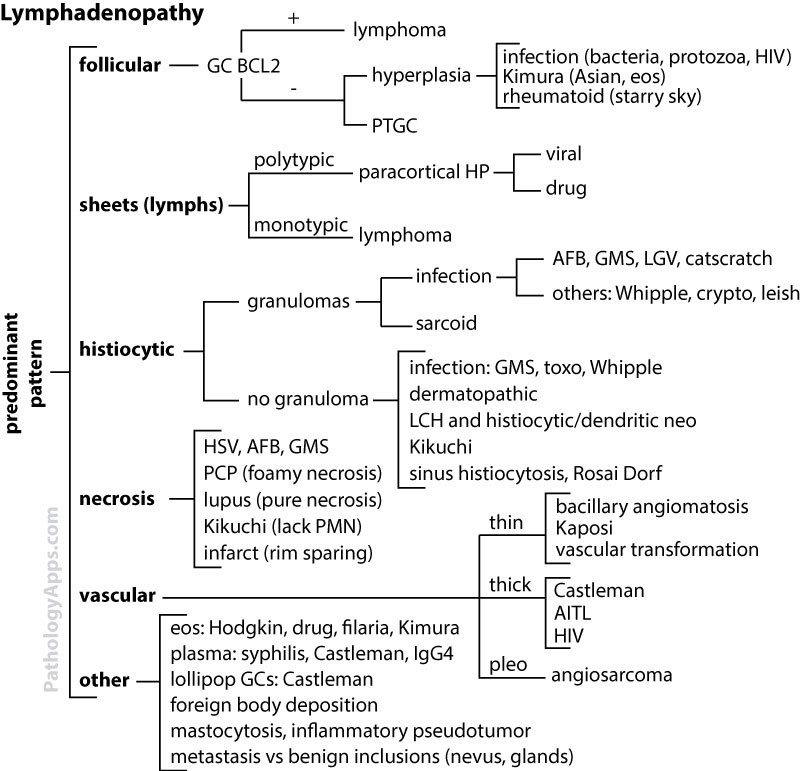
Common Causes
Lymphadenopathy may be the only clinical finding or one of several nonspecific findings, and the discovery of swollen lymph nodes will often raise the specter of serious illness such as lymphoma ...
Related Conditions
The common cause of Lymphadenopathy is an infection (bacterial, viral or fungal). Allergy to a vaccine or medication can also cause Lymphadenopathy. Cancer can also cause Lymphadenopathy. Diseases or medical conditions which affect the tissue which binds, supports and protects our organs can also cause Lymphadenopathy.
How serious is lymphadenopathy?
Other, less common etiologies responsible for adenopathy include nodal accumulation of inflammatory cells in response to an infection in the node ( lymphadenitis ), neoplastic lymphocytes or macrophages (lymphoma), or metabolite-laden macrophages in storage diseases ( Gaucher disease ).
What is causing lymphadenopathy?
You must see your doctor if you sense pain and swelling in those regions where the presence of lymph nodes can be felt. Any of those symptoms, if persist for more than 2-3 days, need doctor’s check-up. Your medical visits will continue until your doctor assures that you have recovered.
What are the less common etiologies of lymphadenopathy?
When to see Doctor for swollen lymph nodes?

What is the most common cause of lymphadenopathy?
HEAD AND CERVICAL In children, acute and self-limiting viral illnesses are the most common etiologies of lymphadenopathy.
What are the two main causes of lymphadenopathy?
Swollen lymph nodes usually occur as a result of infection from bacteria or viruses. Rarely, swollen lymph nodes are caused by cancer. Your lymph nodes, also called lymph glands, play a vital role in your body's ability to fight off infections.
Does lymphadenopathy always mean cancer?
Doctors call it lymphadenopathy. Swollen lymph nodes are a sign that your immune system is fighting off infection or illness. Swollen lymph nodes are more likely to be benign than malignant. Benign means the lymph nodes don't contain cancer cells.
What are signs of lymphadenopathy?
What are the signs and symptoms of lymphadenopathy?A painful, warm, or red lump under your skin.More tired than usual.Skin rash.Unexplained weight loss.Enlarged spleen (organ that filters blood)Fever or night sweats.
Is lymphadenopathy serious?
Although the finding of lymphadenopathy sometimes raises fears about serious illness, it is, in patients seen in primary care settings, usually a result of benign infectious causes. Most patients can be diagnosed on the basis of a careful history and physical examination.
Can lymphadenopathy be cured?
