
Common Causes
Some of the areas that carotid arteries help supply with blood include the:
- brain
- face
- scalp
- roof of the mouth
- tongue
- seventh cranial nerve
- oral cavity
- teeth
- ears
- supporting muscles in the face and neck
Related Conditions
The place where the internal and external carotid arteries meet to make the common carotid artery is called the carotid sinus (dilated area in the carotid bifurcation); this is a kind of neurovascular structure, which contains baroreceptors ("baro" is the Greek word for pressure or stretch). NCBI.
What does the carotid artery do?
Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries). The blockage increases your risk of stroke, a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or seriously reduced. Stroke deprives your brain of oxygen.
Is carotid artery the same as carotid sinus?
Some people with a carotid artery dissection may benefit from surgery to repair the carotid artery dissection. Most cases of carotid artery dissection will heal on their own in the first few months. Therefore, surgery is usually only recommended for people who continue to get stroke symptoms despite taking anti-blood clotting medications.
What does having carotid artery disease mean?
Does carotid artery dissection have a cure?
What are the parts of the carotid artery?
What causes problems with the carotid arteries?
How are carotid artery conditions diagnosed?
How can I keep my carotid arteries healthy?
What is the most serious outcome of carotid artery disease?
What is the cause of carotid blockage in the neck?
Why do my arteries narrow?
See 4 more
About this website
What do they do for a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid endarterectomy, the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. After making an incision along the front of your neck, the surgeon opens the affected carotid artery and removes the plaques. The artery is repaired with either stitches or a graft.
Can you live with a blocked carotid artery?
They are the carotid arteries, and they carry blood to the brain. If one of them is narrowed or blocked, it can lead to a stroke. Doctors can test for a narrowed carotid artery, but it's usually not a good idea. In fact, the test may do more harm than good.
What causes clogged carotid arteries?
Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis.
How serious is a carotid artery?
Carotid artery disease reduces the flow of oxygen to the brain. The brain needs a constant supply of oxygen to work. Even a brief pause in blood supply can cause problems. Brain cells start to die after just a few minutes without blood or oxygen.
What are the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid Artery Blockage SymptomsBlurred vision or vision loss.Confusion.Memory loss.Numbness or weakness in part of your body or one side of your body.Problems with thinking, reasoning, memory and speech.
How can I naturally unblock my carotid artery?
Eat a heart-healthy dietAdd more good fats to your diet. Good fats are also called unsaturated fats. ... Cut sources of saturated fat, such as fatty meat and dairy. Choose lean cuts of meat, and try eating more plant-based meals.Eliminate artificial sources of trans fats. ... Increase your fiber intake. ... Cut back on sugar.
Which side of the neck is the carotid artery?
There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
Does your neck hurt when your carotid artery is blocked?
It is linked with physical changes that can happen in a carotid artery in your neck. Your neck may feel tender in the area of the artery. The pain often goes up the neck to the jaw, ear, or forehead.
How do I get rid of plaque in my neck arteries?
Treatment for severe carotid stenosis involves eliminating the artery blockage. The most common way to do that is with a surgery called “carotid endarterectomy.” It's performed by making an incision along the front of the neck, opening the carotid artery and removing the plaque.
Which artery is the most common to have blockage?
When this happens, patients may go into cardiac arrest. Statistically, Niess said widow-makers are more likely to lead to brain injury and irregular heartbeat. Although blockages can occur in other arteries leading to the heart, the LAD artery is where most blockages occur.
Does aspirin reduce plaque in arteries?
Now, a team led by a University of Florida Health researcher has found that aspirin may provide little or no benefit for certain patients who have plaque buildup in their arteries. Aspirin is effective in treating strokes and heart attacks by reducing blood clots.
Can you feel a blocked artery in your neck?
The plaque or clot can travel through the bloodstream and get stuck in one of your brain's smaller arteries. Carotid artery disease often does not cause symptoms until the blockage or narrowing is severe. One sign may be a bruit (whooshing sound) that your doctor hears when listening to your artery with a stethoscope.
Can you live with a 100 percent blocked carotid artery?
A network of blood vessels at the base of the brain, called the circle of Willis, can often supply the necessary blood flow. Many people function normally with one completely blocked carotid artery, provided they haven't had a disabling stroke.
At what percentage of carotid artery blockage requires surgery?
Surgery is the best option for symptomatic patients with 70% to 99% blockage in the carotid artery. However, it can also be considered for patients with 50% to 69% blockage. Doctors agree that surgery is the most effective option for patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis.
Can carotid artery blockage be treated with medication?
