Definitions of Age Matrix Terms:
| State | Age of Criminal Responsibility/Majority | Age Juvenile Case Can Be Transferred to ... | Maximum Parole Age | Maximum Probation Age |
| Arkansas | 18 | 14 | 21 | 21 |
| California | 16 | 16 | N/A | 25 |
| Colorado | 18 | 15 | 21 | Open--If a person commits a crime as a j ... |
| Connecticut | 18 | 15 | N/A - Effective 7/1/18, delinquency comm ... | Court may place adjudicated delinquent ( ... |
What is the age limit for juvenile court in California?
Under California law, prior to SB 439, the juvenile court had jurisdiction over allchildren under the age of 18. There was not a minimum age of a child where the court could not hear a case. New Laws under Senate Bill 439
Who is treated as a juvenile in California?
Who Is Treated As a Juvenile in California? Generally, any individual age 18 or older is considered an adult and treated as such in California.
When does juvenile court jurisdiction end in California?
Juvenile court jurisdiction terminates when the ward reaches the age of 21. 3. What in the juvenile court process? The California juvenile court process begins with the arrest of a minor.
Why do California’s juvenile and adult courts have different court processes?
Because the two courts deal with different offenders and focus on different outcomes, the two courts have different court processes. Below are 11 ways California’s juvenile courts distinguish themselves from the adult criminal court process…

What age is considered a juvenile in California?
Definitions of Age Matrix Terms:StateCivil Age of MajorityAge Juvenile Case Can Be Transferred to Adult CourtCalifornia1816Colorado1815Connecticut1815Delaware181448 more rows•Jan 20, 2022
Can a 12 year old be charged with a crime in California?
While California law prohibits prosecution of children less than 14 years of age, in some situations a minor who is at least 14 years old may be tried as an adult. In fact, California law specifies certain crimes for which a minor 14 years and older must be prosecuted in adult court.
How long is juvenile life in California?
Teens faced life sentences, now only six years under California's new juvenile offender law. A California law enacted this year raised the age at which juvenile offenders can be tried as adults from 14 to 16.
How old are you to be a juvenile?
While an adult is usually a person over 18 (or in some cases, over 21), juvenile refers to persons under the age of 18 years. Therefore, 'juvenile' and 'minor' are two different terms, an important detail in criminal cases. Some cases deal with 'adults' and 'minors,' and others deal with 'juveniles' and 'adults.
What is the youngest age to go to jail?
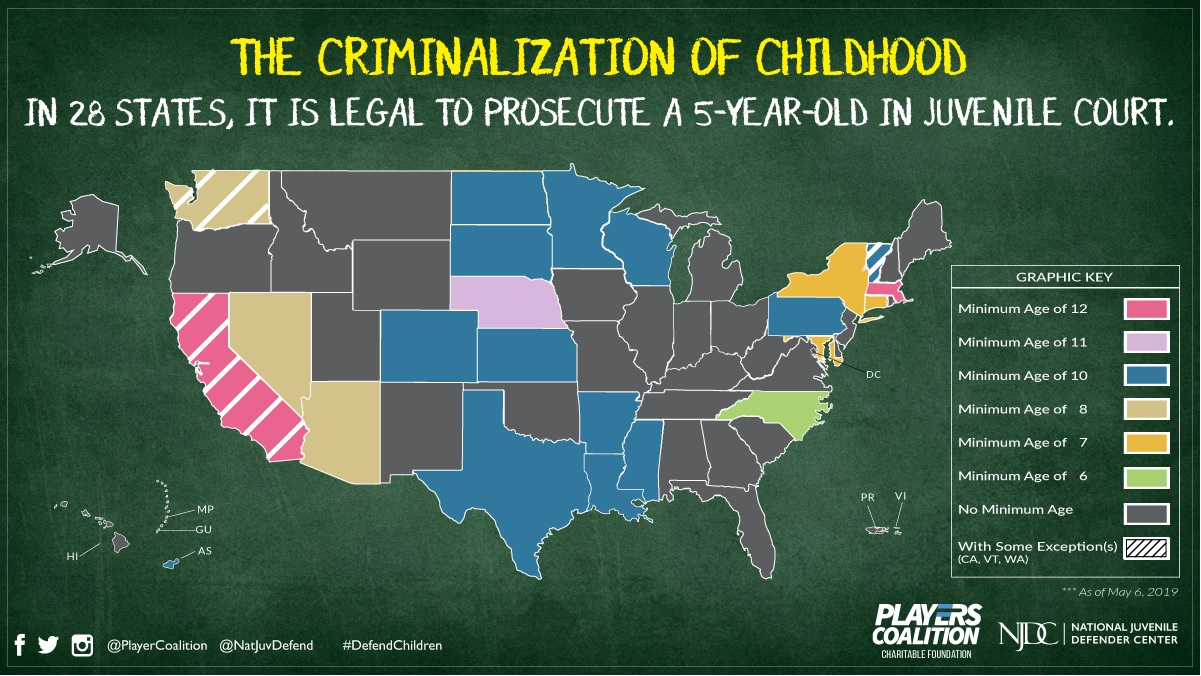
In the United States the age varies between states, being as low as 6 years in South Carolina and 7 years in 35 states; 11 years is the minimum age for federal crimes.
