
Why are alkenes more polar than alkanes?
Alkenes tend to be slightly more polar than alkanes, however, for two reasons: The more weakly held electrons in the pi bond are more polarizable (contributing to instantaneous dipole moments), and the vinylic bonds tend to be slightly polar (contributing to a permanent dipole moment).
Why are alkynes less stable than alkenes?
Why are alkynes less stable than alkenes? Its because electrons on multiple carbon-carbon bonds are more exposed and unstable. The relative bond strength of a multiple carbon-carbon bonds such us alkyne and alkanes is smaller than normal single bond of an alkene thus making it less stable and reactive.
What are the functions of alkanes?
What are the functions of alkanes? The first four alkanes are used for heating and cooking or electricity. For example,methane is used within natural gas. Propane and butane are found within liquid petroleum gas. Alkanes with five to eight carbons,pentane to octane,are volatile.
What are the similarities between an alkane and alkene?
Many of the physical properties of alkenes and alkanes are similar: they are colorless, Nonpolar and combustible. Alkenes exist naturally in all three states. The first three alkenes are gases and the next fourteen are liquids. Alkenes higher than these are all solids. The melting point of the solids also increases with increase in molecular mass.
What are alkanes alkenes and alkynes give one example of each?
→ Examples : Ethylene ( C2H2 ) or ethene; Pentene ( C5H10 ). Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons which have atleast one carbon- carbon triple bond. Their general formula is CnH2n−2 . You can see that these have 2 hydrogen atoms less than their corresponding alkane.
What are alkanes?
Alkanes are organic compounds that consist entirely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms and lack any other functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and can be subdivided into the following three groups: the linear straight-chain alkanes, branched alkanes, and cycloalkanes.
How alkanes alkenes and alkynes are named?
In the case of alkenes and alkynes, hydrocarbon chain with the double and triple bond is chosen as parent chain. The parent chain is named with the help of Greek alphabets such as hepta, octa etc. For alkanes suffix '-ane' is used, for alkenes, the suffix '-ene' is used and the suffix 'yne' is used for alkynes.
What is the difference between alkene and alkyne?
Alkenes have double bonds; alkynes have triple bonds. Both undergo addition reactions.
What defines an alkene?
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons (e.g, containing only carbon and hydrogen) unsaturated compounds with at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond. Another term used to describe alkenes is olefins. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond. Nomenclature of Alkenes.
What does alkene mean?
Definition of alkene : any of numerous unsaturated hydrocarbons having one double bond specifically : any of a series of open-chain hydrocarbons CnH2n (such as ethylene)
What are the 10 alkynes?
The first 10 alkynes are:Ethyne C2H2.Propyne C3H4.Butyne C4H6.Pentyne C5H8.Hexyne C6H10.Heptyne C7H12.Octyne C8H14.Nonyne C9H16.More items...•
What is difference between alkane and alkene?
Alkanes are known as saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes are known unsaturated hydrocarbons as it contains a C=C bond in its structure. The C=C is its functional group. Alkanes does not contain any pi bonds or double bonds in its structure.
What is definition alkyne?
Definition of alkyne : any of a series of open-chain hydrocarbons CnH2n−2(such as acetylene) having one triple bond.
What is an example of an alkyne?
Ethyne is used to make a variety of other compounds. The following are a few examples of these applications: Ethyne is most commonly used to make organic compounds such as ethanol, ethanoic acid, and acrylic acid....Alkynes Homologous Series.NameMolecular FormulaEthyneC2H2PropyneC3H41-ButyneC4H61-PentyneC5H85 more rows
What are the first 10 alkenes?
List of AlkenesPropene (C3H6)Butene (C4H8)Pentene (C5H10)Hexene (C6H12)Heptene (C7H14)Octene (C8H16)Nonene (C9H18)Decene (C10H20)More items...
What is the formula of alkane?
CnH2n+2Alkanes are organic compounds that consist of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. The formula for Alkanes is CnH2n+2, subdivided into three groups – chain alkanes, cycloalkanes, and the branched alkanes.
What is alkane with example?
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. By saturated hydrocarbons, it means alkanes have single hydrogen and carbon atoms in their chemical formula. Formula of alkane is CnH2n+2. Methane, propane, ethane, and butane are four alkanes.
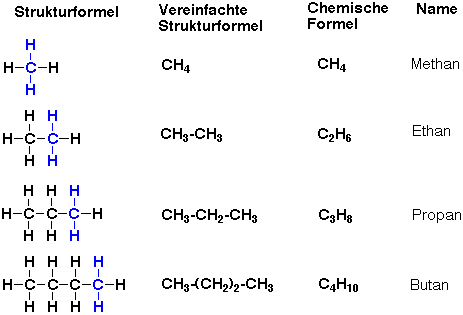
What are the 4 alkanes?
The first four alkanes are methane, ethane, propane, and butane with the Lewis symbols shown below.
What are the first 10 alkanes?
First 10 Alkanes – Properties Methane. Ethane. Propane. Butane. Pentane. Hexane. Heptane. Octane.More items...•
Where can we find alkanes?
The alkanes are isolated from natural gas and petroleum. Natural gas contains mainly methane, with smaller amounts of other low‐molecular‐weight alkanes. Petroleum, which is a complex mixture of many compounds, is the main source of all other alkanes.
Alkene nomenclature
In this tutorial, Jay names alkenes, discusses the stability of alkenes, and introduces the E/Z system.
Naming and preparing alkynes
In this tutorial, Jay covers the nomenclature and preparation of alkynes, the acidity of terminal alkynes, and the alkylation of alkynes.