Mild to moderate blockages in the carotid artery are treated with medications called antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin, that block the formation of blood clots. In addition, treatment involves identifying and reducing risk factors, such as cigarette smoking and high blood pressure.
What is life expectancy after carotid artery surgery?
In the present study the 5-year survival was 78.2% and the 10-year survival was 45.5% for the asymptomatic cohort.
Carotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and Treatment
Your doctor may also use a test to diagnose carotid artery disease. Possible tests include the following: Carotid ultrasound (standard or Doppler). This noninvasive, painless screening test uses ...
Carotid artery disease - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Causes. Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery.
Carotid Artery Disease A Pain in the Neck – and Much More
Medically Reviewed by Christopher G. Cunningham, MD. Carotid artery disease is the major cause of stroke and a leading cause of disability in the United States.
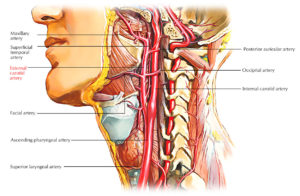
Internal Carotid Artery Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps
The common carotid artery is found bilaterally, with one on each side of the anterior neck. Each common carotid artery is divided into an external and internal carotid artery. These arteries ...
How to treat carotid artery disease?
Treatment of carotid artery disease usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication and sometimes surgery.
What causes a carotid artery to narrow?
A carotid artery may become so narrowed by atherosclerosis that not enough blood is able to reach portions of your brain. Ruptured plaques. A piece of a plaque may break off and flow to smaller arteries in your brain.
What causes a buildup of plaque in the arteries?
Causes. Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis.
How many strokes are caused by carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease causes about 10 to 20 percent of strokes. A stroke is a medical emergency that can leave you with permanent brain damage and muscle weakness. In severe cases, a stroke can be fatal. Carotid artery disease can lead to stroke through: Reduced blood flow.
What is the name of the blood vessel that delivers blood to the brain?
Carotid artery. Carotid artery. The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries).
What is the process of clogging the carotid arteries?
This process is called atherosclerosis. Carotid arteries that are clogged with plaques are stiff and narrow. Clogged carotid arteries have trouble delivering oxygen and nutrients to vital brain structures that are responsible for your day-to-day functioning.
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when a blood clot blocks or plugs an artery?
Ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks or plugs an artery leading to the brain. A blood clot often forms in arteries damaged by the buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis).
What is the function of the carotid arteries?
Function. The carotid arteries transport oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain and head. Some of the areas that carotid arteries help supply with blood include the: Without adequate blood flow and oxygen, brain cells will die off, resulting in brain damage.
How many carotid arteries are there in the neck?
There are two carotid arteries: one on the left and one on the right. In the neck, each of them branches off into an internal carotid artery and an external carotid artery. The position of the branched carotid arteries is where a person can feel the pulse in their neck, just under the jaw. There are an additional eight major divisions.
What does it mean when someone has a stroke?
slurred or incoherent speech. a headache. A stroke is a medical emergency. Anyone who witnesses someone possibly having a stroke should call 911 or the local emergency number immediately. A doctor may use several different tests to determine whether a person has carotid artery disease or has had a stroke or TIA.
What causes a carotid artery to narrow?
This narrowing reduces the amount of oxygen-rich blood that can flow through these vessels. The most common cause of carotid artery disease is atherosclerosis, which is a buildup of plaques comprising fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing carotid artery disease?
These include: diabetes. being male. having an elevated level of fats in the blood. obesity. reaching an older age. a diet high in saturated fats. family history.
Why do you need a stent?
The stent helps hold the artery open, reducing the risk of blockages.
What is the role of the arteries in the body?
Arteries play a vital role in transporting oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
What are the two divisions of the carotid artery?
In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. Like all arteries, the carotid arteries are made of three layers of tissue: Intima, the smooth innermost layer. Media, the muscular middle layer.
How many layers are there in the carotid artery?
Like all arteries, the carotid arteries are made of three layers of tissue:
What is the procedure to open a narrowing carotid artery?
Carotid endarterectomy: A surgery to open a narrowing, or stenosis, caused by cholesterol plaque in the carotid artery. A vascular surgeon cuts open the carotid artery, removes the plaque, and sews the artery closed. Statins: Cholesterol-lowering medicines taken in pill form daily.
What causes a sudden blood clot in the carotid artery?
Stroke: A sudden blood clot in the carotid artery can interrupt blood flow to the brain, causing a stroke. Fragments of cholesterol plaque in the carotid artery may also travel into the brain to cause a stroke.
What is the cause of vasculitis in the carotid artery?
Carotid artery vasculitis: Inflammation of the carotid artery, due to an autoimmune condition or an infection.
