
What actions did the Congress of Vienna take? To bring about a balance of power in Europe and prevent further conflict, they developed what became known as the Concert of Europe, beginning with the Congress of Vienna. The Congress of Vienna dissolved the Napoleonic world and attempted to restore the monarchies Napoleon had overthrown.
Full Answer
What is the most important goal of the Congress of Vienna?
The objective of the Congress of Vienna was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
Why was the Congress of Vienna considered a success?
The Congress of Vienna was a success because the congress got a balance of power back to the European countries. The congress also brought back peace among the nations. Europe had peace for about 40 years. Furthermore, who benefited from the Congress of Vienna?
What were the chief goals of Congress of Vienna?
What were the chief goals of the Congress of Vienna? To preserve peace through a balance of power and restore monarchies Why did the Vienna peacemakers redraw the map of Europe? Tried to contain French ambitions of expansion
Was the Congress of Vienna successful in its goals?
The congress of Vienna was successful in implementing its goals in the European system. A new concept for Europe was coined out of the old order and developed to suit the continent. Though the countries that attended the congress might not be in power in contemporary times, their opinions had a significant effect on reshaping Europe and the view of power.
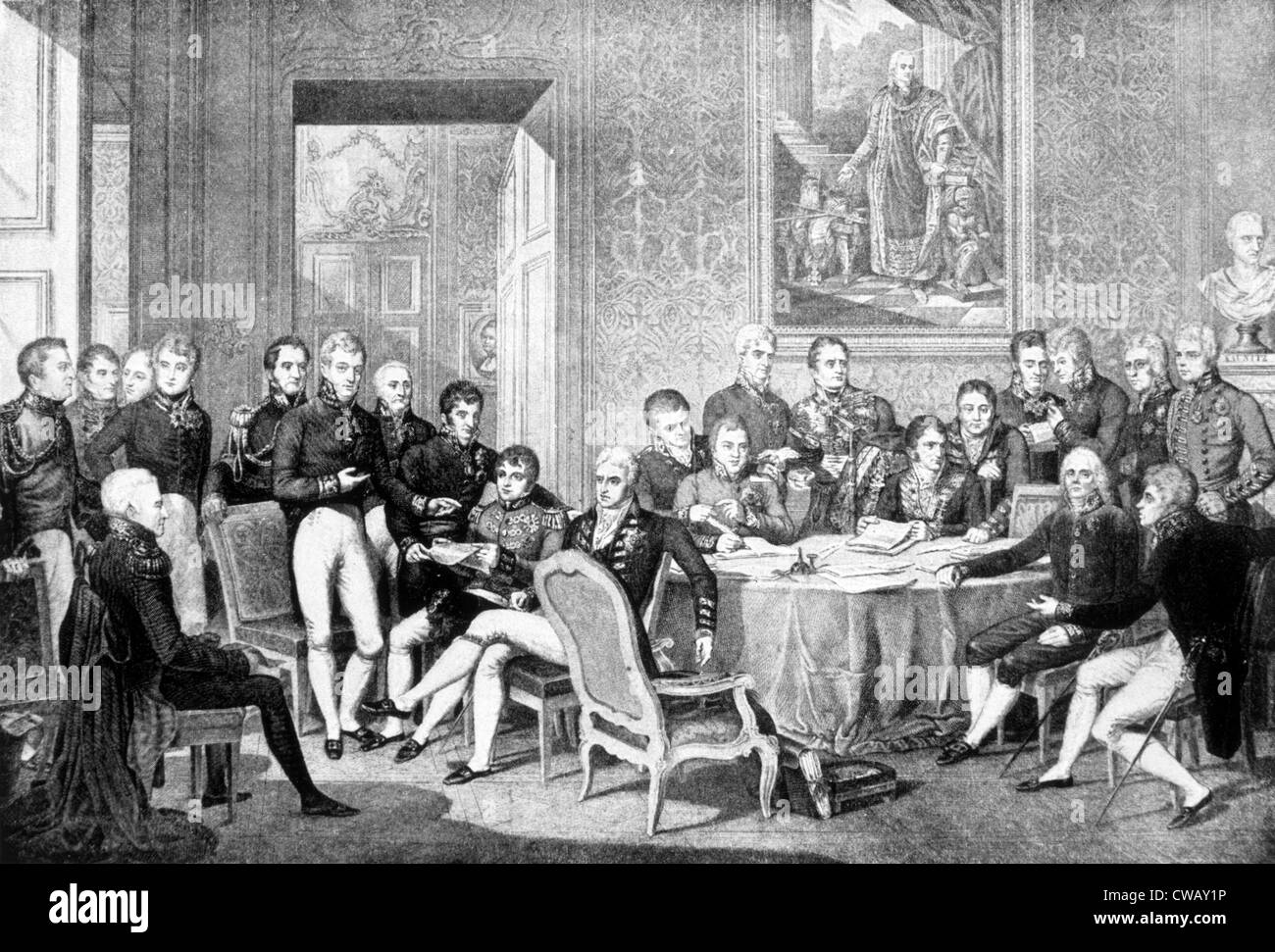

What actions did Congress of Vienna take?