In most cases, lymphadenitis clears up quickly with proper treatment, but it may take more time for lymph node swelling to go away. Be sure to let your healthcare provider know if your lymphadenitis symptoms come back.
What viruses cause lymphadenopathy?
Viral etiologies of lymphadenopathy include HIV, mononucleosis caused by EBV or CMV, roseola, HSV, varicella, and adenovirus. Bacterial etiologies of lymphadenopathy include Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Salmonella, Syphilis, and Yersinia.
What stage is cancer when it is in the lymph nodes?
stage 3 – the cancer is larger and may have spread to the surrounding tissues and/or the lymph nodes (or "glands", part of the immune system) stage 4 – the cancer has spread from where it started to at least 1 other body organ, also known as "secondary" or "metastatic" cancer.
How common is lymphadenopathy?
Lymphadenopathy is common and actually a good thing. The swelling in these pea- or bean-sized lymph nodes are one of your body's natural reactions to illness or infection.
What antibiotic is used for swollen lymph nodes?
Analgesics can help to control pain in patients with lymphangitis, and anti-inflammatory medications can help to reduce inflammation and swelling. Antibiotics, including the following, can be used in the treatment of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (GABHS) and S aureus infections: Dicloxacillin. Cephalexin.
Is lymphadenopathy a diagnosis?
Lymphadenopathy is palpable enlargement of ≥ 1 lymph nodes. Diagnosis is clinical. Treatment is of the causative disorder.
What is the best antibiotic for lymphadenitis?
Antibiotics should be targeted against S. aureus and group A streptococcus, and should include a 10-day course of oral cephalexin (Keflex), amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin), or clindamycin (Cleocin).
What viruses cause lymphadenopathy?
Viral etiologies of lymphadenopathy include HIV, mononucleosis caused by EBV or CMV, roseola, HSV, varicella, and adenovirus. Bacterial etiologies of lymphadenopathy include Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Salmonella, Syphilis, and Yersinia.
How long does it take for lymphadenopathy to resolve?
Enlarged glands will usually resolve within 1–2 months in 60% of patients. However, 25% of patients take 2–4 months to return to normal, 8% take 4–6 months and in 6% the enlarged lymph nodes do not return to normal until much later.
Is lymphadenopathy a disease?
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes.
How common is lymphadenopathy?
Lymphadenopathy is common and actually a good thing. The swelling in these pea- or bean-sized lymph nodes are one of your body's natural reactions to illness or infection.
How to determine etiology of lymphadenopathy?
Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups.
What is lymphadenopathy in the lymphatic system?
Lymphadenopathy is a term that refers to the swelling of lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small glands that are responsible for filtering fluid from the lymphatic system. They are divided into sections known as follicles, which are subdivided into B zones and T zones, which represent the base location of lymphocytic maturation. ...
What is the term for the swelling of lymph nodes?
Lymphocytes are the integral agents involved in searching for target proteins and travel through lymph nodes, which are diffusely placed throughout the body. Lymphadenopathy is a term that refers to the swelling of lymph nodes.
What is the function of lymphatic fluid?
Lymphatic fluid moves throughout the lymphatic system, transitioning from the organs to lymphoid capillaries, lymphatic vessels, and finally lymph nodes for foreign antigen filtration. Foreign substances are presented to the lymphoid cells, which lead to cellular proliferation and enlargement. Under microscopy, cellular proliferation in lymphoid follicles may be identified as several mitotic figures.[5] As lymphatic capsules stretch due to increased activity, patients may experience localized tenderness.
How big should a lymph node be?
In general, the size of a normal lymph node in the adult population should be less than 1 cm; however, there are exceptions to this rule. [1]
What is non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma:There is partial or widespread loss of the lymph node by a single cell lineage. Lymphoid cells can either proliferate in a disorderly manner or as those that mimic follicular center structures.
Which lymph node is superior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Anterior cervical lymph nodes are superior and inferior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Posterior cervical lymph nodes are posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
What causes lymphadenopathy?
There are various causes of lymphadenopathy, but the most common is a viral infection. Others infections, caused by bacteria or parasites can also lead to lymphadenopathy. Some of the infections which cause lymphadenopathy include the common flu, tonsillitis, measles, skin infections ear infections, gingivitis, teeth infections, mononucleosis, mumps and infections of the wounds. Infections such as tuberculosis or some sexually transmitted diseases also cause the swelling of the lymph nodes. Disorders of the immune system can also cause lymphadenopathy, especially HIV, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
How to treat lymphadenopathy?
