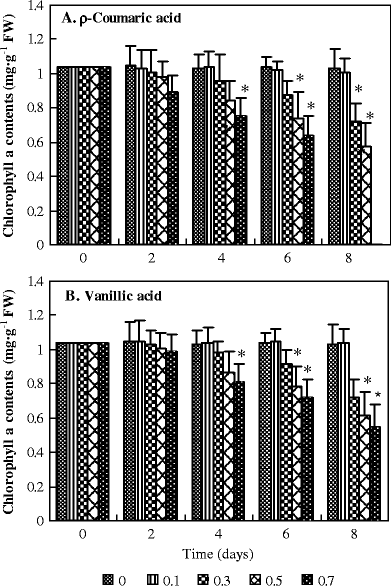
The allelochemicals produced by the plants are composed of various compounds such as alkaloids, cyanohydrins, lactones, organic acids, amino acids, fatty acids, flavonoids, tannins, and other compounds. Allelopathic compounds are synthesized in different plant tissues such as leaves, flowers, fruits, roots, rhizomes, stems, and pollen.
What are Allelopathic plants?
Some allelopathic plants, such as sunflower, walnut, and sorghum, are able to suppress the growth of a long list of other plants with their chemical powers. These three plants release allelopathic chemicals through their root systems and while their plant parts decay.
What chemicals have allelopathy properties?
Various types of chemicals, including phenolics, hydroxamic acids, and short-chain fatty acids, have been identified as having allelopathic properties. Allelopathy is thought to be involved with plant species succession, and occurs both in agricultural and natural landscapes.
What is allelopathy and how does it affect weed management?
Allelopathy holds potentials for selective biological weed management. The phenomenon of allelopathy refers to chemical interactions between all types of plants. In this process, the chemical exudates or leachates released from leaves, stems, or roots of a plant can inhibit the growth of a neighboring one.
Is Eucalyptus allelopathic?
The leaf litter and root exudates of some Eucalyptus species are allelopathic for certain soil microbes and plant species. The tree of heaven, Ailanthus altissima, produces allelochemicals in its roots that inhibit the growth of many plants. The possible application of allelopathy in agriculture is the subject of much research.
Why do plants have allelopathic compounds?
Allelopathic Trees Trees are great examples of allelopathy in plants. For instance, many trees use allelopathy to protect their space by using their roots to pull more water from the soil so other plants cannot thrive. Some use their allelochemicals to inhibit germination or impede the development of nearby plant life.
What are the consequences of allelopathic chemicals?
The toxic chemicals may inhibit shoot/root growth, they may inhibit nutrient uptake, or they may attack a naturally occurring symbiotic relationship thereby destroying the plant's usable source of a nutrient.
What are some examples of allelopathic plants?
Allelopathic Plants Some plants and trees those are well known as allelopathic are Black Walnut (Juglans nigra), Ailanthus or Tree-Of-Heaven (Ailanthus altissima), Fragrant Sumac (Rhus aromaticus), Rice (Oryza sativa), Pea (Pisum sativum), sorghum etc.
What is allelopathy in plants?
Allelopathy is defined as the effects (stimulatory and inhibitory) of a plant on the development of neighboring plants through the release of secondary compounds. Autoallelophaty is the beneficial or harmful effect of a plant species on itself.
What are the types of allelopathy?
Allelopathy refers to a negative or positive effect on one type of plant, by a chemical produced by another type of plant. Various types of chemicals, including phenolics, hydroxamic acids, and short-chain fatty acids, have been identified as having allelopathic properties.
What are the benefits of allelopathy?
Various studies have reported the advantages of allelopathic effects in agricultural systems, such as weed control, inhibition of pests, disease, improvement of soil nutrition, and microbial interactions. Ultimately, allelopathy of most plants has effect on plant growth.
Are tomatoes allelopathic?
The volatile substances from leaves inhibited seed germination and seedling growth of receptor plants in laboratory tests. Inhibitory response varied with the concentration of compounds. These findings suggest that the tomato plant may have an interesting allelopathic potential.
What does allelopathy mean?
Definition of allelopathy : the suppression of growth of one plant species by another due to the release of toxic substances.
What causes allelopathy?
Allelopathy occurs when one plant species releases chemical compounds, either directly or indirectly through microbial decomposition of residues, that affect another plant species.
