
The bronchial arteries follow the arborization of the bronchial tree and supply oxygenated blood to the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles and to the connective tissue of the lungs. The first branches of the bronchial arteries include small arteries to the esophagus, pericardium, and mediastinum. Want to thank TFD for its existence?
What does the bronchial artery do?
The bronchial artery is the primary blood vessel responsible for supplying the lungs with oxygenated, clean blood. There are two of these arteries, one supplying the left lung, and the other supplying the right. The artery generally originates at the thoracic aorta, which is the primary blood vessel of the heart.
Do all arteries have thick walls and carry oxygenated blood?
The main function of the arteries is to circulate or to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to different parts of the human body. Walls of the arteries are thick because they have to withstand the high pressure released from the heart during the process of pumping the blood.
Do arteries only carry oxygen rich blood?
Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart, while veins carry oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. An easy mnemonic is “A for ‘artery’ and ‘away’ (from the heart).” (The exceptions to this general rule are the pulmonary vessels. How many arteries go to your heart?
Are bronchial veins high in oxygen?
The lungs have dual blood supplies. The bronchial circulation is part of the systemic circulation and has a high pressure and high oxygen content. Bronchial arteries most often arise from the descending aorta and “feed” the bronchial tree as far as the respiratory bronchiole. Branches also nourish most of the mediastinal visceral pleura.
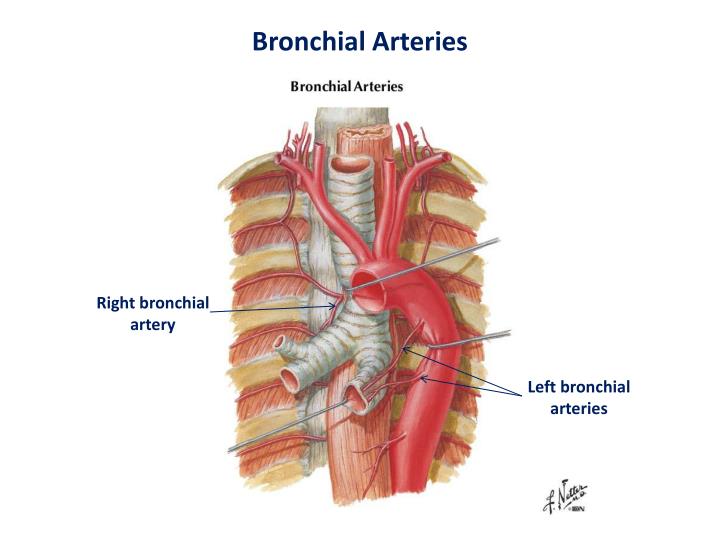
How many bronchial arteries are there?
In most individuals, there are two to four bronchial arteries present, arising either independently or from a common trunk. Theright bronchial artery usually (78% of people) arises within a common stem, with the first aortic intercostal (intercostobronchial artery) from the posteromedial aspect of the descending aorta.
Where does bronchial artery come from?
The left bronchial arteries (superior and inferior) usually arise directly from the thoracic aorta. The single right bronchial artery usually arises from one of the following: 1) the thoracic aorta at a common trunk with the right 3rd posterior intercostal artery. 2) the superior bronchial artery on the left side.
Where do bronchial arteries drain into?
Bronchial vessels supply blood to the lower trachea, the bronchi, and to the smaller airways as far as the respiratory bronchioles. Blood from the proximal part of the bronchial circulation around the bronchi drains via the pleurohilar bronchial veins into the azygous vein and into the superior vena cava.
Why does the left lung have 2 bronchial arteries?
There is usually one bronchial artery on the right, which arises from the third posterior intercostal artery or from the upper left bronchial artery. The left bronchial arteries usually number two and arise from the descending thoracic aorta inferior to the origin of the third posterior intercostal artery.
How many bronchial arteries are there to each lung?
There are most commonly 3 main bronchial arteries, one right and two left. In addition, there are often additional smaller bronchial arteries arising from the descending thoracic aorta 7.
Do bronchial arteries carry oxygenated blood?