Synthesis using alkynes
In this tutorial, Jay demonstrates how to use Dr. Schwartz's organic flowsheet to solve synthesis problems involving alkynes. Always remember, pain is temporary, orgo is forever!
Which is more reactive, alkynes or alkenes?
They are also known as acetylenes. Alkynes are more reactive than alkenes and alkanes; they show more polymerization and oligomerization. The polymers formed are called polyacetylenes and show semiconducting properties.
Why are alkanes not reactive?
Alkane compounds are not very reactive; this is because the carbon bonds are stable and do not break easily. They have no functional groups attached to the carbon atoms. Alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons which mean they are compounds with one or more double bonds or one or more triple bonds between carbon atoms.
What are the different types of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes, alkenes and alkynes are all hydrocarbons with different structures and thus different physical and chemical properties.
What is the difference between alkanes and saturated hydrocarbons?
Alkanes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which mean they are compounds with a single bond between the atoms. Saturated hydrocarbons are saturated with hydrogen and are the simplest. They are represented in general as CnH2n+2 in case of non-cyclic structures or straight-chain structures. They are also called paraffins.
Which hydrocarbon is the most stable?
3.Alkanes are the most stable hydrocarbons as the carbon bonds are difficult to break. They have remained unchanged for millions of years; alkenes are less stable than alkanes and more stable than alkynes; alkynes are more reactive than alkanes and alkenes. 4.Alkanes are also called paraffin; alkenes are also called olefin or olefin;
Is propane a gas or liquid?
They can be gases as, propane, they can be liquids, for example, benzene, or they can be low-melting solids and waxes, for example, polystyrene. There are four classifications of hydrocarbons; saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes, unsaturated hydrocarbons or alkenes and alkynes, cycloalkanes, and aromatic hydrocarbons or arenes.
What is the double bond between alkanes and alkenes?
The double bond that differentiates between alkanes and alkenes helps in the production of styrofoam. It contributes to create foamy but light texture to the styrofoam. The connection between the atoms are slightly lose and therefore it makes styrofoam a light but flammable material.
Why are alkynes important?
Alkynes is very important in the preparation of startingg material such as the highly used polymers. Some derivation of alkylenes work for starting materials in various compound. For instance, vinyl chloride that is alkynes derivation is starting material for PVC. Whereas another derivation of alkynes, clorophene, is a good starting material in the preparation of rubber neoprene.
What is the purpose of alkenes in fruit?
The use of alkenes that common people may not know is as artificial ripening. The double bond in alkenes help to make the ripening process of fruits faster. Artificial ripening is laboratory processed additive to help farmers not to lose the unripe fruits during harvesting by letting the rest of the fruits ripe using artificial ripening. This chemical may come in liquid and used by spraying it to the fruit. In three days there usually signs of ripening on the fruit.
What is the main compound of methane?
Alkanes is the main compound of methane or natural gas. Methane is also present in volcanic crust. Thus, this is why people able to cook fuelless in a crate of volcanic area due to methane as the source of the heat. Alkanes in methane is also widely used in industry especially in gas production.
How does acetylene work?
Acetylene works by bonding in the compound in welding process to physically merge two things without causing damage to the core compound of the material. Organic Solvent. Alkynes as pure compound is an organic solvent for organic chemicals. Some of the most useful compounds for industry are derivates of alkynes.
What industry uses alkynes?
One of industry that uses alkynes the most is in welding industry. The triple bonds in alkynes is really helpful to weld hard material such as steel and wire. Therefore, alkynes plays important role in welding industry especially in torches production.
Which compound has a triple bond?
The rule goes to alkynes that has at least triple bond in its hydrocarbon structure. Even though they come from the same hydrocarbon compound, the different bond leads to different use in industry. There are several uses of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes in industry.
What are Alkanes?
Alkanes are organic compounds that consist of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. The formula for Alkanes is CnH2n+2, subdivided into three groups – chain alkanes, cycloalkanes, and the branched alkanes.
What are the physical properties of alkanes?
Physical Properties of Alkanes. 1. The Solubility of Alkanes. Due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen and covalent nature of C-C bond or C-H bond, alkanes are generally non-polar molecules. As we generally observe, polar molecules are soluble in polar solvents whereas non-polar molecules are soluble in ...
How many covalent bonds are there in an alkane?
In a long chain alkane molecule, additional carbon atoms are attached to each other with the help of a single covalent bond. Each atom is attached to the sufficient hydrogen atoms to develop a total of four single covalent bonds. This long-chain structure is known as octane. An eight-carbon alkane has a molecular formula – C 8H 18 ...
Why do alkanes melt?
The Melting Point of Alkanes. The melting point of alkanes follow the same trend as their boiling point that is, it increases with increase in molecular weight. This is attributed to the fact that higher alkanes are solids and it’s difficult to overcome intermolecular forces of attraction between them.
What is the formula for organic compounds?
Molecular formulas, such as that of octane give the number of each kind of atom in a molecule of a compound. The molecular formula of C8H18 may apply to several alkanes, each one of which has unique chemical, physical and toxicological properties. These different compounds are designated by structural formulas showing the order in which the atoms in a molecule are arranged. Compounds that have the same molecular, but different structural formulas are called structural isomers.
Why do chemists use line angle formulas?
Chemists use line-angle formulas because they are easier and faster to draw than condensed structural formulas. Structural formulas for alkanes can be written in yet another condensed form.
How many carbon atoms are in a hydrocarbon?
For example in the diagram, the four hydrocarbon molecules contain 8 carbon atoms each. In one of the molecules, all the carbon atoms are in a straight chain and in two they are in branched chains, whereas in a fourth, 6 of the carbon atoms are in a ring.
