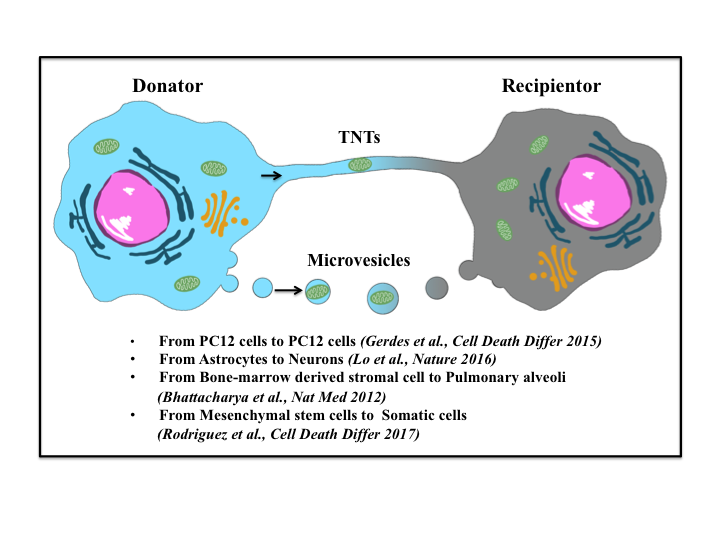
Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas).
How to get better cell signal?
How to Improve Mobile Signal Strength
- Toggle Airplane Mode or Reboot Your Phone. ...
- You're Holding It Wrong. ...
- Get a New SIM (or Clean Yours) If you've been with your carrier for a long time, your SIM card may not contain the data to connect to the latest ...
- Change Your G. ...
- Use Wi-Fi. ...
- Check Your Bands (and Get a New Phone) Carriers add new frequencies to their networks every few years. ...
Is there any way to improve cell signal?
8 Ways to Increase Your Cell Signal Indoors
- Try a Different Room. The strength of a cellphone signal often varies widely inside a building. ...
- Change Your Surroundings. It's sometimes possible to improve cellphone signal in a specific room by changing a few things around.
- Remove Your Phone Case. ...
- Turn Airplane Mode On and Off. ...
- Check Your SIM Card. ...
- Get a Signal Booster. ...
- Use Wi-Fi Calling. ...
- Switch Carriers. ...
How do I improve my cell signal?
Learn more about coaxial cable wiring. An outdoor antenna picks up a weak cell phone signal and routes it to the amplifier by coaxial cable. The indoor amplifier boosts signal strength and sends it to an indoor antenna through coaxial cable. The indoor antenna broadcasts a stronger signal inside your house.
How do you improve cell signal?
Boost your wireless signal
- Boost your indoor cell coverage up to 3,000 square feet with Cell Booster and 15,000 square feet with Cell Booster Pro 2
- Provide reliable indoor voice calling and texting
- Create seamless indoor coverage with consistent data speeds

What are cell signals called?
Synaptic signaling This process is named for the synapse, the junction between two nerve cells where signal transmission occurs. When the sending neuron fires, an electrical impulse moves rapidly through the cell, traveling down a long, fiber-like extension called an axon.
What is an example of cell signaling?
Cell signaling (also called signal transduction) describes the ability for cells to respond to stimuli from their environment. Some examples include wound healing after injury, activation of the immune system in response to pathogens, and changes in gene expression during different developmental stages.
What are the 5 types of cell signaling?
There are four categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, autocrine signaling, and direct signaling across gap junctions.
What is cell signaling and why is it important?
Cell signaling underlies critical cellular decisions such as development, cell growth and division, differentiation, migration, apoptosis, and it essentially provides the coordination required for the functionality of multicellular organisms.
What happens during cell signaling?
Cell signaling is the fundamental process by which specific information is transferred from the cell surface to the cytosol and ultimately to the nucleus, leading to changes in gene expression.
What are the 3 stages of cell signalling?
Cell signalling takes place in the following three stages: Binding of the signal molecule to the receptor. Signal transduction, where the chemical signals activate the enzymes. Finally, the response is observed.
What are the four types of cell signaling?
Depending on the ligand's origin (from the same cell, from the neighbour cell or from far distance), recptor-ligand interaction and signaling pathway activation is classified into four different types: autocrine, endocrine, paracrine and juxtacrine.
What kind of signals do cells receive?