The bronchial arteries carry oxygenated blood to the lungs as part of the general systemic circulatory system.
What is the difference between pulmonary and bronchial circulation?
Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. The separate system is known as the bronchial circulation supplies blood to the tissue of the larger airways of the lung.
What do the bronchial veins drain?
The deep bronchial veins drain into the main pulmonary vein or left atrium, while the superficial bronchial veins on the right side of the body drain into the azygos vein, and the veins on the left drain into the accessory hemiazygos vein or the left superior intercostal vein.
What artery supplies the bronchial tree and alveoli?
The bronchial arteries arise from the descending aorta with considerable anatomic variation. The one or two bronchial arteries that supply each lung in the majority of individuals8,9 arise from the area near the first and second intercostal arteries.
Which vessels are the three main arterial branches emerging from the aortic arch?
Aortic Arch Branches. There are three major branches of the aortic arch: the brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian (literally “under the clavicle”) artery.
Course
The bronchial arteries are located in the posterior mediastinum. They arise most commonly from the thoracic aorta (but may also arise from other vessels) at the T3 - T8 levels, most often from the T5 - T6 level. There are usually three main bronchial arteries, one on the right side and two on the left.
Left bronchial arteries
There are usually two left bronchial arteries that typically arise directly from the descending thoracic aorta:
Right bronchial artery
There is typically a single right bronchial artery. It usually originates from one of the following vessels:
Supply
The bronchial arteries provide arterial blood supply to the trachea, the bronchi, and the connective tissue of the lungs. They form anastomoses with branches of the pulmonary artery, supplying the visceral pleura on their way. Each bronchial artery also gives off a branch that supplies the middle third of the esophagus.
What is the bronchial artery?
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part of the respiratory system.
What is the function of the bronchial arteries?
The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs. They travel with and branch with the bronchi, ending about at the level of the respiratory bronchioles. They anastomose with the branches of the pulmonary arteries, and together, they supply the visceral pleura of the lung in the process.
Why is the bronchial artery sacrificed?
Largely for this reason, bronchial artery circulation is usually sacrificed during lung transplants, instead relying on the persistence of a microcirculation (presumably arising from the deoxygenated pulmonary circulation) to provide perfusion to the airways. Aneurysms of the bronchial artery may mimic aortic aneurysms.
What are the differences between pulmonary and bronchial arteries?
It is easy to confuse the bronchial arteries with the pulmonary arteries, because they both supply the lungs with blood, but there are important differences: artery. function. circulation. diameter. pulmonary arteries. supplies deoxygenated blood pumped from the right ventricle. pulmonary circulation. relatively large.
Which veins return blood to the left heart?
Note that much of the oxygenated blood supplied by the bronchial arteries is returned via the pulmonary veins rather than the bronchial veins. As a consequence, blood returning to the left heart is slightly less oxygenated than blood found at the level of the pulmonary capillary beds.
Which arteries are enlarged and tortuous in chronic pulmonary thromboembolic hypertension?
The bronchial arteries are typically enlarged and tortuous in chronic pulmonary thromboembolic hypertension.
Which bronchial artery is on the left side?
2) the superior bron chial artery on the left side. 3) any number of the right intercostal arteries mostly the third right posterior.
What are the bronchial arteries?
The bronchial arteries represent approximately 1% of the blood supply to the lungs and do not participate in gas exchange. They provide systemic blood supply to the airways, esophagus, posterior mediastinum, portions of the visceral pleura, and mediastinal lymph nodes, as well as to the pulmonary arteries themselves through their vasa vasorum. When normal, the bronchial arteries are not typically well visualized on thoracic aortography. In patients with various cardiopulmonary disorders, including chronic lung infections, lung tumors, inflammatory lung disease, pulmonary vasculitis, congenital heart disease, and chronic pulmonary vascular obstruction, the bronchial arteries can become enlarged as a major source of collateral circulation. In these settings, the risk of hemoptysis from a bronchial artery source exists. Imaging of the bronchial arteries is therefore an important step in the management of these patients. Although evaluation of the bronchial arteries has relied on thoracic aortography and selective bronchial artery angiography, computed tomography (CT) imaging of the bronchial arteries has become more technically feasible and can yield valuable information in the diagnostic workup of a patient with hemoptysis.