They included the establishment of a confederated Germany, the division of French protectorates and annexations into independent states, the restoration of the Bourbon kings of Spain, the enlargement of the Netherlands to include what in 1830 became modern Belgium, and the continuation of British subsidies to its ...
What were 3 outcomes of the Congress of Vienna?
Results of Congress of Vienna The results of the Congress of Vienna were established new borders and the main five countries were given different territories. Some countries got exactly what they wanted. Russia was able to obtain Poland. Austria got to control the German Confederation.
What did the Congress of Vienna try to accomplish?
The Congress of Vienna was an international congress aiming to restore peace and to restructure Europe, which was in a mess after almost two centennaries of war and the monomanic attempts of Napoleon to conquer Europe. It was a quest for a balance of powers, so that future wars and revolutions could be prevented.
What were the four major outcomes of the Congress of Vienna?
The Congress had four major objectives: to establish a balance of power, to encourage conservative regimes, to contain France, and to learn to work together for peace.
What were the decisions taken in Vienna Treaty?
The major final agreements were as follows. In return for acquiring Poland, Alexander gave back Galicia to Austria and gave Thorn and a region around it to Prussia; Kraków was made a free town. The rest of the Duchy of Warsaw was incorporated as a separate kingdom under the Russian emperor's sovereignty.
What was one result of the Congress of Vienna?
The Congress of Vienna was a success because the congress got a balance of power back to the European countries. The congress also brought back peace among the nations. Europe had peace for about 40 years.
What were the major proposals of the Vienna Congress?
1.To restore the feudal order deposed during the Napoleonic wars which held by European countries in the old dynasty. 2.To prevent France from comeback. 3.To stop the victors from re-division of Europe's territory.
What were the 3 main goals of the Congress of Vienna?
The 3 main goals of the Congress of Vienna were to balance the powers of Europe to coexist peacefully, enclose France's borders, and restore conser...
What were the results of the Congress of Vienna?
The results of the Congress of Vienna were new borders throughout Europe, France had to pay restitution but still remained a large power in Europe,...
What does Congress of Vienna mean in history?
The Congress of Vienna ended the Napoleonic reign in history. The major powers of Europe set aside some of their differences to depose the horrible...
Was the Congress of Vienna successful?
The Congress of Vienna was successful for about forty years. However, because of the way the borders were drawn and which country obtained which la...
What did the Congress of Vienna do?
The Congress of Vienna set new borders and decided on methods to keep the peace in Europe after Napoleon Bonaparte's disastrous reign. It redesigne...
Why was the Congress of Vienna so important?
The Congress of Vienna was so important because it helped calm Europe and restore some semblance of peace and order after Napoleon's disastrous rei...
Why was the Congress of Vienna criticized?
The Congress of Vienna has frequently been criticized by 19th century and more recent historians for ignoring national and liberal impulses, and for imposing a stifling reaction on the Continent. It was an integral part in what became known as the Conservative Order, in which the democracy and civil rights associated with the American and French Revolutions were de-emphasized.
Who represented Austria in the Congress?
Austria was represented by Prince Metternich, the Foreign Minister, and by his deputy, Baron Johann von Wessenberg. As the Congress's sessions were in Vienna, Emperor Francis was kept closely informed.
What was the Treaty of Chaumont?
