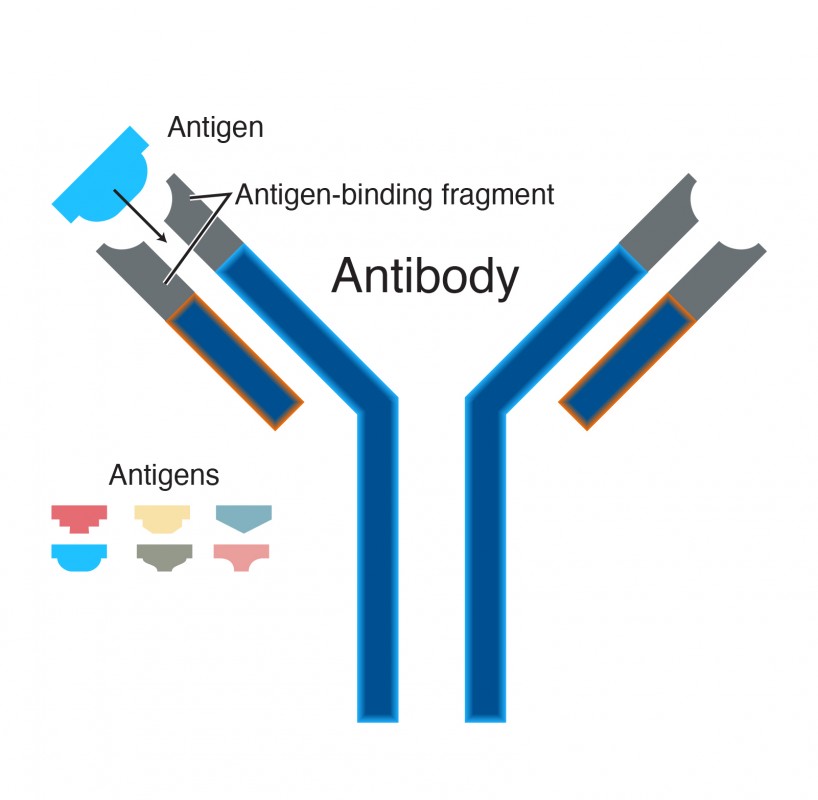
An antigen is a molecule that stimulates an immune response by activating lymphocytes, which are white blood cells that fight disease. Antigens may be present on invaders such as cancer cells, bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi, and transplanted organs and tissues.
How do lymphocytes identify antigens?
Through receptor molecules on their surfaces, lymphocytes are able to bind antigens (foreign substances or microorganisms that the host recognizes as “nonself”) and help remove them from the body. Each lymphocyte bears receptors that bind to a specific antigen.
How is an antigen recognized?
Antigen recognition by B cells involves direct binding of immunoglobulin to the intact antigen and, as discussed in Section 3-8, antibodies typically bind to the surface of protein antigens, contacting amino acids that are discontinuous in the primary structure but are brought together in the folded protein.
How do lymphocytes Recognise cells?
They recognise specific antigens on invading pathogens . Antigens are molecules, often proteins, located on the surface of cells that trigger a specific immune response. Lymphocytes detect that the proteins and pathogens are foreign - not naturally occurring within the body - and produce antibodies .
Are antigens recognized by lymphocyte receptors?
Both T and B lymphocytes have the property of antigen recognition through molecules expressed on their cell surfaces (antigen receptors). This is immunoglobulin (Ig) on B cells and the T cell receptor (TCR) on T cells. On any one cell, all the antigen receptors will be identical.
What cells recognize antigens?
The receptors on these T cells recognize a linear, two-dimensional peptide sequence (between 8 to 12 amino acids in length) from the antigen bound to the MHC molecules expressed on the surface of the antigen-presenting cells.
What is an antigen How does the immune system recognize antigens?
Antigens are substances (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, or bacteria. Nonliving substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles (such as a splinter) can also be antigens. The immune system recognizes and destroys, or tries to destroy, substances that contain antigens.
How do lymphocytes recognize pathogens?
Lymphocytes are another type of white blood cell. They recognise proteins on the surface of pathogens called antigens . Lymphocytes detect that these are foreign, ie not naturally occurring within the body, and produce antibodies . This can take a few days, during which time you may feel ill.
What do antigens do?
Any substance that causes the body to make an immune response against that substance. Antigens include toxins, chemicals, bacteria, viruses, or other substances that come from outside the body. Body tissues and cells, including cancer cells, also have antigens on them that can cause an immune response.
What are antigens in the blood?
Antibodies and antigens They're part of your body's natural defences. They recognise foreign substances, such as germs, and alert your immune system, which destroys them. Antigens are protein molecules found on the surface of red blood cells.
Can each lymphocyte Recognise more than one antigen?
A lymphocyte is different from all other cells in the body because it has about 100,000 identical receptors on its cellular membrane that enable it to recognize one specific antigen.
How do T and B lymphocytes recognize different antigens quizlet?
*How do T and B lymphocytes recognize different antigens? Each lymphocyte has antigen receptors in its plasma membrane, which can bind to only one specific antigen.
Where do lymphocytes acquire antigen specific receptors?
Lymphocyte antigen receptors, in the form of immunoglobulins on B cells and T-cell receptors on T cells, are the means by which lymphocytes sense the presence of antigens in their environment.
How do you know if an antigen is positive?
A positive antigen test result in an asymptomatic, unexposed individual should be immediately followed by a PCR test to verify the positive result. This follow-up specimen should be collected within 24 hours of the original test, if possible, and no more than 48 hours after the antigen test.
How does a rapid antigen test work?
The SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test is a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of specific antigens of SARS-CoV-2 present in the human nasopharynx. This test is intended to detect specific antigens from the SARS-CoV-2 virus in individuals suspected of COVID-19.
Why can the body recognize so many different antigens?
The variability of antibody molecules allows each antibody to bind a different specific antigen, and the total repertoire of antibodies made by a single individual is large enough to ensure that virtually any structure can be recognized.
How accurate is a COVID-19 antigen test?
Overall performance of at-home COVID-19 antigen tests However, at-home COVID-19 antigen tests are generally expected to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus at least 80% of the time when someone is infected. When you perform an at-home COVID-19 antigen test, and you get a positive result, the results are typically accurate.
The Immune System
How It Works
- The body needs to be able to recognize what belongs and what doesn’t, and antigens are an important part of that process.When the body identifies an antigen, it will initiate an immune response. When receptors on white blood cells bind to antigens, this triggers white blood cell multiplication and starts the immune response.
The Role of Antigens
- Antigens are immune response initiators. They can be bound by white blood cells, including leukocytes, which are the cells of the adaptive immune system. Leukocytes include B cells and T cells. B cells make antibodies that can also bind to antigens. After an antigen gets bound to a B cell receptor, antibodies are produced.
The Role of Antibodies
- Antibodies are created by cells within the immune system. They bind to antigens and promote the elimination of threatening pathogens from the body. They neutralize the threat by alerting other parts of the immune system to take over.
Significance
- Antigens are an important part of the immune response because they help your body recognize harmful threats to get rid of them.
Testing Relevance
- Tests for antigens and antibodies can be done with blood samples. These tests can help diagnose illnesses, prevent immune reactions, or check to see whether you have responded to a vaccine.
A Word from Verywell
- Antigens can often be confused with antibodies, but the two hold very distinct positions when it comes to warding off pathogens that could lead to detrimental infection within the body. The antigen acts as an antibody generator and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent) by the body's immune system. Antigens may not be the main attraction when it comes to immunity, …