Conclusion. Cells typically receive signals in chemical form via various signaling molecules. When a signaling molecule joins with an appropriate receptor on a cell surface, this binding triggers a chain of events that not only carries the signal to the cell interior, but amplifies it as well.
How do cells recognize signals?
How Cells Recognize and Respond to Signals. Large proteins called receptors help cells recognize signals sent to them. Receptors can be located both inside and outside of the cell or anchored into a cellular membrane. Signaling happens when specific molecules bind to their particular receptors.
What happens when cells don't communicate?
But even so, cell communication can break down. The result is uncontrolled cell growth, often leading to cancer. Cancer can occur in many ways, but it always requires multiple signaling breakdowns. Often, cancer begins when a cell gains the ability to grow and divide even in the absence of a signal.
What is an example of paracrine signaling?
Examples of paracrine signaling include responses to allergens, tissue repair, the formation of scar tissue, and blood clotting.
What is an example of endocrine signaling?
In endocrine signaling hormones are produce by an endocrine gland and sent through the blood stream to distant cells. Hormones can be: small lipophilic molecules that diffuse through the cell membrane to reach cytosolic or nuclear receptors. Examples are progesterone and testosterone, as well as thyroid hormones.
What is an example of a signal transduction pathway?
The types of receptors and their second messengers do have similarities but can also be vastly different from each other. Some examples of signal transduction pathways include vision and touch and hormones.
What is cell signaling in plants?
In plants, as in animals, cells are in constant communication with one another. Plant cells communicate to coordinate their activities in response to the changing conditions of light, dark, and temperature that guide the plant's cycle of growth, flowering, and fruiting.
What is cell to cell signalling?
Cell to cell signalling refers to the transfer of information from one cell to another. Cells signal either by direct contact or by releasing certa...
What are the different types of cell signalling?
The different types of cell signalling include: Paracrine signalling Autocrine signalling Endocrine signalling Direct Contact
What is the importance of cell signalling?
Cell signalling is an important factor in life. The cells receive the signals and respond to the extracellular environment, thereby, allowing growt...
What is cell signaling?
Cell signaling is how a tiny gland within the brain can react to external stimuli and coordinate a response. In response to stimuli like light, odors, or touch, the gland can, in turn, release a hormone that activates responses in diverse body systems to coordinate a response to a threat or opportunity.
How does cell signaling work?
Cell signaling can occur through a number of different pathways, but the overall theme is that the actions of one cell influence the function of another. Cell signaling is needed by multicellular organisms to coordinate a wide variety of functions.
How Does Insulin Signal a Cell to Take in Glucose?
Insulin, a small protein produced by the pancreas, is released when glucose levels in the blood get far too high.
What is the function of ligands in a receptor?
In general, a ligand will activate a receptor and cause a specific response. Receptors are typically protein molecules, as seen in blue below. The orange ligand can be many different types of molecules, but it forms an induced fit with the receptor that is very specific.
How many classifications are there for signaling molecules?
Signaling molecules are currently assigned one of five classifications.
Why is cell signaling important?
Cell signaling serves a vital purpose in allowing our cells to carry out life as we know it. Moreover, thanks to the concerted efforts of our cells via their signaling molecules, our body is able to orchestrate the many complexities that maintain life.
What cells must communicate with muscle cells to create movement?
Nerve cells must communicate with muscle cells to create movement, immune cells must avoid destroying cells of the body, and cells must organize during the development of a baby. Some forms of cell signaling are intracellular, while others are intercellular. Intracellular signals are produced by the same cell that receives the signal.
Why is cell signalling important?
Cell signalling is an important factor in life. The cells receive the signals and respond to the extracellular environment, thereby, allowing growth, development and immunity. Explore Your Knowledge!
What are the stages of cell signalling?
Cell signalling takes place in the following three stages: Binding of the signal molecule to the receptor. Signal transduction, where the chemical signals activate the enzymes. Finally, the response is observed.
What binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase?
A ligand binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase that results in the dimerization of the kinase domains. The tyrosine kinase domains of the dimer then phosphorylate that allows the intracellular proteins to bind the phosphorylated sites and activate.
What are the two types of cell signalling pathways?
The cell signalling pathways are either mechanical or biochemical. The cell signalling is categorized based on the distance it must travel. For instance, hydrophobic ligands include steroids and vitamin D3. These can diffuse across the plasma membrane of target cells and bind to the intracellular cells.
How does intercellular signaling work?
