
What is a base pH example?
Orange juice is mildly acidic (pH = approximately 3.5), whereas baking soda is basic (pH = 9.0). Acids are substances that provide hydrogen ions (H+) and lower pH, whereas bases provide hydroxide ions (OH–) and raise pH.
What is pH of acids and bases?
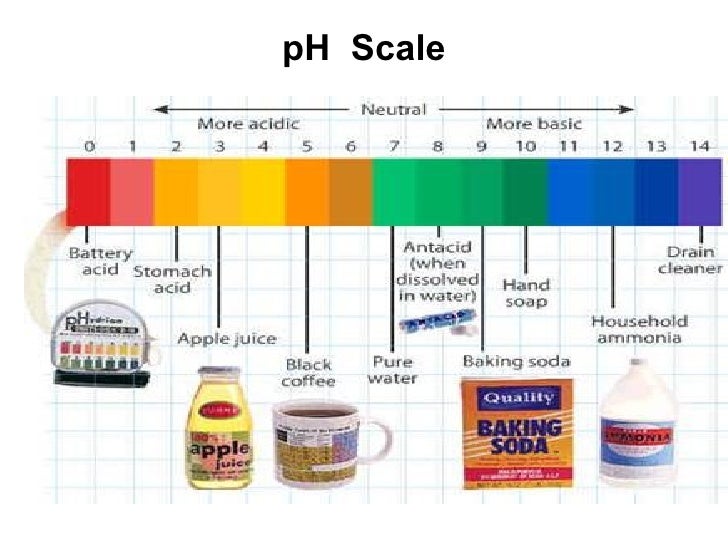
The pH scale Anything below 7.0 is acidic, and anything above 7.0 is alkaline, or basic. pH scale, ranging from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic/alkaline) and listing the pH values of common substances.
Is water a base?
Pure water is neither acidic or basic; it is neutral.
Is milk an acid or base?
Milk — pasteurized, canned, or dry — is an acid-forming food. Its pH level is below neutral at about 6.7 to 6.9. This is because it contains lactic acid.
What is the pH means?
A measure of how acidic or basic a substance or solution is. pH is measured on a scale of 0 to 14. On this scale, a pH value of 7 is neutral, which means it is neither acidic nor basic. A pH value of less than 7 means it is more acidic, and a pH value of more than 7 means it is more basic.
What is pH full explanation?
The full form of pH is “Potential of Hydrogen”. pH is known as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration. Hence the meaning of the name pH is explained as the strength of hydrogen or power of hydrogen.
What is pH stand for?
pH, explained The abbreviation pH stands for potential hydrogen, and it tells us how much hydrogen is in liquids—and how active the hydrogen ion is.
What is pH value of acid?
The standard value of an acid on a pH scale is between 0 - 7 while the substances that are basic have the value ranging between 7 - 14. For strong acids like hydrochloric acid (Hcl), the value of pH is around 0 to 1.
What is pH scale in chemistry?
The pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions, the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The pH-scale is normally between 0 and 14. Aque...
What is the best pH for the human body?
For our blood and body tissues the optimum pH is about 7.2. (The use of saliva and urine test strips will show a much lower pH level due to the pro...
What is pH full form?
PH stands for Hydrogen potentials. It refers to the concentration of the hydrogen ions in a solution. This is the indicator of a solution’s acidity...
Is pH of water important?
PH is a function of the acid / basic water content. Water with more free hydrogen ions is acidic and water with more free hydroxyl ions is basic. B...
What happens if your pH is too high?
An increase in alkaline causes a rise in pH levels. When the acid levels are too high in the blood, it’s called acidosis. This is called alkalosis...
What causes high pH in water?
The cause of the unbalanced pH is the soil, bedrock, or other underlying composition from which the water source comes. High alkaline water is a co...
What is the pH of blood?
Humans have a typical pH range from 7.35 to 7.45. That means blood is of course very alkaline or normal. Your stomach acid, by contrast, has a pH o...
Who discovered the pH?
Exactly 100 years ago, Carlsberg ‘s director of chemistry, Søren Sørensen, developed a vital diagnostic tool for measuring acidity, thus helping to...
How to measure pH?
To measure pH, a piece of pH test paper or an indicator stick is dipped into the liquid. The color of the dipped paper/stick is then matched to a color key that comes with the container of pH test paper or indicator sticks. Each color on the key represents a different pH.
What is pH?
Acidity and alkalinity are measured with a logarithmic scale called pH. Here is why: a strongly acidic solution can have one hundred million million, or one hundred trillion (100,000,000,000,000) times more hydrogen ions than a strongly basic solution! The flip side, of course, is that a strongly basic solution can have 100,000,000,000,000 times more hydroxide ions than a strongly acidic solution. Moreover, the hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion concentrations in everyday solutions can vary over that entire range.
What is an acid or a base?