What is the oldest age for juvenile detention?
In 47 states, the maximum age of juvenile court jurisdiction is age 17. In 2020, Vermont became the first state in the nation to expand juvenile court jurisdiction to 18. Three states-- Georgia, Texas and Wisconsin--now draw the juvenile/adult line at age 16.
Can a 17 year old go to jail in California?
The majority of 16 and 17-year-olds who come into court facing felony charges remain in juvenile court and are not tried as adults. The District Attorney must make a special motion asking the court to transfer a qualifying case into adult court.
How old do you have to be to go to jail in California?
What's the age threshold for jail? Unlike 18 other states, California doesn't have one. A child of any age can be incarcerated here, and it's not just theoretical. Some prosecutors and judges still see juvenile halls and probation camps as the best places to straighten out preteens.
Can juveniles get death penalty?
The United States Supreme Court prohibits execution for crimes committed at the age of fifteen or younger. Nineteen states have laws permitting the execution of persons who committed crimes at sixteen or seventeen. Since 1973, 226 juvenile death sentences have been imposed.
Is minor and juvenile the same?
Minor is a person under the age of full legal responsibility. The court will take account of the wishes of a minor. A juvenile is a young person below the age at which normal criminal prosecution is possible 18 in most of the countries.
Can a 13 year old go to jail?
Some states allow children to be prosecuted as adults at 10, 12, or 13 years old. Children as young as eight have been prosecuted as adults. Each year, judges transfer dozens of children under 14 to adult court. Prosecutors charge other young kids directly in adult court.
Who is a juvenile?
A "juvenile" is a person who has not attained his eighteenth birthday, and "juvenile delinquency" is the violation of a law of the United States committed by a person prior to his eighteenth birthday which would have been a crime if committed by an adult.
How old do you have to be to go to juvenile court in California?
Generally speaking, minors under the age of 18 are tried in the California juvenile court system. But there are cases in which younger minors can be tried in adult court. 2.1 Minors under 18 generally go to juvenile court.
How many minors were tried in California?
Over 18,000 minors were placed in a secure facility or in the California Youth Authority. As a result of “get tough on juvenile crime” initiatives, 1,115 minors were sent to adult court to be tried as adults. 2.
What is the CYA in California?
CYA is now called the Division of Juvenile Justice and housed within the California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation.
What is juvenile delinquency court?
Juvenile delinquency court is a court dedicated to adjudicating felony and misdemeanor crimes allegedly committed by minors. Juvenile court also handles “status offenses” like truancy and curfew violations. Status offenses only constitute criminal acts when committed by juveniles.
What is the purpose of a minor in a camp?
But when a minor is placed on probation, or committed to camp or DJJ, the purpose is to rehabilitate the minor. Kids in the juvenile court justice system are supposed to get the education, treatment and services they need to move past their crimes, reunite with their families and become productive citizens. 1.2.
What is the law that allows a minor to be charged with a crime?
On September 30, 2018, California Governor Jerry Brown signed into law SB 439. This bill only allows the court to assume jurisdiction over a minor under 12 years old, if that child is charged with murder or rape, sodomy, oral copulation, or sexual penetration by force, violence, or threat of great bodily harm.
Can a minor serve probation?
A minor can be a ward of the court but still allowed to serve out probation at home. In other cases, the minor might be placed in foster care, in a group home or in a county probation camp. 1.1. Goal of rehabilitation. In theory, the California juvenile justice system is designed to “rehabilitate” offenders.
When did juvenile crime peak in California?
The State of Juvenile Crime in California. Juvenile crime peaked in California in 1974 and then decreased through 1987. This decrease occurred at the same time as the proportion of juveniles in California's population was declining. Juvenile crime has increased since 1987.
How many juvenile arrests were there in California in 1993?
For example, the overall juvenile arrest rate for California in 1993 was 6,772.8, which means that there were about 6,773 juvenile arrests for every 100,000 youth under the age of 18. Crime Is Underreported.