What does an allelopathic plant do to other plants?
Allelopathy is a survival mechanism that allows certain plants to compete with and often destroy nearby plants by inhibiting seed sprouting, root development, or nutrient uptake. 1 Other organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can also be allelopathic.
What plant kills other plants?
The invasive strain of Phragmites australis, or common reed, believed to have originated in Eurasia, exudes from its roots an acid so toxic that the substance literally disintegrates the structural protein in the roots of neighboring plants, thus toppling the competition.
What is allelopathy and how it is useful in agriculture?
Allelopathy is a chemical mechanism that provides plants with an advantage for competing for limited resources (Singh et al., 1999; He et al., 2012b; Gioria and Osborne, 2014). The ability of plants to suppress weeds is thus determined by crop allelopathy and competitiveness.
What does an allelopathic plant do to other plants?
Allelopathy is a survival mechanism that allows certain plants to compete with and often destroy nearby plants by inhibiting seed sprouting, root development, or nutrient uptake. 1 Other organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can also be allelopathic.
What type of distribution is likely to arise as a result of allelopathy?
What type of distribution is likely to arise as a result of allelopathy? why? A clustered distribution because allelopathy affects its surrounding soil.
What does allelopathy mean?
Definition of allelopathy : the suppression of growth of one plant species by another due to the release of toxic substances.
Can plants be toxic to other plants?
Plants are able to release chemical compounds from their roots into the soil, where the substances decay or are modified by microbes. Some of these products are toxic when the roots of neighboring plants take them up.
What is allelopathy based on?
However, like many allelopathy studies, it was based on artificial lab experiments and unwarranted extrapolations to natural ecosystems. In 1970, Science published a study where caging the shrubs to exclude rodents and birds allowed grass to grow in the bare zones.
How can Allelopathy be used in agriculture?
The possible application of allelopathy in agriculture is the subject of much research . Current research is focused on the effects of weeds on crops, crops on weeds, and crops on crops. This research furthers the possibility of using allelochemicals as growth regulators and natural herbicides, to promote sustainable agriculture. A number of such allelochemicals are commercially available or in the process of large-scale manufacture. For example, leptospermone is an allelochemical in lemon bottlebrush ( Callistemon citrinus ). Although it was found to be too weak as a commercial herbicide, a chemical analog of it, mesotrione (tradename Callisto), was found to be effective. It is sold to control broadleaf weeds in corn but also seems to be an effective control for crabgrass in lawns. Sheeja (1993) reported the allelopathic interaction of the weeds Chromolaena odorata ( Eupatorium odoratum) and Lantana camara on selected major crops.
How does allelopathy affect the environment?
While the former is caused by the addition of a harmful chemical agent to the environment, the latter is caused by the removal of essential nutrients (or water). Often, both mechanisms can act simultaneously. Moreover, some allelochemicals may function by reducing nutrient availability. Further confounding the issue, the production of allelochemicals can itself be affected by environmental factors such as nutrient availability, temperature and pH. Today, most ecologists recognize the existence of allelopathy, however many particular cases remain controversial.
What is the name of the biological phenomenon that produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth?
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon by which an organism produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms. These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have beneficial (positive allelopathy) or detrimental (negative allelopathy) effects on ...
What is an allelochemical?
Allelochemicals are a subset of secondary metabolites, which are not required for metabolism (i.e. growth, development and reproduction) of the allelopathic organism. Allelochemicals with negative allelopathic effects are an important part of plant defense against herbivory. The production of allelochemicals is affected by biotic factors such as ...
What is an allopathic interaction?
Allelopathic interactions are an important factor in determining species distribution and abundance within plant communities, and are also thought to be important in the success of many invasive plants.
What is the role of alloliopathy in forest?
Allelopathy has been shown to play a crucial role in forests, influencing the composition of the vegetation growth, and also provides an explanation for the patterns of forest regeneration. The black walnut (Juglans nigra) produces the allelochemical juglone, which affects some species greatly while others not at all.
What Makes a Plant Allelopathic?
Related to plants, it means that a plant can cause an adverse reaction in other plants, bacteria, fungi, and various kinds of soil life.
What are some examples of allopathic properties?