Where do bronchial arteries originate?
Certain typical features may be seen, however. The bronchial arteries arise from the descending thoracic aorta in approximately 70% of individuals, usually at the T5 to T6 thoracic vertebral body level. This configuration is considered the orthotopic origin of the bronchial arteries. Based on cadaveric studies, the most common orthotopic pattern is of a right intercostobronchial trunk and two separate left bronchial arteries. The right intercostobronchial trunk has branches supplying the bronchi and the chest wall, and it typically originates from the posteromedial wall of the aorta. The left bronchial arteries typically arise along the anterior wall of the aorta, although an origin from the right posteromedial aorta or even the right intercostobronchial trunk has been observed. Occasionally, a right and left bronchial artery will arise from a common trunk along the anterior thoracic aorta ( Fig. 45-1 ). Less common or aberrant sites of origin of the bronchial arteries include the thoracic aortic arch (typically from the concavity, but also from the convexity), the subclavian artery and its branches, the internal thoracic artery, the brachiocephalic trunk, and the abdominal aorta (see Fig. 45-1 ). Important anastomoses of the bronchial arteries include contributions to the anterior spinal artery, branches to the esophagus, anastomoses to the coronary arteries, and anastomoses to the pulmonary arteries, particularly in the setting of chronic lung disease. Of these anastomoses, contributions to the anterior spinal artery are the most feared aspect of bronchial artery intervention because inadvertent embolization results in potential paralysis. Evaluation of the bronchial arteries has traditionally required catheter angiography. The improved quality of high-resolution multidetector row CT (MDCT) has enabled visualization of the origin and course of the bronchial arteries before intervention and can be a helpful aid in the evaluation of hemoptysis.
What are the techniques used to improve visualization of the origin and course of the bronchial arteries?
Sagittal, coronal, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional reformation techniques may all be used to improve visualization of the origin and course of the bronchial arteries.
Which artery should always be scrutinized before intervention?
A potential communication of the bronchial arteries with the anterior spinal artery should always be scrutinized before intervention.
What is the bronchial artery?
The bronchial arteries arise from their parent vessels at the T3-T8 levels , most commonly between T5-T6 level (~70%; range 64-80%) where it is termed an orthotopic origin 5. There are most commonly 3 main bronchial arteries, one right and two left. In addition, there are often additional smaller bronchial arteries arising from the descending thoracic aorta 7.
What is the diameter of the bronchial arteries?
They are small caliber arteries, with a diameter of 1.5 mm at the origin, tapering down to approximately 0.5 mm at the pulmonary hila level 6 .
How many left and right bronchial arteries are there?
Bronchial artery anatomy is variable, most commonly classified according to Cauldwell classification . A classic pattern of two left and one right main bronchial arteries is found in ~70% of patients.
Which bronchial artery passes to the left of the esophagus?
Proximally, the left bronchial artery passes to the left of the esophagus, while the right bronchial artery may pass to the right or left of the esophagus 8. Their small branches form a network of arteries running along the external bronchial surface, with penetrating branches to supply the submucosal arterial network and sometimes ...
Which artery supplies oxygenated blood to the supporting structures of the lung?
Bronchial artery. The bronchial arteries are the major supply of high-pressure oxygenated blood to the supporting structures of the lung, including the pulmonary arteries, yet they are responsible for only 1% of the lung blood flow overall.
Where does the right bronchial artery originate?
The right bronchial artery has a common origin with a posterior intercostal artery called the intercostobronchial trunk ( ICBT) and arises from the right anteromedial aspect of the thoracic aorta 8.
Where is the superior left bronchial artery?
superior left bronchial artery: arises from the aorta near the level of the aortic arch, lateral to the carina, and posterior to the left main bronchus. inferior left bronchial artery: arises from the aorta parallel to the superior artery, but inferior to the left main bronchus.
bronchial branches
branches of arteries, vessels, or nerves distributed to the bronchi; the following have branches so named: 1) thoracic aorta; 2) internal thoracic artery; 3) vagus nerves.
bronchial arteries
The first blood vessels to branch from the aorta at the end of the aortic arch, which supply blood to the lungs and the bronchioles.
