What are alpha drugs?
These drugs help lower blood pressure but also may be used to ease symptoms of an enlarged prostate. Alpha blockers are a type of blood pressure medication. They lower blood pressure by preventing a hormone called norepinephrine from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins.
What drugs are alpha 1 agonists?
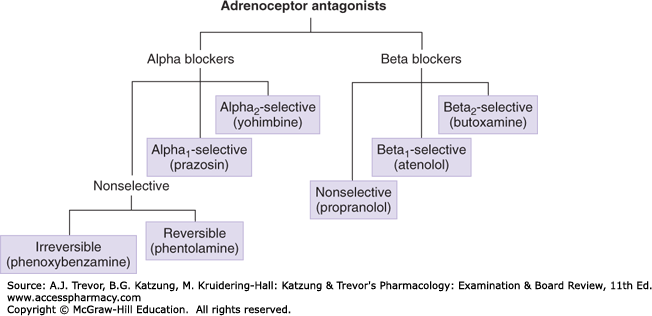
Alpha-1 agonists: metaraminol, methoxamine, ozymetazoline, phenylephrine. Alpha-1 antagonist: doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin, terazosin. Alpha-2 agonists: brimonidine, clonidine, dexmedetomidine, guanabenz, guanfacine.
Which medication is an alpha one blocker?
Alpha blockers are a class of adrenergic blockers that work by antagonizing alpha adrenoceptors in the body. Examples include Cardura, Cardura XL (doxazosin), Minipress (prazosin), terazosin, Flomax (tamsulosin), Uroxatral (alfuzosin ER) , Rapaflo (silodosin), and Dibenzyline (phenoxybenzamine).
What is the difference between Alpha 1 and Alpha 2 blockers?
The blocking of alpha 1 receptors causes the widening of the blood vessels by inhibiting the action of catecholamines that cause vasoconstriction. The blocking of alpha 2 receptors increases the release of norepinephrine. This reduces the force of the vasodilation caused by the blocking of alpha 1 receptors.
What does Alpha 1 do to the heart?
Decades of evidence from gain and loss-of-function studies in isolated cardiac myocytes and numerous animal models demonstrate important adaptive functions for cardiac alpha-1-ARs to include physiological hypertrophy, positive inotropy, ischemic preconditioning, and protection from cell death.
Does Alpha 1 increase heart rate?
alpha 1-adrenoceptor activation can increase heart rate directly or decrease it indirectly through parasympathetic activation.
Who should not take alpha-blockers?
Kidney disease, circulatory diseases or respiratory infections. Non-selective alpha-blockers may not be an option if you have one or more of these conditions.
Do alpha-blockers help with anxiety?
Alpha-Blockers May Help Relieve Insomnia, Anxiety in MG Patients.
How can I lower my blood pressure fast and naturally?
AdvertisementLose extra pounds and watch your waistline. Blood pressure often increases as weight increases. ... Exercise regularly. ... Eat a healthy diet. ... Reduce salt (sodium) in your diet. ... Limit alcohol. ... Quit smoking. ... Get a good night's sleep. ... Reduce stress.More items...
Which antipsychotic medication is the most potent alpha 1 blocker?
Tamsulosin is most potent alpha 1 blocker and has the most selectivity for alpha 1a receptors. It has no beta-blocking activity.
What is the safest alpha-blocker for BPH?
BPH is a frequent issue, especially in ageing men, many of whom cannot tolerate typical alpha blockers. Silodosin provides an additional alpha-1A receptor antagonists, especially targeting symptoms of nocturia, frequency and incomplete voiding.
What is the best alpha-blocker for BPH?
Alpha blockers are the most effective, least costly, and best tolerated of the drugs for relieving LUTS. Four long-acting alpha 1 blockers are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of symptomatic LUTS/BPH: terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin.
Is epinephrine an alpha 1 agonist?
So reflect for a moment: If norepinephrine or epinephrine is the neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system and it interacts with all the receptors we just described, then we know that norepinephrine or epinephrine stimulates the alpha, beta-1 and beta-2 receptors and thus it is an alpha agonist, a beta-1 ...
Is pseudoephedrine an alpha 1 agonist?
Pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine are Alpha-1 agonists. Mechanism of Action: Alpha-1 agonists stimulate alpha receptors in the respiratory tract, causing constriction of blood vessels and shrinkage of swollen nasal mucous membranes, thus increasing airway patency and reducing nasal congestion.
Is clonidine an alpha agonist?
Clonidine is in a class of medications called centrally acting alpha-agonist hypotensive agents. Clonidine treats high blood pressure by decreasing your heart rate and relaxing the blood vessels so that blood can flow more easily through the body.
What drugs are alpha-2 antagonists?
Antidepressants, Alpha-2 Antagonistsmirtazapine.Remeron.Remeron SolTab.