Types of Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are chemically defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them...
- Proteins. Proteins are another class of indispensable biomolecules, which make up around 50per cent of the cellular dry...
- Nucleic Acids. Nucleic acids refer to the genetic material found in the cell that carries all the...
What is the formula of a carbohydrate?
The general formula for carbohydrates is Cx(H2O)y. Carbohydrates (or sugars) were originally believed to be “hydrates of carbon,” because they have the general formula C x (H 2 O)y. Structure with an open chain. The structure is hemi-acetal.
What are the four major categories of biomolecules?
Types of Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates. Polysaccharides, commonly known as carbohydrates are macromolecules. ...
- Proteins. Proteins are polymers, made up of monomeric units of 20 amino acids. ...
- Lipids. Lipids are a macromolecule, which is water-insoluble. ...
- Nucleic Acids. ...
- Biomolecules – Questions. ...
What are the four main biomolecules and their functions?
The 4 biomacromolecules and their functions are:
- Proteins: Functions: Form a part of cell membrane and cytoplasm. Form apoenzyme part of enzymes. Carry genetic information carried by genes. ...
- Nucleic acids: Carry and express genetic information. During translation, amino acids attach to tRNA before peptide bond formation.
- Carbohydrates: Act m
What are the four classes of biomolecules?
What are the 4 categories of biomolecules?
- Nucleic Acids. The nucleic acids are DNA and RNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, respectively.
- Proteins.
- Carbohydrates.
- Lipids.

What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are biomolecules comprising carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. They are an important source of energy. They are sugars, starch and fi...
How are the carbohydrates classified?
Carbohydrates are classified into the following: Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
How are the carbohydrates important to our body?
Carbohydrates provide energy to the body. It breaks down into glucose and enters our bloodstream. The body cells utilize glucose to produce ATP.
Name a few sources of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are obtained from a variety of sources such as bread, milk, potatoes, cookies, corn, etc.
How are the carbohydrates digested?
Carbohydrates start being digested in the mouth by the action of salivary amylase. They are not completely broken down in the stomach, but in the i...
What are simple carbohydrates? Give examples.
Simple carbohydrates are the ones that are quickly broken down by the body to be converted into energy. Fruits, milk and milk products are the main...
How are complex carbohydrates different from simple carbohydrates?
Complex carbohydrates are the ones in which the sugar molecules are strung in long, complex chains. Peas, beans, vegetables and grains are the impo...
What are the three types of simple carbohydrates?
Three types of simple carbohydrates include: Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides
Name some bad carbohydrates that are harmful to the body.
The bad carbs include: White bread Sugary drinks Pastries Candies and chocolates
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of carbon and water.
What are disaccharides made of?
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides join together. An example is sucrose. Sucrose is formed from a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of fructose.
What are some examples of aldehydes?
Some are aldehydes, like glucose and are referred as aldoses ; other are ketones, like fructose and are referred as ketoses. 2. Disaccharides. Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides join together. An example is sucrose. Sucrose is formed from a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of fructose.
What is the reaction of aldehyde and ketose?
This means that, when heated with an alkaline solution of copper (II) sulphate (a blue solution called benedict’s solution), the aldehyde or ketone group reduces Cu2+ ions to Cu+ ions forming brick red precipitate of copper (I) oxide. In the process, the aldehyde or ketone group is oxidised to a carboxyl group (–COOH). This reaction is used as test for reducing sugar and is known as Benedict’s test. The results of benedict’s test depends on concentration of the sugar. If there is no reducing sugar it remains blue (Figure 8.14).
Is cellulose an organic compound?
Cellulose is one of the most abundant organic compound in the biosphere.
What is the classification of carbohydrates?
The carbohydrates are further classified into simple and complex which is mainly based on their chemical structure and degree of polymerization.
Where are carbohydrates found?
They are found in grains, vegetables, fruits and in milk and other dairy products. They are the basic food groups which play an important role in a healthy life. The food containing carbohydrates are converted into glucose or blood sugar during the process of digestion by the digestive system. Our body utilizes this sugar as a source ...
What are the three main ways the body obtains energy?