Whether a liquid is an acid or a base has to do with hydrogen ions (abbreviated with the chemical symbol H + ). In water (H 2 O), a small number of the molecules dissociate (split up). Some of the water molecules lose a hydrogen and become hydroxide ions (OH − ). The "lost" hydrogen ions join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions (H 3 O + ). For simplicity, hydronium ions are referred to as hydrogen ions H +. In pure water, there are an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. The solution is neither acidic or basic.
What is the name of the ions that join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions?
The "lost" hydrogen ions join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions (H 3 O + ). For simplicity, hydronium ions are referred to as hydrogen ions H +. In pure water, there are an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. The solution is neither acidic or basic. An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions.
What scale do you use to measure hydrogen ion concentration?
In order to deal with these large numbers more easily, scientists use a logarithmic scale, the pH scale. Each one-unit change in the pH scale corresponds to a ten-fold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
How to measure pH in a solution?
pH test paper and indicator sticks are pieces of paper or stiffer sticks that contain pH indicators (chemicals that change color depending on how acidic or basic a solution is). To measure pH, a piece of pH test paper or an indicator stick is dipped into the liquid. The color of the dipped paper/stick is then matched to a color key that comes with the container of pH test paper or indicator sticks. Each color on the key represents a different pH. An example of a used pH indicator stick and the corresponding color key is shown below in Figure 1. pH meters are electronic devices that used to measure pH. They consist of a probe that is dipped in a solution, and a digital readout. pH meters are even more precise than pH test paper or indicator sticks. Table 2 below discusses what types of pH measuring devices are best for different science project applications, and offers a quick link to purchasing different pH test papers and indicator sticks.
What is the pH of pure water?
What the equation means is just what we said before: for each 1-unit change in pH, the hydrogen ion concentration changes ten-fold. Pure water has a neutral pH of 7. pH values lower than 7 are acidic, and pH values higher than 7 are alkaline (basic).
What is the pH scale used for?
The pH scale is used to rank solutions in terms of acidity or basicity (alkalinity). Since the scale is based on pH values, it is logarithmic, meaning that a change of 1 pH unit corresponds to a ten-fold change in H ion concentration. The pH scale is often said to range from 0 to 14, and most solutions do fall within this range, although it’s possible to get a pH below 0 or above 14. Anything below 7.0 is acidic, and anything above 7.0 is alkaline, or basic.
What is the pH of blood?
The pH inside human cells (6.8) and the pH of blood (7.4) are both very close to neutral. Extreme pH values, either above or below 7.0, are usually considered unfavorable for life. However, the environment inside your stomach is highly acidic, with a pH of 1 to 2. How does the stomach get around this problem? The answer: disposable cells! Stomach cells, particularly those that come in direct contact with stomach acid and food, are constantly dying and being replaced by new ones. In fact, the lining of the human stomach is completely replaced about every seven to ten days.
What happens if you add too many H ions to the equation?
If too many H ions build up, the equation above will be pushed to the right, and bicarbonate ions will absorb the H to form carbonic acid. Similarly, if H concentrations drop too low, the equation will be pulled the left and carbonic acid will turn into bicarbonate, donating H ions to the solution. Without this buffer system, the body’s pH would fluctuate enough to put survival in jeopardy.
What buffers maintain pH?
For instance, one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid (H CO) and its conjugate base, the bicarbonate ion (HCO ). Carbonic acid is formed when carbon dioxide enters the bloodstream and combines with water, and it is the main form in which carbon dioxide travels in the blood between the muscles (where it’s generated) and the lungs (where it’s converted back into water and CO, which is released as a waste product).
What does the letter "l" mean in parentheses?
The letters in parentheses just mean that the water is liquid (l), and that the ions are in aqueous (water-based) solution (aq).
How much pH do humans need to survive?
For instance, human blood needs to keep its pH right around 7.4, and avoid shifting significantly higher or lower – even if acidic or basic substances enter or leave the bloodstream.
What does the square brackets around H mean?
The square brackets around the H just mean that we are referring to its concentration. If you plug the hydrogen ion concentration of water (1 × 10 M) into this equation, you’ll get a value of 7.0, also known as neutral pH. In the human body, both blood and the cytosol (watery goo) inside of cells have pH values close to neutral.
How is the pH scale calculated?
The pH scale can be traced to a series of standard solutions whose pH is defined by international agreement. By calculating the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode, primary pH standard values are calculated using a concentration cell with transference.
How is pH determined?
The pH level, or possible level of hydrogen, in your body is determined by the food and type of drink you consume . The pH is the concentration of the hydrogen ions. This calculation is based on a 0 to 14 scale.
What is pH?
pH is defined as the negative logarithm of H + ion concentration. Hence the meaning of the name pH is justified as the power of hydrogen.
Why does a Water Source Change pH?
The pH of a source of water can naturally vary. Some types of rock and soil , such as limestone, can more effectively neutralize acid than other rock and soil types, such as granite.
What does pH mean in math?
