- Cells are the basic units of life and are very small in size, ranging from approximately 1 to 100 micrometers. ...
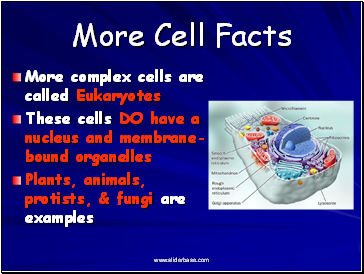
- There are two major types of cells: eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells have a membrane bound nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus that is membrane bound.
- A cell's nucleoid region or nucleus contains the cell's DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which contains the cell's encoded genetic information.
- Cells reproduce by different methods. Most prokaryotic cells reproduce by binary fission while eukaryotic cells can reproduce asexually or sexually.
- The facts about cells.
- Cells are too small to see without a microscope.
- There are two main types of cells.
- Prokaryotes were the earliest and most basic forms of life on Earth.
- There are more bacteria in the body than human cells.
- Cells contain DNA.
- Cells contain structures called organelles which have specific roles.
What are 3 things found in all cells?
What are the 5 things that all cells have in common?
- plasma membrane. controls in/out of cell.
- chromosomes. DNA, instructions for protein synthesis.
- ribosomes. manufacture proteins.
- metabolic enzymes. building and breaking down molecules.
- cytoskeleton. skeleton of cell that proteins can move by.
What are some interesting facts about cells?
There Are Four Main Classes
- Totipotent Stem Cells. These stem cells would eventually develop into the cells that make up an embryo and then a fetus. ...
- Multipotent Stem Cells. These are able to develop into many different types of cells, but only when part of the same tissue or organ.
- Pluripotent Stem Cells. Pluripotent cells include embryonic stem cells. ...
- Unipotent Stem Cells. ...
What are the three main types of cells?
Three principal types of cells may be distinguished—choanocytes, archaeocytes, and pinacocytes–collencytes.
What is the function of a cell?
Six Main Cell Functions
- Provide Structure and Support. Like a classroom is made of bricks, every organism is made of cells. ...
- Facilitate Growth Through Mitosis. In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. ...
- Allow Passive and Active Transport. ...
- Produce Energy. ...
- Create Metabolic Reactions. ...
- Aids in Reproduction. ...

What are 3 facts about cells?
Facts about CellsCell is Too Small to be Seen Without Magnification. ... There are Two Primary Types of Cells. ... Prokaryotic Single-Celled Organisms were the Earliest and Most Primitive Forms of Life on Earth. ... There are More Bacterial Cells in the Body than Human Cells. ... Cells Contain Genetic Material.More items...•
What are 5 facts about cells for kids?
Fun Facts About CellsThey were discovered by the scientist Robert Hooke.One of the largest known cells is the ostrich egg which can weigh over three pounds.When many cells of the same kind are together in a group, it's call tissue.The word cell comes from the Latin word cellula, which means small compartment.More items...
What are 3 things cells do?
They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Cells have many parts, each with a different function.
What are the 3 most important cells?
There are three major types of blood cell: red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body. white blood cells, which are part of the immune system. platelets, which help blood clot to prevent blood loss after injury.
What is unique about a cell?
Cells provide structure and function for all living things, from microorganisms to humans. Scientists consider them the smallest form of life. Cells house the biological machinery that makes the proteins, chemicals, and signals responsible for everything that happens inside our bodies.
What is true about cells?
Cells are the basic structures of all living organisms. Cells provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food and carry out important functions. Cells group together to form tissues?, which in turn group together to form organs?, such as the heart and brain.
What is found in all cells?
All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and 4) ribosomes, ...
What is a cell made of?
A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell. The nucleus is a structure inside the cell that contains the nucleolus and most of the cell's DNA. It is also where most RNA is made.
Who invented cell?
Robert HookeInitially discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, the cell has a rich and interesting history that has ultimately given way to many of today's scientific advancements.
How long does a cell live?
On average, the cells in your body are replaced every 7 to 10 years. But those numbers hide a huge variability in lifespan across the different organs of the body. Neutrophil cells (a type of white blood cell) might only last two days, while the cells in the middle of your eye lenses will last your entire life.
How big is a human cell?
The average size of a human skin cell is about 0.03 millimeters across. A single human sperm cell is about 0.05 millimeters in length.
How many cells are on the earth?
For those the total number is estimated to be somewhere in the range of 1030. For humans the latest published number is 3.72 × 1013, so even with a few billion in total (109×1013=1022) we probably don't even matter for the total cell count.
What is a cell for kids?
0:101:21The Cell | Educational Video for Kids - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut do you know what a cell is the cell is the smallest part of a living organism.MoreBut do you know what a cell is the cell is the smallest part of a living organism.
How long do cells live for?
On average, the cells in your body are replaced every 7 to 10 years. But those numbers hide a huge variability in lifespan across the different organs of the body. Neutrophil cells (a type of white blood cell) might only last two days, while the cells in the middle of your eye lenses will last your entire life.
What is the smallest cell?
Mycoplasma gallicepticumThe smallest cell is Mycoplasma gallicepticum. It is about 10 micrometer in size.
What are cells made of?
All cells are made from the same major classes of organic molecules: nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
How long do cells live?