The treatment of lymphadenopathy depends on the underlying cause. If lymphadenopathy was caused by a bacterial infection, you may be given antibiotics. In case of viral infection, swelling of the lymph nodes will go away after you are cured from the infection. In case you experience pain, you may take some painkillers or Aspirin to reduce the inflammation. More severe conditions, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis require special treatment. If lymphadenopathy is a consequence of cancer, you will receive cancer treatment which may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy or surgery.
What is the name of the condition where the lymph nodes become swollen and their function becomes impaired?
Lymphadenopathy is a condition when the lymph nodes become swollen and their function becomes impaired. The lymph nodes are an important part of the immune system, so in case of any damage, you may be prone to the various diseases. You may feel the enlarged lymph nodes on your neck, under the jaw, behind the ears, on the back of the head, armpits and groins. The first symptom of lymphadenopathy is enlargement of the lymph nodes. The other symptoms are pain or tenderness of the lymph nodes, redness of the skin where the affected lymph node is and hardened lymph nodes. You may also experience symptoms which are characteristic for flu, such as fever, sore throat and runny nose.
How to get rid of lymph nodes when you are sick?
This will help your body heal and you will need less time to recover. Drink plenty of fluids each day and take some painkillers to ease pain. You can also apply warm compressions on the affected lymph nodes.
Definition
The body has approximately 600 lymph nodes, but only those in the submandibular, axillary or inguinal regions may normally be palpable in healthy people. 1 Lymphadenopathy refers to nodes that are abnormal in either size, consistency or number.
Epidemiology
Our understanding of the epidemiology of lymphadenopathy in family practice is limited by the scarcity of relevant literature. Only one study 4 provides reliable population-based estimates. Findings from this Dutch study revealed a 0.6 percent annual incidence of unexplained lymphadenopathy in the general population.
Diagnostic Approach to Lymphadenopathy
The algorithm in Figure 2 provides a diagnostic framework for the evaluation of lymphadenopathy. The algorithm emphasizes that a careful history and physical examination are the core of the evaluation.
Unexplained Lymphadenopathy
When, after the initial evaluation and after exploration of the “diagnostic” and “suggestive” branches of the algorithm ( Figure 2 ), a cause for the lymphadenopathy remains unexplained, the physician must decide whether to pursue a specific diagnosis.
Initial Management
Many patients worry about the cause of their abnormal lymph nodes. To adequately address their fears, the physician should ask the patient about his or her concerns and respond to questions about specific diagnoses. When biopsy is deferred, the physician should explain to the patient the rationale for waiting.
What Are The Causes Of Lymphadenopathy?
Many different conditions can cause swelling of the lymph nodes. Especially the lymph nodes in the head and neck region can enlarge after many different reasons.
How Is Lymphadenopathy Treated?
Treatment for lymphadenopathy depends on its cause. There are dozens of different causes that can lead to lymph node swelling, and it is very important to identify the cause.
What Is Lymphadenopathy? What Is LAP?
Lymphadenopathy (lymphadenopathy / LAP for short ) is the swelling of the lymph nodes after various reasons. Lymph nodes are part of the immune system and are found all over our body.
How long does it take for lymph node swelling to go away?
The most important distinction at this point is the duration of the LAP. In most cases, lymph node swelling disappears within 2 weeks . If lymph node swelling persists for more than 2 weeks, you may need to see a doctor.
What causes swollen lymph nodes in the groin area?
Sexually transmitted infections ( STIs ) can cause swollen lymph nodes , typically in the groin area .
Why do lymph nodes swell?
Every person will encounter lymphadenopathy at some point in their life. Due to any infection , the lymph nodes will swell and LAP will occur.
What does it mean when your lymph nodes are swollen?
If you experience lymph node swelling in more than one body part, this is considered diffuse lymphadenopathy and may be a sign of significant disease.
What causes lymphadenopathy in the throat?
Localized lymphadenopathy may occur as a result of infection or inflammation of nearby structures such as the throat, common cold, bronchitis, dental decay, conjunctivitis, ear infection , and infection of the salivary glands. In other cases, cervical lymphadenopathy can be indicative of a more generalized infection as a result ...
Why are my lymph nodes so small?
When the lymph nodes accumulate excessive amounts of lymphocytes, they can increase in size and become swollen. Cervical lymph nodes are usually very small and cannot be felt upon touch unless an underlying infection or inflammatory process has triggered an increase in size.
What is cervical lymphadenopathy?
Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to the swelling of lymph nodes located in the neck. Lymph nodes, situated all over the body, are part of the lymphatic system, which works to protect the body against microbes, maintain adequate fluid levels, absorb nutrients, and remove certain waste products. Lymphocytes, or white blood cells, are activated in the lymph nodes, after which they travel into the bloodstream to defend the body against microbes. When the lymph nodes accumulate excessive amounts of lymphocytes, they can increase in size and become swollen.
What are the most important facts to know about cervical lymphadenopathy?
Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to the enlargement of cervical lymph nodes, or the lymph nodes in the neck region. It often serves as an important clinical indicator of an underlying condition, most commonly of infectious origin. Localized lymphadenopathy may occur as a result of infection or inflammation of nearby structures such as the throat, common cold, bronchitis, dental decay, conjunctivitis, ear infection, and infection of the salivary glands. In other cases, cervical lymphadenopathy can be indicative of a more generalized infection as a result of systemic conditions, such as certain cancers, autoimmune disorders, and chronic infections. Therefore, a thorough review of medical history and a physical exam, in addition to any necessary testing, imaging, and biopsy, can help in the differential diagnosis to better identify the underlying cause. Treatment for cervical lymphadenopathy will vary based on the underlying cause, and will typically resolve with appropriate treatment of the underlying condition.
What is the name of the disease that causes a large number of inflammatory cells to grow?
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of abnormal inflammatory cell masses, and commonly targets the lymph nodes. Kawasaki disease, a rare inflammatory disease in children, usually presents with cervical lymphadenopathy. Rare causes of cervical lymphadenopathy include Kikuchi–Fujimoto disease, a self-limiting condition typically seen in young ...
What causes lymph nodes to swell?
Systemic lupus erythematosus, also known as lupus, is an inflammatory autoimmune disorder that often results in the swelling of lymph nodes throughout the body. Similarly, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that typically affects the joints ...
Can lymphadenopathy be generalized?
In some cases, lymphadenopathy can be generalized due to a systemic disease affecting organs far away from the neck. Generalized cervical lymphadenopathy is often seen in chronic infections, cancerous conditions, autoimmune disorders, and some other miscellaneous conditions. Chronic infections such as AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, ...
Why do my lymph nodes swell?
The swelling in these pea- or bean-sized lymph nodes are one of your body’s natural reactions to illness or infection. That tells doctors that your body’s healthy and robust immune system is working to clear away infection and/or invading viruses or bacteria.
What does it mean when your lymph nodes are swollen?
When swollen lymph nodes are found in two or more areas (generalized swollen lymph nodes), it usually points to a more serious systemic (meaning it’s all over your body) disease. These are wide-ranging and include: Autoimmune diseases (like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis ). Toxoplasmosis.
What does it feel like to have swollen lymph nodes?
Those lumps probably feel soft and tender to the touch — and may even hurt a little.
How to keep a swollen lymph node from catching a virus?
If you hate the discomfort of having swollen lymph nodes, your best bet is to take extra steps to keep from catching common viruses through: Proper handwashing. Avoiding touching your eyes and nose. Staying away from those who are sick.
How many lymph nodes are there in the body?
You also have lymph nodes throughout your body that you can’t feel. There’s a network of about 600 of them (the exact count actually varies by person) in your:
Why does my neck swell?
What causes swollen lymph nodes? The most common cause of lymph node swelling in your neck is an upper respiratory infection, which can take 10 to 14 days to resolve completely. As soon as you start feeling better, the swelling should go down as well, though it may take a few weeks longer to go away completely.
Can phenytoin cause swollen lymph nodes?
Your doctor will make sure your swollen lymph nodes aren’t caused by any of your medications. Some drugs, like the anti-seizure medication phenytoin (Dilantin®) can cause swollen lymph nodes. Doctors only worry about swollen lymph nodes when they enlarge for no apparent reason.
What is the most important factor in predicting the probability of whether the lymphadenopathy is due to a benign?
Age is the most important factor in predicting the probability of whether the lymphadenopathy is due to a benign or malignant lesion.
What is a streaking lymphadenopathy?
Lymphangitic streaking is a sign consistent with cutaneous infection. The presence or absence of associated signs or symptoms in patients with adenopathy should not alter the general approach, since both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients may have pathologic lymphadenopathy. Abnormal nodes may be tender, warm, erythematous, or fluctuant. The nodes may be hard or rubbery, fixed or mobile. In general, qualitative characteristics such as node consistency are not particularly helpful in distinguishing benign from malignant lesions. Although rock-hard adenopathy is associated with metastatic cancer, Hodgkin disease, or tuberculosis, each of these disorders also commonly presents with soft nodes. A tender node suggests an inflammatory lesion, but malignant nodes that are rapidly expanding or contain hemorrhage may also be tender. Sinus tract formation is associated with infectious causes of lymphadenopathy (eg, actinomycosis and mycobacterial species), but very large malignant nodes may also form sinus tracts.