What is the name of the blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face?
All rights reserved. The carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain.
Which artery supplies blood to the brain, neck, and face?
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions:
How to treat carotid artery disease?
The options include: Carotid endarterectomy, the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. After making an incision along the front of your neck, the surgeon opens the affected carotid artery and removes the plaques. The artery is repaired with either stitches or a graft.
What is a carotid stent?
Carotid stenting. In carotid stenting, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A metal mesh tube (stent) is inserted into the vessel to serve as a scaffold that helps prevent the artery from narrowing again. The catheter and the filter — which catches any debris ...
What is the procedure for carotid stenting?
Carotid angioplasty and stenting, if the blockage is too difficult to reach with carotid endarterectomy or you have other health conditions that make surgery too risky. You are given local anesthesia and a tiny balloon is threaded by catheter to the area of the clog. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a small wire mesh coil (stent) is inserted to keep the artery from narrowing again.
How is carotid endarterectomy done?
Treatment. In carotid endarterectomy, your surgeon opens the carotid artery to remove atherosclerotic plaques. In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A filter is inserted to catch any debris that may break off during the procedure.
What is the sound of a narrowed artery?
The exam generally includes listening for a swooshing sound (bruit) over the carotid artery in your neck, a sound that's characteristic of a narrowed artery.
How to treat a blockage in the carotid artery?
Recommendations may include quitting smoking, losing weight, eating healthy foods, reducing salt and exercising regularly.
What to do if you have a blockage in your arteries?
If blockage is severe, or if you've already had a TIA or stroke, your doctor may recommend removing the blockage from the artery.
What is carotid artery disease?
The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that carry blood and oxygen to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed, it’s called carotid artery disease. It may also be called carotid artery stenosis. The narrowing is caused by atherosclerosis. This is the buildup of fatty substances, calcium, and other waste products inside the artery lining. Carotid artery disease is similar to coronary artery disease, in which buildup occurs in the arteries of the heart and can cause a heart attack.
What are the complications of carotid artery disease?
The main complication of carotid artery disease is stroke. Stroke can cause serious disability and may be fatal.
How is carotid artery disease diagnosed?
Along with a complete medical history and physical exam, tests for carotid artery disease may include:
What is a duplex scan of the carotid artery?
Carotid artery duplex scan. This test is done to assess the blood flow of the carotid arteries. A probe called a transducer sends out ultrasonic sound waves. When the transducer (like a microphone) is placed on the carotid arteries at certain locations and angles, the ultrasonic sound waves move through the skin and other body tissues to the blood vessels, where the waves echo off of the blood cells. The transducer sends the waves to an amplifier, so the doctor can hear the sound waves. Absence of or faintness of these sounds may mean blood flow is blocked.
What causes a narrowing of the arteries?
The narrowing is caused by atherosclerosis. This is the buildup of fatty substances, calcium, and other waste products inside the artery lining. Carotid artery disease is similar to coronary artery disease, in which buildup occurs in the arteries of the heart and can cause a heart attack. Carotid artery disease reduces the flow ...
How does smoking affect the arteries?
Quit smoking. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk for carotid artery disease and cardiovascular disease. All nicotine products, including electronic cigarettes, constrict the blood vessels. This decreases blood flow through the arteries.
What to do if carotid artery is less than 50% narrowed?
If a carotid artery is less than 50% narrowed, it is often treated with medicine and lifestyle changes. If the artery is between 50% and 70% narrowed, medicine or surgery may be used, depending on your case.
What is the term for the narrowing of the carotid arteries?
Carotid artery disease is also called carotid artery stenosis. The term refers to the narrowing of the carotid arteries. This narrowing is usually caused by the buildup of fatty substances and cholesterol deposits, called plaque. Carotid artery occlusion refers to complete blockage of the artery. When the carotid arteries are obstructed, you are ...
How to treat carotid artery stenting?
Carotid artery stenting (CAS). Carotid artery stenting (CAS) is a newer treatment option. It’s less invasive than carotid endarterectomy and is performed in a catheterization laboratory. With CAS, a small puncture is made in the groin. A specially designed catheter is threaded to the area of narrowing in the carotid artery. Once in place, a small balloon tip is inflated for a few seconds to open the artery. Then, a stent is placed in the artery and expanded to hold the artery open. A stent is a small tube that acts as a scaffold to provide support inside your artery. The stent is usually made of metal and is permanent. It can also be made of a material that the body absorbs over time. Some stents have medicine that helps keep the artery from getting blocked again. CAS is a newer procedure, and there is still some controversy as to how well it prevents strokes caused by carotid artery disease. Research suggests that the standard CEA may be safer than CAS, which may raise the risk of stroke or death post procedure.