What percentage of arrests were juveniles in 1993?
Juveniles Account for a Significant Number of All Arrests. 1993. In 1993, juveniles accounted for 16 percent of all felony arrests in California. Juveniles accounted for 26 percent of all property arrests and 14 percent of violent crime arrests, in 1993.
What is juvenile justice?
The juvenile justice system also consists of a large number of nonlaw enforcement agencies. Social services agencies, schools, and community-based organizations all provide services to both juveniles "at-risk" of committing crimes and to juveniles who have committed crimes. The State of Juvenile Crime in California.
How is juvenile justice different from adult justice?
Generally, the juvenile system emphasizes treatment and rehabilitation, while the adult system concentrates on punishment of offenders.
What percentage of juveniles were arrested for property crimes in 1993?
Juvenile arrests for property crime (burglary, theft, motor vehicle theft, forgery, and arson) accounted for about 57 percent of all juvenile felony arrests in 1993 and arrests for violent crime (homicide, rape, robbery, assault, and kidnapping) accounted for almost 24 percent of all juvenile arrests.
Why are juvenile arrest rates higher than adults?
There is evidence that a major reason that arrest rates for juveniles are higher than for adults is that young men tend to be arrested in large groups on suspicion of committing a crime or at the scene of a crime, although charges may never be filed. Juvenile arrest rates peaked in 1974.
What is a DJJ program?
DJJ Programs. DJJ provides academic and vocational education, medical care, and treatment programs that address violent, criminogenic, and sex offender behavior, as well as substance abuse and mental health needs while maintaining a safe and secure environment conducive to learning.
When will DJJ close?
DJJ will no longer accept new commitments after June 30, 2021, with some exceptions defined in SB 823. SB 92 sets a defined closure date of June 30, 2023 for all DJJ facilities. This builds on the Administration’s commitment to providing more treatment and rehabilitative services for youth closer to home.
What age can a juvenile court in California have jurisdiction?
The bill prevents California’s juvenile court system from assuming jurisdiction over minor children under the age of 12. Sexual penetration. The juvenile court still has jurisdiction in these cases, even when an offender is under 12, provided that the crimes were committed by the use of force, violence, menace, or threat of bodily injury. ...
How old is a minor in California?
The minor is between 12 and 17 years of age; and, The minor violates any law of California, or the United States, or a municipal ordinance. The bill states that the juvenile court system still has jurisdiction over a child under the age of 12 when the minor commits: Murder, Rape, Sodomy, Oral copulation, and.
What crimes does a juvenile court have jurisdiction over?
However, for the latter four crimes, a juvenile court only has jurisdiction over these cases when a child commits the crimes by use of force, violence, duress, menace, and threats of bodily injury.
What does SB 439 mean?
SB 439 does, though, inform that they could be provided by school-, health, and community-based services. Laws Prior to Senate Bill 439. SB 439 significantly changed California’s law on juvenile court system jurisdiction.
How old do you have to be to get into juvenile justice?
Currently, 20 states have a minimum age for entry into the juvenile justice system. The range goes from age 6 (in North Carolina) to age 12. Earlier this year, Massachusetts became the first state to set a minimum age at 12. California has now followed the lead.
Does Nevada have a juvenile court?
The juvenile court still has jurisdiction in ... Four Tips for Early Termination of Probation in Nevada. Senate Bill 439 was signed into law by Gov. Brown in September 2018. The bill prevents California’s juvenile court system from assuming jurisdiction over minor children under the age of 12. The bill does not apply to children ...
What age can a juvenile be tried as an adult in California?
Crimes listed under 707 (b) of the California Welfare and Institutions Code. 6. In certain circumstances, a juvenile age 16 or 17 can be tried as an adult for any criminal offense.
Why are there two juvenile courts in California?
Because the two courts deal with different offenders and focus on different outcomes, the two courts have different court processes. Below are 11 ways California’s juvenile courts distinguish themselves from the adult criminal court process…. 1. A minor in a juvenile case is not entitled to a jury trial.
How long does it take to get a juvenile in custody?
3. Minors taken into custody for a crime must be brought to court within 48 hours of their arrest to be advised of the charges against them. This first hearing in a juvenile court process is called the detention hearing.
What are the four hearings in juvenile court?
An attorney can help you through the California juvenile court process. The four hearings involved in the juvenile court process are: Detention Hearing: Determines whether the juvenile can be released to his or her parents or must stay in custody during the case. Fitness Hearing: Determines if the juvenile’s case will be heard in juvenile ...
Why is it important to retain a juvenile attorney?