Brassicas. All brassicas, such as cabbage, mustard, kale, rapeseed, radish, and more have some allelopathic properties. Mustard, for example, has the power to suppress many fungal pathogens in the soil if tilled into the soil. Some kinds of radish have a particular knack for suppressing johnsongrass.
What is an allele plant?
Allelopathic plants are a bit like kryptonite to their victims by making them weak so that they can’t fulfill their natural function. The impacts can be broad-ranging such as being directed at all broadleaf plants. Or, they can be limited only to certain plants or specific soil life forms.
Why do plants exude alleles?
Often, the plant roots exude allelopathic chemicals as a way to protect themselves as they grow. Also, decaying plant matter my leach those chemicals into the ground. Generally, once the plant matter is fully decayed, the allelopathic properties tend to time out.
What is the chemical in marigolds?
The roots of some types of marigolds, namely French-type marigold (Tagetes patula), release a chemical (alpha-terthienyl) in the soil that prevents root-knot nematode eggs from hatching. A lot of gardeners will plant marigolds intermittently throughout their gardens as a general preventative to help control root-knot populations.
Which plants release allopathic chemicals?
Sunflower, Walnut, and Sorghum. Some allelopathic plants, such as sunflower, walnut, and sorghum, are able to suppress the growth of a long list of other plants with their chemical powers. These three plants release allelopathic chemicals through their root systems and while their plant parts decay.
Does straw release chemicals?
Also, the dried plant matter (a.k.a. straw) may release some general allelopathic chemicals early on in decomposition. I use wheat in between my garden rows to control summer weeds and find it more effective than most other mulches in hot weather.
What is Allelopathy?
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon where one plant inhibits the growth of another. How? Through the release of allelochemicals, certain plants can greatly affect the growth of other plants either in a good or bad way by leaching, decomposition, etc. In essence, plant allelopathy is used as a means of survival in nature, reducing competition from plants nearby.
What are the properties of plants that are allelopathic?
Plant Allelopathy. Various parts of plants can have these allelopathic properties, from the foliage and flowers to the roots, bark, soil, and mulch. Most all allelopathic plants store their protective chemicals within their leaves, especially during fall. As leaves drop to the ground and decompose, these toxins can affect nearby plants.
What are some examples of allelopathy?
Allelopathic Trees. Trees are great examples of allelopathy in plants. For instance, many trees use allelopathy to protect their space by using their roots to pull more water from the soil so other plants cannot thrive. Some use their allelochemicals to inhibit germination or impede the development of nearby plant life.
Which trees have alleles?
Other trees that are known to exhibit allelopathic tendencies include maple, pine, and eucalyptus.
Is Allelopathy a Mother Nature's disease?
Printer Friendly Version. Image by nickkurzenko. Plant allelopathy is all around us, yet, many people have never even heard of this interesting phenomenon. Allelopathy can have an adverse effect in the garden, resulting in reduced seed germination and plant growth. On the other hand, allelopathic plants may also be considered Mother Nature’s own ...
How does Allelopathy occur?
Allelopathy occurs when one plant species releases chemical compounds, either directly or indirectly through the microbial decomposition of residues, that affect another plant species. It can have your hard work undone for you in as little as one season. As people become more and more concerned (rightly so) about the use of chemicals like glycerophosphate, the research into and use of allelopathy is becoming more popular. If you haven’t heard this phenomenon don’t feel like you are missing something – you have probably been using it in some form in your garden already without knowing the scientific term for it.
What is Allelopathy in gardening?
What is Allelopathy? In every garden there are those plants that just don’t seem to do well in close proximity to others. No matter what you do – give extra water, fertiliser, compost – they just don’t thrive and some just down right die back despite your greatest efforts.
What is the term for the harmful effects of one plant on another plant?
Allelopathy refers to the usually harmful effects of one plant on another plant. Pronounced AL- LEL-O-PATHY this effect can result from both crop and weed species, from the release of biochemicals, known as allelochemicals, from plant parts by leaching, root exudation, volatilization, residue decomposition, and other processes in both natural and agricultural systems. Allelopathy is characteristic of certain plants, algae, bacteria, coral, and even fungi. But how do we avoid it or even better, can we use it to our advantage?
What was the name of the plant that was used to treat alfalfa?
Theophrastus, who lived around 300 BC noticed the inhibitory effects of pigweed, a type of Amaranth, on alfalfa better known as Lucerne.