What test is used to diagnose carotid artery disease?
Your doctor may also use a test to diagnose carotid artery disease. Possible tests include the following: Carotid ultrasound (standard or Doppler).
What is the term for the hardening of the arteries on the inside of the heart?
Like the arteries that supply blood to the heart -- the coronary arteries -- the carotid arteries can also develop atherosclerosis or “hardening of the arteries” on the inside of the vessels.
Why do doctors listen to neck arteries?
That’s why it’s important to see your doctor regularly for physical exams. Your doctor may listen to the arteri es in your neck with a stethoscope. If an abnormal sound, called a bruit, is heard over an artery, it may reflect turbulent blood flow. That could indicate carotid artery disease. Listening for a bruit in the neck is a simple, safe, ...
How much more likely is a person to have a stroke if they have a TIA?
Findings show that someone who has experienced a TIA is 10 times more likely to suffer a major stroke than a person who has not had a TIA.
Is atherosclerosis a family history?
Family history of atherosclerosis, either coronary artery disease or carotid artery disease. Men younger than age 75 have a greater risk than women in the same age group. Women have a greater risk than men older than age 75. People who have coronary artery disease have an increased risk of developing carotid artery disease.
Why do we need to open the carotid artery?
If there is severe narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery, a procedure may be necessary to open the artery and increase blood flow to the brain, to prevent a future stroke.
How to prevent carotid artery disease?
Lifestyle changes. To prevent carotid artery disease from progressing, these lifestyle changes are recommended by your doctor and the National Stroke Association: Quit smoking and using tobacco products. Control high blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease. Have regular checkups with your doctor.
What happens when plaque builds up in the carotid artery?
Plaque buildup can lead to narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery which, when significant, can put an individual at increased risk for stroke.
What is the best treatment for carotid stenosis?
Carotid endarterectomy is the traditional surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. Carotid endarterectomy has been proven to be beneficial for symptomatic patients with a 50 percent or greater carotid stenosis (blockage) and for asymptomatic patients with a 60 percent or greater carotid stenosis.
What causes a narrowing of the carotid artery?
Carotid artery disease, also called carotid artery stenosis, is the narrowing of the carotid arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholestero l, fat and other substances traveling through the bloodstream, such as inflammatory cells, cellular waste products, proteins and calcium. These substances stick to the blood vessel walls over time as people age, and combine to form a material called plaque.
Where is the incision for carotid artery blockage?
During the procedure, an incision is made in the neck at the site of the carotid artery blockage. The surgeon removes the plaque from the artery and when the plaque removal is complete, the surgeon stitches the vessel closed. Blood flow to the brain is restored through its normal path.
Can a carotid artery be a sign of a stroke?
There may not be any symptoms of carotid artery disease. However, there are warning signs of a stroke. A transient ischemic attack (also called TIA or "mini-stroke") is one of the most important warning signs of a stroke. A TIA occurs when a blood clot briefly blocks an artery that supplies blood to the brain.
How to tell if you have carotid artery disease?
"Most people have no symptoms," says Aaron Aday, MD, a cardiovascular expert at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville. In rare cases, you may have ringing in your ears or fainting. Your doctor may suspect carotid artery disease if: 1 A whooshing sound, called a bruit, can be heard through a stethoscope placed on your neck. 2 Your eye doctor detects plaque in an artery that brings blood to your eye. 3 You have signs or symptoms of a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke.
What is the procedure to remove a blockage in the carotid artery?
For a severe blockage, your doctor may recommend carotid endarterectomy — a surgery to remove the blockage — or placement of a stent in the artery to keep it open. Because there are risks with either procedure, including about a 5 percent chance of stroke or death, according to Harvard Health Publishing, it's important to find an experienced heart surgeon.
What is it called when you have plaque in your arteries?
Over time, a waxy substance called plaque builds up in your arteries, narrowing them and making it harder for oxygen-rich blood to travel throughout your body, says the N ational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). When it occurs in the carotid arteries, it's called carotid artery disease.
What test can tell if your carotid artery is narrowed?
An ultrasound test can help determine if your carotid artery is narrowed and, if so, how severe the problem is, according to SVS.
What is the waxy substance that builds up in the arteries?
Over time, a waxy substance called plaque builds up in your arteries, narrowing them and making it harder for oxygen-rich blood to travel throughout your body, says the N ational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). When it occurs in the carotid arteries, it's called carotid artery disease.