Cells within the human body have different lifespans based on the type and function of the cell. Cells can live anywhere from a few days to a year. Certain cells of the digestive tract live for just a few days. Some cells of the immune system live about six weeks, and pancreatic cells can live as long as a year.
What are the two types of cells?
There Are Two Primary Types of Cells 1 Eukaryotic Cells - These have a true nucleus that is enclosed within a membrane. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are organisms that contain eukaryotic cells 2 Prokaryotic Cells - These have a nucleus not enclosed in a membrane. Bacteria contain prokaryotic cells.
What is the process of a cell destroying itself?
When a cell becomes damaged or undergoes some types of infection, it will self-destruct by a process called apoptosis. Apoptosis works to ensure proper development and to keep the body’s natural process of mitosis in check. A cell’s inability to undergo apoptosis can result in the development of cancer.
What was the first cell microscope?
Cells range in size from 1 to 100 micrometers. The first cell seen under a microscope was that of a cork, comprised of dead plant cells, by Robert Hooke in 1665. With today’s advanced microscopes, such as the scanning electron microscope, cell biologists are able to obtain detailed images of the smallest cell structures.
Where do bacteria live?
Scientists have estimated that roughly 95 percent of all cells in the body are bacteria. The vast majority of these microbes can be found in the digestive tract. Billions of bacteria also live on the skin.
How do prokaryotic cells replicate?
Most prokaryotic cells replicate by a process called binary fission. This is a type of cloning process in which two identical cells are derived from a single cell. Eukaryotic cells are also capable of reproducing asexually through a process called mitosis.
How many cells are there in the human body?
Scientists estimate that our bodies contain anywhere from 75 to 100 trillion cells. In addition, there are hundreds of different types of cells in the body. Cells do everything from providing structure and stability to providing energy and a means of reproduction for an organism.
How big are cells?
Cells range in size from 1 to 100 micrometers. The study of cells, also called Cell Biology would not have been possible without the invention of the microscope. With the advance microscopes of today, such as the Scanning Electron Microscope and Transmission Electron Microscope, cell biologists are able to obtain detailed images of the smallest of cell structures.
What are the two main types of cells?
Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic Cell s are the two main types of cells. Eukaryotic cells are called so because they have a true Nucleus that is enclosed within a membrane. Animals, Plants, fungi and protists are examples of organisms that contain eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archeans.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Human Cells actively (in great part by an integral—transmembrane—ion pump ) transport ions against their concentration gradient. This creates a “membrane potential” which in excitable cells allows for the potential of reversal (depolarization) and subsequent electrical signaling along cellular processes and amongst cells.
What is a living cell?
Biological/Living Cells are high variance building blocks to the boundless tissues that comprise structures like leaves—more comprehensively: botanical life in general. Of course, not to mention mammalian (e.g Human) tissues and organs, in aggregate, also. Unicellular organisms are also, as their title suggests specialized/functionally and environmentally adapted cells (i.e the Bacterium).
What are the responsibilities of organelles?
Organelles have a wide range of responsibilities within a cell that include everything from providing energy to producing hormones and enzymes.
How many cells are in a baby's uterus?
Ovum and sperm fertilize with each other and grow as one cell in a womans uterus. And after birth a newborn babies body contains 3 trillions of cells.
What is the basic function of a cell?
< p style=”text-align: justify;”> The cell is basic functional in human which means that it’s a self-contained and totally operational living entity. Humans are cellular organisms with various differing kinds of cells that work along to sustain life. Alternative non-cellular parts in body adds water, macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids), micronutrients (vitamins, minerals) and electrolytes. However a collection of cells that operate along to perform a similar activity is known as tissue. Masses of tissue work together to make an organ that performs specific functions in body. Despite this structural organization, all activity boils right down to the cell – a complex unit that creates life possible.
Which cell is the largest in the human body?
The largest cell in Human body is the feminine egg and hence smallest is male sperm cell.
What is a collection of cells that operate along to perform a similar activity?
However a collection of cells that operate along to perform a similar activity is known as tissue. Masses of tissue work together to make an organ that performs specific functions in body. Despite this structural organization, all activity boils right down to the cell – a complex unit that creates life possible.
How many hairs does the average human have?
The average head has about 100,000 hairs. Nerve impulses to and from the brain travel as quick as 170 miles per hour. An adult Human body contains about 100 trillion cells. There are nearly 46 miles of nerves in an adult’s body. Fingernails grow 4 times quicker than toenails.
How many miles of blood vessels are there in the human body?
There 60,000 miles of blood vessels in the Human body . Humans lose an Avg. of 40 to 100 strands of hair daily. Also women’s hair is almost half the diameter of men’s hair. The lifetime of a person’s hair is 3 to 7 years on the average.
How many cells does the human body have?
It’s estimated the average human body has about 40 trillion cells.
Who first observed cells?
In 1665, Robert Hooke first observed cells by looking at cork under an early compound microscope.
What are the two classifications of organisms?
Organisms can have one of two classifications, unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest unit of life?
Cells are the smallest biological unit of life found in all organisms.
Which branch of biology deals with the study of cells?
The branch of biology that deals with the study of cells is called cell biology .
Is an eukaryotic cell unicellular or multicellular?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus can be a unicellular or multicellular organism.