Because there is no bail in the juvenile court process, it is extremely important to retain an experienced juvenile attorney as soon as possible to try to convince the judge to release your child at a detention hearing.
What can a judge do for a minor?
If a court judge makes a decision against a minor for a serious crime, the judge can sentence the minor to time in a probation camp, a foster or group home, the California Division of Juvenile Justice (prison for minors), or juvenile hall.
What happens if a juvenile is unfit for juvenile court?
If the court determines the juvenile will benefit from the programs in juvenile court, he or she will be tried as a minor. If the court determines the juvenile is unfit for the programs, he or she will be tried as an adult. 7.
More Information
For more general information on this subject and related topics, feel free to check out FindLaw’s family law section, as well as the links listed below. You may also find FindLaw’s How Long Do Parents' Legal Obligations to Their Children Continue? article to be helpful depending on your situation.
Get Professional Legal Help with Your California Legal Ages Concerns
California and all other states set age limits and age-related guidelines for marriage, alcohol consumption, curfew, emancipation, and other matters. If you have additional questions about the law or need legal counsel, you should get in touch with a family law attorney in your area.
When did the state of California end the prosecution of its youngest offenders?
The state also ended the prosecution of its youngest offenders in 2018, limiting the jurisdiction of juvenile courts to those ages 12-17 in all cases except murder and rape, and effectively ending the prosecution of children 11 and younger.
How many minors were arrested in California in 2018?
California arrested 17,200 minors under the age of 17 for felonies in 2018, and more than half were black and 36% Latino, according to statistics from the California Department of Justice. The same year, about 14,400 people aged 18 and 19 were arrested on felony charges. An analysis by CJCJ estimates that raising the age ...
When did the juvenile justice system change?
The Legislature further realigned the juvenile justice system in 2007, giving more control to county probation departments in what would later become a model for Gov. Jerry Brown’s reorganization of the adult system. Advertisement.
Who is the executive director of the Center on Juvenile and Criminal Justice?
Daniel Macallair, executive director of San Francisco-based Center on Juvenile and Criminal Justice, said he thinks the probation chiefs association might be largely backing the idea as a way to protect jobs.
Is California removing minors from the correctional system?
Since then, there has been a push from criminal justice advocates to remove minors from California’s adult correctional system.
Is California expanding the juvenile justice system?
California lawmakers will consider expanding the reach of the state’s juvenile justice system so that those under age 21 are automatically tried as minors — an idea backed by some state probation officers, who say teenagers aren’t mature enough to be held responsible in the same way as older offenders. Though few details are included in the ...
Access and Comprehension
Recent studies, including Trust and Confidence in the California Courts, Phase I and II and the Juvenile Delinquency Court Assessment, found that too often parties find it difficult to attend their court hearings. Moreover, when they do attend, they frequently have trouble understanding the court process and what is being said in court.
Dual Status Youth Resources
The resources in this section include publications and fact sheets produced by staff of the CFCC through various research projects, publications from partnering agencies, and links to other useful information relating to these projects.
Continuum of Care Reform (CCR) and Senate Bill 794
CCR comprehensively reforms placement and treatment options for foster children. Many new and important permanent plan options and requirements related to achieving permanence for foster youth were created by Assembly Bill 403 (Stone; Stats. 2015, ch. 773) and Senate Bill 794 (Comm. on Hum. Srvcs; Stats. 2015, ch. 425)
Title IV-E: Foster Care Placement
Below are resources for the juvenile courts, child welfare departments, and probation departments regarding compliance with Title IV-E of the Social Security Act and other provisions of state and federal law related to the foster care placement of dependents and wards.
Keeping Kids in School and Out of Court (KKIS)
This section features resources on truancy and school discipline issues, including research and key statistics, as well as principles and strategies for minimizing these problems and their effects. This information will benefit courts and justice partners working collaboratively to develop ways to address these issues in their communities.
When will juvenile court be open for prosecution?
Counties must have a protocol for addressing alternatives to prosecution for youth under 12 by January 1, 2020, even though juvenile court jurisdiction is no longer permissible starting January 1, 2019.
What is the change in law in California?
The change in law aligns California with the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child and the recommendations of the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Bar Association and the National Academy of Sciences, all recognizing the developmental vulnerabilities of young children in the context of the justice system.
What is the intent of the California law?
The intent of the law is to protect young children from the harms and adverse consequences of justice system involvement and encourage more effective interventions, if appropriate, to improve both children’s well-being and public safety. The change in law aligns California with the United Nations Convention on the Rights ...
What is SB 439?
Mitchell—to establish a minimum age of 12 years old for prosecuting youth in juvenile court in California, except in the most serious cases of murder and forcible rape.