The Treaty of Chaumont in 1814 had reaffirmed decisions that had been made already and that would be ratified by the more important Congress of Vienna of 1814–15. They included the establishment of a confederated Germany, the division of Italy into independent states, the restoration of the Bourbon kings of Spain, and the enlargement of the Netherlands to include what in 1830 became modern Belgium. The Treaty of Chaumont became the cornerstone of the European Alliance that formed the balance of power for decades. Other partial settlements had already occurred at the Treaty of Paris between France and the Sixth Coalition, and the Treaty of Kiel that covered issues raised regarding Scandinavia. The Treaty of Paris had determined that a "general congress" should be held in Vienna and that invitations would be issued to "all the Powers engaged on either side in the present war". The opening was scheduled for July 1814.
What was Talleyrand's policy?
Talleyrand's policy, direct ed as much by national as personal ambitions, demanded the close but by no means amicable relationship he had with Labrador, whom Talleyrand regarded with dis dain. Labrador later remarked of Talleyrand: "that cripple, unfortunately, is going to Vienna.".
What was the first time national representatives came together to formulate treaties?
On the other hand, the Congress was the first occasion in history where, on a continental scale, national representatives came together to formulate treaties instead of relying mostly on messages among the several capitals.
What did the conservative leaders of the Congress seek to do?
More fundamentally, the conservative leaders of the Congress sought to restrain or eliminate the republicanism and revolution which had upended the constitutional order of the European old regime, and which continued to threaten it.
How many states were there in the German Confederation?
A German Confederation of 39 states, under the presidency of the Austrian Emperor, formed from the previous 300 states of the Holy Roman Empire. Only portions of the territories of each of Austria and Prussia were included in the Confederation (roughly the same portions that had been within the Holy Roman Empire).
Congress of Vienna
During the early 19th century, Europe was recovering and rebuilding itself after the Napoleonic Wars. The Napoleonic Wars ravaged the entire continent of Europe. To attempt to prevent this type of war and destruction from ever occurring, the leading nations wanted to assemble a meeting to discuss strategy.
Congress of Vienna Delegates
The leaders of the Congress of Vienna were British Foreign Minister Robert Steward, Lord Castlereagh, Tsar Alexander I of Russia, and Austrian Chancellor Klemens von Metternich. Two other major players were French Foreign Minister Charles Maurice de Talleyrand and Prussian Prince Karl August von Hardenberg.
Congress of Vienna Goals
The goals of the Congress of Vienna were to create a needed balance of powers throughout Europe after the disastrous reign of Napoleon, enclose France within its borders, install a conservative order, and coexist peacefully in the long term. Each major delegate had their own agenda and goals.
What was the Congress of Vienna about?
Essentially, the Congress of Vienna was about. re-installing the absolutistic monarchies in Europe before the French Revolution of 1789, also known as the Restauration. legitimising the ruling monarchies and fiefdoms. re-structuring Germany’s internal affairs.
Which countries were involved in the Congress of Vienna?
Through their heads of state and senior diplomats the five European super powers Russia, Great Britain, Prussia, Austria and France took part at the Congress of Vienna. In addition, the other German courts, previously sovereign cities, Switzerland and other European states sent delegates to Vienna. All in all, approximately 200 rulers ...
What was the Wiener Kongress?
Briefly put, the Wiener Kongress was one of the most significant international political summits in Europe. After the Congress of Vienna re-conciled the multiple conflicts of interest between the European powers it created a period of almost 40 years without major European wide conflicts. On a negative note, the summit resulted in ...
What battle did Napoleon Bonaparte fight in?
Napoleon Bonaparte’s escape from Elba and France’s defeat in the battle of Waterloo, however, thwarted his efforts.
What was the central European capital of the Habsburg Empire?
Vienna as the epicentre of the Central European Habsburg Empire with its vast territories and regional interests, seemed an obvious choice. In September 1814, about six months after the fall of Napoleon, Habsburg Emperor Francis I invited the European rulers and their key diplomats to the Congress of Vienna.
When did the Treaty of Vienna happen?
Treaty Of Vienna. On 9 June 1815, the five signatory states signed the Treaty of Vienna. You can see the newly created territories and their boundaries in the historic map above. The battle of Waterloo was still raging on, ending in Napoleon’s defeat nine days later.
Which country won Poland?
As a result, Russia won large parts of Poland. Prussia lost significant territories of Saxonia. Arthur Wellesley, Duke of Wellington: was British diplomat in France and of British-Irish origin. He took over the negotiations at the Vienna Congress from Lord Castlereagh on 1st February 1815.
What was the impact of the Congress of Vienna?