What is the superficial bronchial vein?
The superficial bronchial veins consist of a subpleural venous network that commences towards the hilum of the lung. Along the way, they receive tributaries that drain the extrapulmonary bronchi. Upon entering the hilum of the lungs, they also drain the visceral pleura around the hilum and hilar lymph nodes.
What is the relationship between the bronchial and pulmonary veins?
The communication between the bronchial and the pulmonary veins is important physiologically. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation, while the bronchial veins belong to the systemic circulation . The pulmonary circulation starts with the pulmonary arteries carrying deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
What percentage of blood is oxygenated in the pulmonary veins?
The mixing that occurs between the oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins and the deoxygenated blood from the bronchial veins ensures that the blood within the pulmonary veins returns to the heart as only around 95 percent oxygenated, instead of 100 percent.
What is the name of the veins that drain the lungs?
Bronchial veins (Venae bronchiales) Bronchial veins are small vessels that form a part of the venous drainage of the lungs. These vessels drain the larger pulmonary bronchi and the area of the lung close to the hilum. The bronchial veins can be divided into two systems; deep and superficial. The deep bronchial veins drain into ...
Which veins terminate in the bronchial vein?
The superficial bronchial veins terminate by draining into the azygos vein on the right, and the accessory hemiazygos or left superior intercostal vein on the left. Just like the deep bronchial bronchial veins, they communicate with the pulmonary veins. Bronchial arteries and veins (overview)
Which vein drains into the pulmonary vein?
The deep bronchial veins drain into the main pulmonary vein or left atrium, while the superficial bronchial veins on the right side of the body drain into the azygos vein, and the veins on the left drain into the accessory hemiazygos vein or the left superior intercostal vein.
How many sets of veins are there in the lungs?
Anatomy and course. The bronchial veins are small veins draining the larger bronchi and other structures of the lung close to the hilum. There are usually two sets of veins for each of the lungs. Each set of bronchial veins is divided into deep and superficial bronchial veins.
Where do bronchial arteries come from?
CT. The bronchial arteries typically arise from the thoracic aorta at the T3-T8 levels. 80% percent of arteries arise from the T5 to T6 level. Enlarged arteries are often seen and dilated tortuous vessels at this level in the mediastinum. In this situation, the proximal bronchial arteries are usually >2 mm 2,7.
What is bronchiectasis pulmonary?
bronchiectasis : especially in those with pulmonary manifestations of cystic fibrosis. those with certain forms of pulmonary hypertension 2. chronic pulmonary embolism 6. following certain repaired of congenital cardiac anomalies. e.g. arterial switch for simple transposition of the great arteries 1.
Overview
Structure
There are typically two left and one right bronchial arteries.
The left bronchial arteries (superior and inferior) usually arise directly from the thoracic aorta.
The single right bronchial artery usually arises from one of the following:
• 1) the thoracic aorta at a common trunk with the right 3rd posterior intercostal artery
• 2) the superior bronchial artery on the left side
Function
The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs. They travel with and branch with the bronchi, ending about at the level of the respiratory bronchioles. They anastomose with the branches of the pulmonary arteries, and together, they supply the visceral pleura of the lung in the process.
Note that much of the oxygenated blood supplied by the bronchial arteries is returned via the pul…
Clinical significance
Bronchial artery is considered dilated when its diameter is more than 2 mm. Several causes of bronchial artery dilatations are: congenital heart or lung diseases, obstructions of pulmonary artery, and lung inflammation.
The bronchial arteries are typically enlarged and tortuous in chronic pulmonary thromboembolic hypertension.
See also
• Bronchial veins
• Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy
External links
• Anatomy figure: 21:06-06 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Branches of the ascending aorta, arch of the aorta, and the descending aorta."
• Histology image: 13903loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Bronchial arteries - anatquest.nlm.nih.gov.