The message carried by the cells is passed through a chain of chemical messengers within the cells. This results in changes in the cell such as alteration in the gene activity or the entire process. Thus, an intercellular signal gets converted into an intracellular signal that stimulates a response.
What is intracellular signal?
Intracellular signals are produced by the same cells that receive the signal. Intercellular signals travel throughout the body. This permits specific glands to produce signals that act on different tissues. Also Read: What are Cells.
Why do multicellular organisms need cell signalling?
Multicellular organisms need cell signalling to regulate different functions. E.g. nerve cells in coordinate with muscle cells to help in body movement. Cell signalling can be intercellular as well as intracellular. Intracellular signals are produced by the same cells that receive the signal.
What is cell signaling?
Cell signaling is a method of communication of one cell with other cells. This is done by following methods like. Synaptic signaling. Cells need to communicate with other cells for the normal physiology of the body.
Where does cell signaling occur?
Here the cell signal occurs in between cells having physical contact with each other. This occurs at the cell membrane level. One cell has a signal molecule, and the other has a receptor moiety on their cell surfaces. But both the cells are physically connected where the signaling occurs.
What is autocrine signaling?
Autocrine signaling. This is a type of cell signal where a cell gives a signal to itself. A signal molecule is released out of the cell. This molecule, in return, acts and gives a signal to the same cell through surface receptors. Examples: The monocytes produce cytokines that affect themselves.
How is the signal passed from one nerve cell to another?
Here the signal is passed from one nerve cells to another through the neurotransmitter.
How is signal given to another cell?
This is a signal which is given by one cell to another cell located in a distant region. The signal molecule is released into the bloodstream. This is then carried away and distributed by the blood to other cells. These distant cells receive the signal.
Why do cells need to communicate with other cells?
Cells need to communicate with other cells for the normal physiology of the body. Sometimes they signal the nearby cells, and other times they signal to distant cells.
Do cells need to be directly connected?
But, the cells need not be directly connected. The signal molecules are released by one cell. These molecules reach nearby cells around and transmit the signal. Examples: Cytokines like the prostaglandins show this type of signaling.
What are the different types of signaling pathways?
Depending on the ligand’s origin (from the same cell, from the neighbour cell or from far distance), recptor-ligand interaction and signaling pathway activation is classified into four different types: autocrine, endocrine, paracrine and juxtacrine.
Where do endocrine signals originate?
Endocrine signals often originate from within the brain, however other glands and organs, including the thyroid gland, stomach, pancreas, liver, kidneys and reproductive organs, also produces hormones. One endocrine signal that must travel a great distance is that of follicle-stimulating hormone ...
What is juxtacrine signaling?
Juxtacrine signaling. Juxtacrine signaling occurs between neighboring cells that are in physical contact with each other. In this case, the signaling molecule is not free, but is instead bound to the membrane of the cell. It may then interact with a receptor on the membrane of an adjacent cell. An example of juxtacrine signaling is ...
What is the term for the molecule secreted by one cell diffuses to another cell in the local neighborhood?
Paracrine signaling. Paracrine signaling occurs between cells in close proximity to each other. Here, a soluble signaling molecule secreted by one cell diffuses to another cell in the local neighborhood.
Which endocrine signal must travel a great distance?
One endocrine signal that must travel a great distance is that of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which is sent from the anterior pituitary gland to the testes or ovaries where it stimulates the maturation of germ cells.
Where do hormones come from?
Endocrine signals often originate from within the brain, however other glands and organs, including the thyroid gland, stomach, pancreas, liver, kidneys and reproductive organs, also produces hormones. One endocrine signal that must travel a great distance is that of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which is sent from the anterior pituitary gland to the testes or ovaries where it stimulates the maturation of germ cells.
Digital Cellular (2G)
With the arrival of 2G (2nd Generation) wireless connectivity, cellular signals moved from the analog to the digital world. 2G signals are clearer and quieter than the analog ones they replaced but they can only handle data transmissions at speeds below 20Kbps.
Packet Based Cellular (2.5G)
2.5G network enhancements bridged the gap between 2G and the massive improvement that came with 3G wireless. With dial-up data transmission speeds of 30Kbps to 90Kbps it's possible to send and receive multimedia and even to surf the Web slowly.