What to do if your artery is less than 60 percent narrowed?
If the artery is less than 60 percent narrowed and isn't causing symptoms, your doctor likely will recommend medical therapy , adds the Society of Vascular Surgeons. This may include cholesterol- and blood pressure-lowering medications and aspirin or another medication to make your blood less sticky.
Can a blocked carotid artery cause a stroke?
Image Credit: SerhiiBobyk/iStock/GettyImages. Your carotid arteries are major blood vessels in your neck. If they become blocked , it could cut off the supply of blood to your brain, causing a stroke. Often, blocked carotid arteries have no symptoms, especially if it's just a partial blockage.
Where is the carotid artery?
The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck .
What is a carotid stent?
Carotid stenting. In carotid stenting, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A metal mesh tube (stent) is inserted into the vessel to serve as a scaffold that helps prevent the artery from narrowing again.
What is the procedure called for a narrowed artery in the neck?
If carotid endarterectomy isn't the best option for you, you might have a procedure called carotid angioplasty and stenting instead of carotid endarterectomy. In this procedure, doctors thread a long hollow tube (catheter) with a small balloon attached through a blood vessel in your neck to the narrowed artery.
How to repair carotid endarterectomy?
Your surgeon will make a cut along the front of your neck, open your carotid artery, and remove the plaque deposits clogging your artery. Then your surgeon will repair the artery with stitches or a patch made with a vein or artificial material. Your surgeon might use another technique that involves cutting the carotid artery and turning it inside out, then removing the plaque.
What is the procedure to remove fatty deposits from the carotid arteries?
Carotid endarterectomy is a procedure to treat carotid artery disease. This disease occurs when fatty, waxy deposits build up in one of the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are blood vessels located on each side of your neck (carotid arteries).
What is the catheter used for in angioplasty?
In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A filter is inserted to catch any debris that may break off during the procedure. Then, a tiny balloon at the end of the catheter is inflated to open the narrowed area.
What are the parts of the carotid artery?
Each carotid artery in the neck divides into two branches. These branches are the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain. The external carotid artery divides into seven branches which supply the head, face and neck.
What causes problems with the carotid arteries?
The most common problems related to the carotid arteries are narrowing or blockages. The most common type of blockages are due to buildup of plaque or atherosclerosis. Narrowing in the carotid artery can also occur due to dissections, which are tears in the lining of the blood vessel. The carotid artery can also enlarge and form aneurysms.
How are carotid artery conditions diagnosed?
For most people, carotid disease does not cause symptoms. It can be found by examination done by your physician or health care provider. Your healthcare provider will listen to your neck with a stethoscope. A whooshing sound, called a bruit (pronounced BREW-ee), can be heard which is caused by the disturbed blood flow from the narrowing in the carotid artery. Healthcare providers are trained to listen for this whooshing sound in the neck.
How can I keep my carotid arteries healthy?
To keep your carotid arteries healthy, you may need to reduce your cholesterol levels. Your provider may prescribe medication to help lower your cholesterol.
What is the most serious outcome of carotid artery disease?
Stroke: The most serious outcome of carotid artery disease is stroke. An ischemic stroke results from blockage of a brain artery leading lack of oxygen to the brain and death of parts of the brain. Carotid artery aneurysm: If the wall of the carotid artery is weak, an aneurysm can form.
What is the cause of carotid blockage in the neck?
They supply essential blood and oxygen to the brain and head. Carotid artery disease is a common but serious condition affecting the carotid arteries. Plaque buildup can cause carotid artery blockages that reduce or prevent blood flow to the brain. Surgery can help.
Why do my arteries narrow?
Stenosis means “narrowing.” Narrowed carotid arteries most often occur because of atherosclerosis, an accumulation of plaque along artery walls. The plaque that blocks or narrows the arteries is the result of a buildup of cholesterol deposits. In some cases, a plaque can rupture or break off leading to pieces of those blockages travelling to the brain and blocking the brain arteries leading to a stroke. Debris or platelets and clot can also form on the atherosclerotic plaque which can break off and block the brain arteries and lead to stroke.
Overview
A vascular murmur sound heard with a stethoscope over the carotid artery.
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- In its early stages, carotid artery disease often doesn't produce any signs or symptoms. The condition may go unnoticed until it's serious enough to deprive your brain of blood, causing a stroke or TIA. Signs and symptoms of a stroke or TIA include: 1. Sudden numbness or weaknessin the face or limbs, often on only one side of the body 2. Sudden trouble speakingan…
Prevention
- Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis. Carotid arteries that are clogged with plaques are stiff and narrow. Clogged carotid arteries have troubl…