Carbohydrates are macronutrients and are one of the three main ways by which our body obtains its energy. They are called carbohydrat es as they comprise carbon, hydrogen and oxygen at their chemical level. Carbohydrat es are essential nutrients which include sugars, fibers and starches. They are found in grains, vegetables, ...
What are the two monomers of carbohydrates?
2. Disaccharides. Two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Examples of carbohydrates having two monomers include- Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose, etc. 3. Oligosaccharides. Carbohydrates formed by the condensation of 2-9 monomers are called oligosaccharides.
What are the components of food?
Carbohydrates are known as one of the basic components of food, including sugars, starch, and fibre which are abundantly found in grains, fruits and milk products. Carbohydrates are also known as starch, simple sugars, complex carbohydrates and so on. It is also involved in fat metabolism and prevents ketosis.
How many sugar molecules are in simple carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates have one or two sugar molecules. In simple carbohydrates, molecules are digested and converted quickly resulting in a rise in the blood sugar levels. They are abundantly found in milk products, beer, fruits, refined sugars, candies, etc.
Where are polysaccharides found?
They are abundantly found in lentils, beans, peanuts, potatoes, peas, corn, whole-grain bread, cereals, etc. Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates formed by the polymerization of a large number of monomers.
What are the different types of biomolecules?
Types of Biomolecules. There are four major classes of Biomolecules – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids and Lipids. Each of them is discussed below.
What is the class of biomolecules that make up the bulk of the cellular dry weight?
Proteins are another class of indispensable biomolecules, which make up around 50per cent of the cellular dry weight. Proteins are polymers of amino acids arranged in the form of polypeptide chains. The structure of proteins is classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary in some cases. These structures are based on the level of ...
What is the monomeric unit of nucleic acids?
The monomeric unit of nucleic acids is known as nucleotide and is composed of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate. The nucleotides are linked by a 3’ and 5’ phosphodiester bond. The nitrogen base attached to the pentose sugar makes the nucleotide distinct.
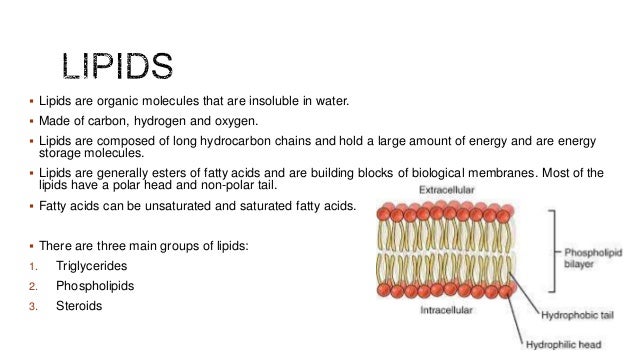
What are lipids in water?
Lipids are organic substances that are insoluble in water , soluble in organic solvents, are related to fatty acids and are utilized by the living cell. They include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, mono-, di- or triglycerides, phospholipids, etc. Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, lipids are not polymeric molecules.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
There are 4 major nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. The DNA structure is described as a double-helix or double-helical structure which is formed by hydrogen bonding between the bases of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
There are two types of nucleic acids namely, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The main function of nucleic acid is the transfer of genetic information and synthesis ...
What are the most essential organic molecules?
Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. These non-living molecules are the actual foot-soldiers of the battle of sustenance of life.
What is the definition of carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates. The term carbohydrate is itself a combination of the “hydrates of carbon”. They are also known as “Saccharides” which is a derivation of the Greek word “Sakcharon” meaning sugar. The definition of carbohydrates in chemistry is as follows: “Optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones or substances which give these on ...
What are the different types of carbohydrate?
