance, predominantly respiratory alkalosis, was evident in 26 patients.
What is the relevance of ketoacidosis in DKA?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can lead to diabetic coma (passing out for a long time) or even death. When your cells don ’t get the glucose they need for energy, your body begins to burn fat for energy, which produces ketones.
Why electrolyte imbalances commonly occur in the patient with diabetic ketoacidosis?
In summary, hyperglycemia in DKA causes an osmotic diuresis, which results in severe fluid and electrolyte deficit. If left untreated, fluid deficit can be sufficiently severe to cause acute renal failure. FIG 2. Osmotic diuresis in DKA causes polyuria, glycosuria and electrolyte depletion.
When managing diabetic ketoacidosis which intervention is appropriate?
Fluid replacement is one of the most important initial therapeutic interventions in the management of DKA. Patients are usually dehydrated and correcting this deficit will result in significant metabolic improvement (Kitabchi et al, 2004).
Is diabetic ketoacidosis the same as metabolic acidosis?
There are several types of metabolic acidosis: Diabetic acidosis (also called diabetic ketoacidosis and DKA) develops when substances called ketone bodies (which are acidic) build up during uncontrolled diabetes.
What causes diabetic acidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is usually triggered by: An illness. An infection or other illness can cause your body to produce higher levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol. Unfortunately, these hormones counter the effect of insulin — sometimes triggering an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Does diabetic ketoacidosis cause hyperkalemia or hypokalemia?
Although hypokalemia is common in DKA, hyperkalemia is the more likely problem in patients on hemodialysis.
What is it called when your blood is too acidic?
When the levels of acid in your blood are too high, it’s called acidosis. When your blood is too alkaline, it is called alkalosis.
What is the balance of acid and base?
What is acid-base balance? Your blood needs the right balance of acidic and basic (alkaline) compounds to function properly. This is called the acid-base balance. Your kidneys and lungs work to maintain the acid-base balance. Even slight variations from the normal range can have significant effects on your vital organs.
What is the difference between hyperchloremic and lactic acidosis?
This is usually due to uncontrolled type 1 diabetes. Hyperchloremic acidosis is when your body loses too much sodium bicarbonate, often after severe diarrhea. Lactic acidosis is when too much lactic acid builds up. This can be due to:
Why does alkalosis occur in the respiratory system?
Respiratory alkalosis is when your blood has low levels of carbon dioxide. This can be caused by a number of factors, including: When you have al kalosis your carbon dioxide levels are low. This causes your body to release more bicarbonate to return your blood pH level back to normal.
What is it called when too much lactic acid builds up?
Lactic acidosis is when too much lactic acid builds up. This can be due to:
What causes chronic respiratory acidosis?
The cause could be from an organ deformity, an infection, or some type of inflammation. Each cause may require a different treatment ranging from antibiotics to a breathing machine.
How to prevent respiratory acidosis?
You can take steps to help prevent some of the conditions that lead to respiratory acidosis. Maintain a healthy weight. Take sedatives only under strict doctor supervision and never combine them with alcohol. Do not smoke.
What is a DKA?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with significant fluid and electrolyte loss. DKA occurs mostly in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
What causes a loss of potassium and sodium?
Hyperglycemia due to insulin deficiency causes an osmotic diuresis that leads to marked urinary losses of water and electrolytes. Urinary excretion of ketones obligates additional losses of sodium and potassium. Serum sodium may fall due to natriuresis or rise due to excretion of large volumes of free water.
What is the cause of diuresis?
It causes nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and can progress to cerebral edema, coma, and death. DKA is diagnosed by detection of hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis in the presence of hyperglycemia.
Why does insulin deficiency cause a rise in glycerol levels?
Serum levels of glycerol and free fatty acids rise because of unrestrained lipolysis, as does alanine because of muscle catabolism. Glycerol and alanine provide substrate for hepatic gluconeogenesis, which is stimulated by the excess of glucagon that accompanies insulin deficiency.
What are the two main ketoacids?
The major ketoacids produced, acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid, are strong organic acids that create metabolic acidosis. Acetone derived from the metabolism of acetoace tic acid accumulates in serum and is slowly disposed of by respiration.
Why does glycerol and alanine increase?
Serum levels of glycerol and free fatty acids rise because of unrestrained lipolysis, as does alanine because of muscle catabolism . Glycerol and alanine provide substrate for hepatic gluconeogenesis, which is stimulated by the excess of glucagon that accompanies insulin deficiency.
What should be measured for diabetic ketoacidosis?
In patients suspected of having diabetic ketoacidosis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine, glucose, ketones, and osmolarity should be measured. Urine should be tested for ketones. Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement.
Respiratory alkalosis
A respiratory imbalance occurs when there is too much, or too little, carbon dioxide in arterial blood. The higher the level, the more acidic, the lower the level, the more basic.
Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis is a condition when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces.
Metabolic alkalosis
For metabolic disorders, the two key lab values to pay attention to are pH and bicarbonate (HCO3). HCO3 is excreted by the kidneys and acts as a buffer for the acid-base system. Too little can result in metabolic alkalosis, too much can lead to metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis
A patient experiencing metabolic acidosis will have a pH of less than 7.35 and an HCO3 of less than 21.
Full Transcript
Hi, I'm Meris. And in this video, we're going to be talking about acid-base imbalances. I'm going to be following along using our Fundamentals of Nursing flash cards. These are available on our website, leveluprn.com. And if you already have a set for yourself, I'm going to be starting on card number 99. Let's get started.
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
Other conditions that can lead to metabolic alkalosis are kidney damage caused by a severe loss of fluids or ingestion of a large amount of baking soda.
What are the two conditions that can lead to a blood pH imbalance?
A blood pH imbalance can lead to two conditions: acidosis and alkalosis.
How do the kidneys and lungs maintain pH?
How the lungs and kidneys maintain the pH balance. The lungs control your body’s pH balance by releasing carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a slightly acidic compound. It’s also a waste product produced by cells in the body as they use oxygen. The cells release it into your blood, and it’s taken to your lungs.
How do you know if you have respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis are muscle cramping and twitching. You may also notice tingling in your fingers, toes, and lips, as well as irritability.
How do kidneys help the body maintain pH balance?
Your brain constantly monitors this in order to maintain the proper pH balance in your body. The kidneys help the lungs maintain acid-base balance by excreting acids or bases into the blood. The kidneys’ effect on acidity works much more slowly than that of the lungs.
What is the pH balance of the body?
What is pH balance? Your body’s pH balance, also referred to as its acid-base balance, is the level of acids and bases in your blood at which your body functions best. The human body is built to naturally maintain a healthy balance of acidity and alkalinity. The lungs and kidneys play a key role in this process.
What happens if your blood pH is too low?
If the lungs or kidneys are malfunctioning, your blood’s pH level can become imbalanced. Disruption in your acid-base balance can lead to medical conditions known as acidosis and alkalosis. Both conditions require treatment from a medical professional, not simply dietary changes.