It states that the pH equals the negative logarithmic value of the concentration of hydrogen ion (H+)
What does pH mean in chemistry?
pH may be seen as an abbreviation of the power of hydrogen-or, more fully, the concentration of hydrogen ion in a liquid.
What is the pH of groundwater?
Surface water usually has a pH value of 6.5 to 8.5 and groundwater appears to have a pH of 6.0 to 8.5. The pH of a source of water can naturally vary. Some types of rock and soil, such as limestone, can more effectively neutralize acid than other rock and soil types, such as granite.
Why is the pH scale positive?
Because the negative log of [ H +] is used in the pH scale, the pH scale usually has positive values. Furthermore, the larger the pH, the smaller the [ H +].
When was the pH scale invented?
The pH scale was originally introduced by the Danish biochemist S.P.L. Sørenson in 1909 using the symbol p H. The letter p is derived from the German word potenz meaning power or exponent of, in this case, 10. In 1909, S.P.L. Sørenson published a paper in Biochem Z in which he discussed the effect of H + ions on the activity of enzymes. In the paper, he invented the term pH ( purported to mean pondus hydrogenii in Latin) to describe this effect and defined it as the − log[H +]. In 1924, Sørenson realized that the pH of a solution is a function of the "activity" of the H + ion and not the concentration. Thus, he published a second paper on the subject. A better definition would be
What does it mean when a pH is 7?
At pH 7, the substance or solution is at neutral and means that the concentration of H + and OH - ion is the same . If pH < 7, the solution is acidic. There are more H + than OH - in an acidic solution. The pH scale does not have an upper nor lower bound.
What is the name of the ion that is hydrated?
H + and H 3 O + is often used interchangeably to represent the hydrated proton, commonly call the hydronium ion.
What happens when an acid is added to water?
If an acid ( H +) is added to the water, the equilibrium shifts to the left and the O H − ion concentration decreases
What is the pH of H+ ions?
The identity of these solutions vary from one authority to another, but all give the same values of pH to ± 0.005 pH unit. The historical definition of pH is correct for those solutions that are so dilute and so pure the H + ions are not influenced by anything but the solvent molecules (usually water).
Is pOH a basic solution?
If pH >7, the solution is basic. The pOH should be looked in the perspective of OH - instead of H +. Whenever the value of pOH is less than 7, then it is considered basic. And therefore there are more OH - than H + in the solution.
What are Acids?
The term acid is derived from the Latin word ‘acidus’ or ‘acere’, which means sour. The most common characteristic is their sour taste. An acid is a substance that renders ionizable hydronium ion (H3O+) in its aqueous solution. It turns blue litmus paper red .
Classifications of Acids
Organic Acids – The acids that come from organic matter like plants and animals are known as Organic Acids. For Example, citric acid (Citrus fruits), Acetic acid (Vinegar), Oleic acid (Olive oil), etc.
What are Bases?
Bases are ionic substances that when dissolved in water produce negative hydroxide (OH) ions. An ionic compound is one that contains a negative nonmetal ion and a positive metal ion that is held together by an ionic bond.
Classification of Bases
Strong Bases – In the acid-base reaction, a strong base is described as a basic chemical substance that can remove a proton (H+) from (or deprotonate) a molecule of even a relatively weak acid (like water). Hydroxides of alkaline earth metals and alkali metals, such as Ca (OH)2 and NaOH, are two common examples of strong bases.
Strength of Acid: pH
Acids are defined as substances with a pH less than 7.0. As the amount of H+ ion in the solution increases, the value decreases. Strong acids are compounds that rapidly release H+ ions or are completely ionizable in solution. As a result, strong acids have a lower pH value, close to 0 to 1.
Strength of Base: pH
The nature of certain substances is determined by their pH. Bases, on the other hand, are substances having a pH greater than 7.0. As the amount of H+ in the solution drops, the value continues to rise. Strong bases are chemicals that rapidly release the OH- ion in a solution.
Sample Questions
Acid and Bases can be differentiated by using a litmus paper. Litmus paper/solution turns red in acidic solutions and blue in alkaline solutions.
What Is An Acid Or A Base?
What Is Ph?
- Acidity and alkalinity are measured with a logarithmic scale called pH. Here is why: a strongly acidic solution can have one hundred million million, or one hundred trillion (100,000,000,000,000) times more hydrogen ions than a strongly basic solution! The flip side, of course, is that a strongly basic solution can have 100,000,000,000,000 times mo...
How Do You Measure Ph?
- The pH of a liquid or solution is often an important piece of information in science. Measuring pH can be done simply and quickly using pH test paper, pH indicator sticks, or a pH meter. pH test paper and indicator sticks are pieces of paper or stiffer sticks that contain pH indicators(chemicals that change color depending on how acidic or basic a solution is). To mea…
Bibliography
- For more information about acids, bases, and the pH scale, try this reference: 1. Khan Academy. (2009, September 7). Arrhenius acids and bases. Retrieved July 15, 2021.