The main classification of carbohydrate is done on the basis of hydrolysis. This classification is as follow: 1 Monosaccharides: These are the simplest form of carbohydrate that cannot be hydrolyzed any further. They have the general formula of (CH 2 O) n. Some common examples are glucose, Ribose etc. 2 Oligosaccharides: Carbohydrates that on hydrolysis yield two to ten smaller units or monosaccharides are oligosaccharides. They are a large category and further divides into various subcategories. 3 Disaccharides: A further classification of oligosaccharides, these give two units of the same or different monosaccharides on hydrolysis. For example, sucrose on hydrolysis gives one molecule of glucose and fructose each. Whereas maltose on hydrolysis gives two molecules of only glucose, 4 Trisaccharides: Carbohydrates that on hydrolysis gives three molecules of monosaccharides, whether same or different. An example is Raffinose. 5 Tetrasaccharides: And as the name suggests this carbohydrate on hydrolysis give four molecules of monosaccharides. Stachyose is an example. 6 Polysaccharides: The final category of carbohydrates. These give a large number of monosaccharides when they undergo hydrolysis, These carbohydrates are not sweet in taste and are also known as non-sugars. Some common examples are starch, glycogen etc.
What are the simplest forms of carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed?
Monosaccharides: These are the simplest form of carbohydrate that cannot be hydrolyzed any further. They have the general formula of (CH 2 O) n. Some common examples are glucose, Ribose etc. Oligosaccharides: Carbohydrates that on hydrolysis yield two to ten smaller units or monosaccharides are oligosaccharides.
What are the two units of the same or different monosaccharides on hydrolysis?
They are a large category and further divides into various subcategories. Disaccharides: A further classification of oligosaccharides, these give two units of the same or different monosaccharides on hydrolysis. For example, sucrose on hydrolysis gives one molecule of glucose and fructose each.
Which carbohydrate gives three monosaccharides?
Trisaccharides: Carbohydrates that on hydrolysis gives three molecules of monosaccharides, whether same or different. An example is Raffinose. Tetrasaccharides: And as the name suggests this carbohydrate on hydrolysis give four molecules of monosaccharides. Stachyose is an example.
Why are carbohydrates important?
Carbohydrates are responsible for storing chemical energy in living organisms. You must hear all the time when athletes carbo-load before a game. This is so they can provide themselves with extra energy. They are also an important constituent for supporting tissues in plants and even in some animals.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Some common examples are starch, glycogen etc.
What are the three categories of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically important carbohydrates belong to three categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. In this article, we’ll learn more about each type of carbohydrates, as well as the essential energetic and structural roles they play in humans and other organisms.
What is the carbohydrate in potato?
A bit more of the potato's carbohydrate is in the form of fiber, including cellulose polymers that give structure to the potato’s cell walls. Most of the carbohydrate, though, is in the form of starch, long chains of linked glucose molecules that are a storage form of fuel.
What is the name of the sugar that is formed by a dehydration reaction?
For instance, the diagram below shows glucose and fructose monomers combining via a dehydration reaction to form sucrose, a disaccharide we know as table sugar. (The reaction also releases a water molecule, not pictured.)
Which carbons are connected by a glycosidic bond?
In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. Each carbon atom in a monosaccharide is given a number, starting with the terminal carbon closest to the carbonyl group (when the sugar is in its linear form). This numbering is shown for glucose and fructose, above. In a sucrose molecule, the carbon of glucose is connected to the carbon of fructose, so this bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
What is the most common type of sugar?
Monosaccharides. Monosaccharides ( mono - = “one”; sacchar - = “sugar”) are simple sugars, the most common of which is glucose. Monosaccharides have a formula of , and they typically contain three to seven carbon atoms. [How is that formula different from carbohydrates in general?]
How many members does glucose have?
For instance, in solution, glucose’s main configuration is a six-membered ring. Over 99% of glucose is typically found in this form. Even when glucose is in a six-membered ring , it can occur in two different forms with different properties.
What is the structure of aldehyde?
Structure of aldehyde: carbonyl bonded to a H on one side and to an R group (carbon-containing group) on the other. Structure of ketone: carbonyl bonded to R and R' groups (carbon-containing groups) on both sides.
What is a carbohydrate?
carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula…
What are the four types of biomolecules?
The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins . Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, have the unique function of storing an organism’s genetic code —the sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are of critical importance to life on Earth.
What are the most abundant biomolecules?
Proteins also form antibodies and hormones, and they influence gene activity. Likewise, carbohydrates, which are made up primarily of molecules containing atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, are essential energy sources and structural components of all life, and they are among the most abundant biomolecules on Earth.