Which plants release allopathic chemicals?
Sunflower, Walnut, and Sorghum. Some allelopathic plants, such as sunflower, walnut, and sorghum, are able to suppress the growth of a long list of other plants with their chemical powers. These three plants release allelopathic chemicals through their root systems and while their plant parts decay.
Is Allelopathy becoming more popular?
As people become more and more concerned (rightly so) about the use of chemicals like glycerophosphate, the research into and use of allelopathy is becoming more popular.
How does Allelopathy affect plants?
Allelopathy effects of weeds is a biological phenomenon by which a plant produces one or more biochemical compounds that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other plants. Allelopathy is made up of two Greek words one is ‘allele’ and other ‘pithy’. Allelo means mutual or one another. Pathy means suffering. In nature many plant secrets secondary metabolites or phytotoxins that may constrain the growth of diverse other plants. This phenomenon of nature is called allelopathy and the effect may be directly by a living plant or indirectly through the process of plant decomposition. If the metabolite or phytotoxin produces inhibitory effect they are known as allelochemicals. Allelopathy may have beneficial (positive allelopathy) or detrimental (negative allelopathy) effects on the target organisms and the community
What are some examples of allelochemicals?
Allelochemicals of crops and plants may also have selective activity. For example, Leucaena leucocephala, the miracle tree helps for water and soil conservation, revegetation, and livestock nutrition; The toxic amino acid (non-protein) present in this tree leaves inhibit the growth of other trees but not its seedlings. Leucaena species have also been shown to reduce the yield of wheat but increase the yield of rice. The allelopathic effects of fresh shoot aqueous extract of Tithonia diversifolia showed that the radicle and plumule lengths of the maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings were significantly inhibited. The same extract stimulated the growth of older plants of two weeks old and above.
Why is Allelochemicals important?
Using allelochemicals to stimulate the suicidal germination of weed seeds reduces the number.
What are the allelochemicals that suppress weeds?
Various studies have elucidated specific allelochemicals involved in weed suppression, including diterpenoid momilactones in rice; benzoxanoids in the rye; alkaloids and flavonoids in fescue; tabanone in cogongrass; naphthotectone and anthratectone in teak (Tectona grandis); abscisic acid beta-d-glucopyranosyl ester in red pine; cyanamide in hairy vetch; and fatty acid (cyclopropene) in hazel sterculia ( Sterculia foetida ).
What is an allopathic interaction?
Allelopathic interactions are an important factor in determining species distribution and abundance within plant communities and are also thought to be important in the success of many invasive plants.
Can allelochemicals affect crops?
Allelochemicals can be present in soil and can affect crop plants beside it and those to be planted in succession. Furthermore, the effect can vary over a growing season. Although allelochemicals may be more biodegradable than traditional herbicides, they may have undesirable effects on non-target species, necessitating ecological studies before widespread use.

Overview
History
The term allelopathy from the Greek-derived compounds allilon- (αλλήλων) and -pathy (πάθη) (meaning "mutual harm" or "suffering"), was first used in 1937 by the Austrian professor Hans Molisch in the book Der Einfluss einer Pflanze auf die andere - Allelopathie (The Effect of Plants on Each Other - Allelopathy) published in German. He used the term to describe biochemical interactions by means of which a plant inhibits the growth of neighbouring plants. In 1971, Whitt…
Examples
Many invasive plant species interfere with native plants through allelopathy. A famous case of purported allelopathy is in desert shrubs. One of the most widely known early examples was Salvia leucophylla, because it was on the cover of the journal Science in 1964. Bare zones around the shrubs were hypothesized to be caused by volatile terpenes emitted by the shrubs. However, like many allelopa…
See also
• Forest pathology
• Allomone
• Phytochemical
• Semiochemical
Further reading
• anon. (Inderjit). 2002. Multifaceted approach to study allelochemicals in an ecosystem. In: Allelopathy, from Molecules to Ecosystems, M.J. Reigosa and N. Pedrol, Eds. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire.
• Bhowmick N, Mani A, Hayat A (2016), "Allelopathic effect of litchi leaf extract on seed germination of Pea and lafa", Journal of Agricultural Engineering and Food Technology, 3 (3): 233-235.
External links
• Allelopathy Journal
• International Allelopathy Society