The Congress of Vienna was a standout amongst the most vital universal summits of European history; it decided the future limits of Europe, limits that still affect Europe today. The significant forces of the day ruled arrangements, sending their most famous statesman.
Why did the Congress of Vienna come into being?
When each nation decided to come and help each other in case of external threats, The Congress of Vienna came into being for establishing peace in Europe.
What was the role of Klemens von Metternich in the Congress of Vienna?
Metternich’s role in the Congress of Vienna. In European history, Klemens Von Metternich, the foreign minister of Austria had played a significant role in establishing international diplomacy. Metternich, in any case, expected that Russia would turn out to be excessively amazing in this arrangement. To battle the Russian-Prussian coalition, on ...
What kingdoms did Napoleon make Germany?
Rather, the moderately expansive kingdoms of Bavaria, Wurttemberg, and Saxony stayed as Napoleon made them. Be that as it may, no unified Germany would come forward.
What happened after Napoleon's downfall?
After the downfall of Napoleon, Europe was in a state of chaos and it needed re-organization. Thus the Congress of Vienna came into force. The individuals from the Congress were all scared of a solid France, so they created outskirt states. The Netherlands and the Italian Kingdom of Piedmont were built. Prussia got the left bank of the Rhine, ...
When did Napoleon show up in France?
On March 1, 1815, Napoleon showed up in France, having gotten away from outcast in Elba. Promising to return France to brilliance, Napoleon cleared through the nation and raised a military. Louis XVIII immediately fled, and Napoleon attempted at success in a period called the Hundred Days. The Congress of Vienna was stunned ...
Which country took the left bank of the Rhine?
The Netherlands and the Italian Kingdom of Piedmont were built. Prussia got the left bank of the Rhine, while Austria took an area in Northern Italy, including Tuscany and Milan. In Naples, Murat really kept his position of authority for some time. The Bourbons were re-established in Spain.
Overview
The Congress of Vienna (French: Congrès de Vienne, German: Wiener Kongress) of 1814–1815 was an international diplomatic conference to reconstitute the European political order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon I. It was a meeting of ambassadors of European states chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 t…
Preliminaries
The Treaty of Chaumont in 1814 had reaffirmed decisions that had been made already and that would be ratified by the more important Congress of Vienna of 1814–15. They included the establishment of a confederated Germany, the division of Italy into independent states, the restoration of the Bourbon kings of Spain, and the enlargement of the Netherlands to include what in 1830 became modern Belgium. The Treaty of Chaumont became the cornerstone of the Euro…
Participants
The Congress functioned through formal meetings such as working groups and official diplomatic functions; however, a large portion of the Congress was conducted informally at salons, banquets, and balls.
The Four Great Powers had previously formed the core of the Sixth Coalition. On the verge of Napoleon's defeat they had outlined their common position in the Treaty …
Talleyrand's role
Initially, the representatives of the four victorious powers hoped to exclude the French from serious participation in the negotiations, but Talleyrand skillfully managed to insert himself into "her inner councils" in the first weeks of negotiations. He allied himself to a Committee of Eight lesser powers (including Spain, Sweden, and Portugal) to control the negotiations. Once Talleyrand wa…
Final Act
The Final Act, embodying all the separate treaties, was signed on 9 June 1815 (nine days before the Battle of Waterloo). Its provisions included:
• Russia received most of the Duchy of Warsaw (Poland) and retained Finland (which it had annexed from Sweden in 1809 and would hold until 1917, as the Grand Duchy of Finland).
Other changes
The Congress's principal results, apart from its confirmation of France's loss of the territories annexed between 1795 and 1810, which had already been settled by the Treaty of Paris, were the enlargement of Russia, (which gained most of the Duchy of Warsaw) and Prussia, which acquired the district of Poznań, Swedish Pomerania, Westphalia and the northern Rhineland. The consolidatio…
Later criticism
The Congress of Vienna has frequently been criticized by 19th century and more recent historians for ignoring national and liberal impulses, and for imposing a stifling reaction on the Continent. It was an integral part in what became known as the Conservative Order, in which the democracy and civil rights associated with the American and French Revolutions were de-emphasized.
In the 20th century, however, many historians came to admire the statesmen at the Congress, w…
See also
• Diplomatic timeline for 1815
• Precedence among European monarchies
• Concert of Europe
• European balance of power