What are proteins used for in living organisms?
They also serve as transporters, moving nutrients and other molecules in and out of cells, and as enzymes and catalysts for the vast majority of chemical reactions that take place in living organisms. Proteins also form antibodies and hormones, and they influence gene activity.
What is a cell in biology?
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with…
What are the four types of sugars in lipids?
They are built from four types of sugar units— monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Lipids, another key biomolecule of living organisms, fulfill a variety of roles, including serving as a source of stored energy and acting as chemical messengers.
What is the name of the protein that wraps around DNA?
DNA wraps around proteins called histones to form units known as nucleosomes. These units condense into a chromatin fibre, which condenses further to form a chromosome.
What Are Carbohydrates?
The most abundant biomolecules on earth are carbohydrates. From a chemical viewpoint, carbohydrates are primarily a combination of carbon and water, and many of them have the empirical formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of repeated units.
Monosaccharides
In biochemistry, carbohydrates are often called saccharides, from the Greek sakcharon, meaning sugar, although not all the saccharides are sweet. The simplest carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, or simple sugars.
Complex Carbohydrates
The simple sugars form the foundation of more complex carbohydrates. The cyclic forms of two sugars can be linked together by means of a condensation reaction to form a disaccharide. Multiple sugars can be linked to form polysaccharides.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharide molecules may chemically bond to form a disaccharide. The name given to the covalent bond between the two monosaccharides is a glycosidic bond. Glycosidic bonds form between hydroxyl groups of the two saccharide molecules, an example of the dehydration synthesis described later in this chapter.
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides, also called glycans, are large polymers composed of hundreds of monosaccharide monomers. Unlike mono- and disaccharides, polysaccharides are not sweet and, in general, they are not soluble in water. Like disaccharides, the monomeric units of polysaccharides are linked together by glycosidic bonds.
Contributors and Attributions
Nina Parker, (Shenandoah University), Mark Schneegurt (Wichita State University), Anh-Hue Thi Tu (Georgia Southwestern State University), Philip Lister (Central New Mexico Community College), and Brian M. Forster (Saint Joseph’s University) with many contributing authors.
What are the components of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates. It contains a combination of carbon, hydrogen, as well as oxygen. They are present in the ratio of CnH2N. Since sugar is the most fundamental component of almost all types of carbohydrates, they are also called saccharides (as in Greek, sakcharon refers to sugar).
What are the biomolecules that are included in the classification of a biomolecule?
Apart from the major biomolecules like carbohydrates, protein, fat and nucleic acids, classification of biomolecules should also involve the mention of smaller biomolecules like natural products, as well as primary and secondary metabolites.
What are lipids made of?
Lipids are basically esters of alcohol and fatty acid. Lipids can be categorized as the Simple lipids, compound lipids and derived lipids. Simple lipids are the esters of glycerol and fatty acid. They can be subdivided as first Fats and oils, second Fatty Acids- These are again of two types.
How many monosaccharides can be broken down by hydrolysis?
Trisaccharides: On hydrolysis, these can give three molecules of monosaccharide. For example, Raffinose (C18H32O16). Oligosaccharides: By means of hydrolysis, these carbohydrates can be broken into 2-9 molecules of monosaccharides.
What are the building blocks of life?
Biomolecules are the primary building blocks of every living organism. Together, they promote different biological processes, which are necessary for life. They vary in structures and sizes. Biomolecules primarily consist of hydrogen and oxygen. The living systems synthesize four primary types of biomolecules within the body.
What are the four chemicals that make up a biomolecule?
The size of these biomolecules varies in different organisms. They are made from nucleotides. These compounds have any of the four chemicals Guanine, Thymine, Adenine or Cytosine as a base, starch and phosphate. Nucleic acids vary in their properties, functionalities, structure and even in their location in the cell.
What are the different types of carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates can further be subdivided into four types. Monosaccharides: They are the polyhydroxy ketones or Polyhydroxy aldehydes that do not break into simpler carbohydrate molecules. Examples include Gulose, Ribose, Glucose, Mannose, Arabinose, Fructose, and the like. Trisaccharides: On hydrolysis, these can give three molecules ...