How to biopsy lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes may be biopsied by excisional methods (via direct surgical extirpation, mediastinoscopy, open surgery, or laparoscopy) or by needle aspiration (core or fine needle). Gupta et al
What is axillary adenopathy?
Axillary adenopathy, like cervical adenopathy, is usually secondary to infection or malignancy. Hodgkin disease, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, carcinoma of the breast, and melanoma are common. Characteristic infectious causes of axillary lymph nodes include staphylococcal and streptococcal bacterial infections of the arm, cat-scratch fever, tularemia, and sporotrichosis.
Is lymphadenopathy a malignant disease?
Lymphadenopathy limited to the abdomen (mesenteric and/or retroperitoneal) is often malignant. Causes include non-Hodgkin lymphoma, metastatic adenocarcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, Hodgkin disease (characteristically retroperitoneal node involvement and rarely mesenteric involvement), transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hairy cell leukemia, and tuberculosis. A classic sign of gastric adenocarcinoma is the Sister (Mary) Joseph nodule in the umbilical area, which may represent a direct metastatic deposit or an enlarged anterior abdominal lymph node.
Can lymphadenopathy be palpated?
Lymphadenopathy is associated with numerous disorders. An abnormal lymph node may be observed or palpated by the patient , found by a health care worker, or discovered through radiologic evaluation.
Does alcohol cause lymph node pain?
These are characteristic of lymphoproliferative disorders but may also be present in infectious conditions. Some patients with Hodgkin disease may have pain in affected lymph nodes following alcohol ingestion.
Why do lymph nodes swell?
Swollen lymph nodes usually occur as a result of infection from bacteria or viruses. Rarely, swollen lymph nodes are caused by cancer.
What does it mean when your lymph nodes are swollen?
When this occurs, it may indicate an infection, such as HIV or mononucleosis, or an immune system disorder, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
What is the name of the small round or bean shaped cluster of cells that filter lymphatic fluid?
Lymph nodes are small, round or bean-shaped clusters of cells. Inside lymph nodes are a combination of different types of immune system cells. These specialized cells filter your lymphatic fluid as it travels through your body and protect you by destroying invaders.
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Your lymph nodes, also called lymph glands, play a vital role in your body's ability to fight off infections. They function as filters, trapping viruses, bacteria and other causes of illnesses before they can infect other parts of your body. Common areas where you might notice swollen lymph nodes include your neck, under your chin, ...
How to treat swollen lymph nodes?
In some cases, the passage of time and warm compresses may be all you need to treat swollen lymph nodes. If an infection causes swollen lymph nodes, treatment depends on the cause.
What is the disease that targets your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart and lungs?
Lupus — a chronic inflammatory disease that targets your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart and lungs
History
Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy include patient age, duration of lymphadenopathy, exposures, associated symptoms, and location (localized vs. generalized). Table 2 lists common historical clues and their associated diagnoses.
Physical Examination
Overall state of health and height and weight measurements may help identify signs of chronic disease, especially in children. 7 A complete lymphatic examination should be performed to rule out generalized lymphadenopathy, followed by a focused lymphatic examination with consideration of lymphatic drainage patterns.
Generalized Lymphadenopathy
Generalized lymphadenopathy is the enlargement of more than two noncontiguous lymph node groups. 8 Significant systemic disease from infections, autoimmune diseases, or disseminated malignancy often causes generalized lymphadenopathy, and specific testing is necessary to determine the diagnosis.
Diagnostic Approach
Figure 4 provides an algorithm for evaluating lymphadenopathy. 2 If history and physical examination findings suggest a benign or self-limited process, reassurance can be provided and follow-up arranged if lymphadenopathy persists. Findings suggestive of infectious or autoimmune etiologies may require specific testing and treatment as indicated.
Biopsy
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) and core needle biopsy can aid in the diagnostic evaluation of lymph nodes when etiology is unknown or malignant risk factors are present ( Table 4 4, 6, 10 ). FNA cytology is a quick, accurate, minimally invasive, and safe technique to evaluate patients and aid in triage of unexplained lymphadenopathy.