Wideband Cellular (3G)
Most phones today transmit and receive 3G signals at DSL speeds of 144Kbps to Cable speeds of 3Mbps. This dramatic improvement in bandwidth has changed mobile phones from basic communication devices to complete information portals. Now you can stream audio and video files and broadcasts to your phone and load Web sites in seconds.
Ultrawideband Cellular (4G)
As good as 3G is, it's performance can vary widely depending on the signal strength in your area. 4G intends to change this with an even wider bandwidth and speeds up to an unheard of 1 Gbps. It might sound like overkill but this signal's excess capacity makes it possible to get broadband speeds wherever you are.
What is the measurement of cell tower signal?
The signal your phone receives from a cell tower is measured in decibel-milliwatts ( dBm ), a unit of electrical power in milliwatts (mW) expressed on a decibel (dB) scale. There are the three things you need to know about decibel-milliwatts:
What does a signal bar mean?
Signal bars are not an accurate measurement of the strength of the signal your cell phone is receiving. While they do indicate something about the quality of your reception, there’s no industry standard for “ this much signal equals this many bars”—each cell phone manufacturer uses their own calculation. When placed next to each other, two different brands of phones on the same cellular network might display different numbers of bars.
How strong is a mW cell phone?
1 milliwatt (1 mW) is equal to 0 decibel-milliwatts (0 dBm). Since cell phones receive and transmit using much less power than 1 milliwatt (often as low as 0.00000000001 mW or less), cell signal strength is less than 0 dBm and therefore measured in negative numbers . The closer you get to 0 dBm, the stronger the signal; for example, −70 dBm is stronger than −90 dBm, −95 dBm is stronger than −105 dBm, and so forth.
What frequency is cellular transmission?
Different cellular frequencies travel shorter or longer distances. Cellular transmissions in lower frequency ranges (700 MHz LTE and 850 MHz CLR) have more than twice the range of transmissions in higher cellular frequencies (1900 MHz PCS and 1700/2100 MHz AWS).
Why is cellular service slower at 700 MHz?
You might be able to get slower cellular service at 700 MHz inside a large, downtown building but not get faster PCS or AWS service because those higher-frequency bands can’t get through the building’s concrete exterior.
Why does my cell tower signal fluctuate?
Standing still, you’ll commonly see fluctuations of ±5 dB. This is mainly due to user load on the cell tower —the tower antenna’s power has to be spread across all the connected devices. Peak usage times (rush hour, lunch hour, etc.) can result in noticeably lower power for all users.
Where is the signal strength on my phone?
If you have an Android smartphone, look in the phone’s settings under Signal Strength . Exactly where this is found varies between phone models, but it’s usually somewhere in the phone’s settings; possible locations include: Settings > About Phone > Status > Signal Strength.
What is cell phone signal?
Cell phone signals are radio waves, the AM/FM kind, that operate within a certain frequency. They are measured within the following strength ranges:
How to read your iPhone cell signal?
Starting with iOS 11 and 12, Apple has hidden dBm readings in iPhone field test mode. However, depending on your iPhone chipset (Intel or Qualcomm) and your carrier (Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint), there’s a slim chance to find your dBm readings through this workaround.
How many bars is a good signal?
If your outside signal ranges from: -50 to -79 dBm, then it's generally considered great signal ( 4 to 5 bars ). -80 to -89 dBm, then it's generally considered good signal ( 3 to 4 bars ). -90 to -99 dBm, then it's generally considered average signal ( 2 to 3 bars ).
Is there a standard for cell phone signal strength?
There is no industry standard that ties cell phone signal strength to the number of bars on your phone. Even the difference between 4G and LTE is murky to most people. But there is the one true method.
Why is my cell signal blocked?
Geographic features are a common reason for cell signal obstruction. If you live on one side of a mountain, and the only cell tower in your area is on the other, you’re not likely to get good reception.
What Causes Bad Cell Phone Signal?
You’re texting or chatting on your mobile phone, when suddenly your call drops off or your conversation disappears.
How Can I Boost My Poor Cell Phone Signal?
A cell phone signal booster, also known as cellular repeaters and amplifiers, increases your weak signal up to 32 times, whether at home, in your car, or in a public place such as an office building.
How May We Help You?
Wilson Amplifiers is the leading provider of cellular amplifiers. Cell phone amplifiers boost 3G & 4G LTE for any phone with any carrier for home, office, or vehicle.
Why is my phone signal fading?
If you routinely notice service fading in and out as you walk around your home, or if your signal improves when you stand near a window or door, it’s likely your signal is being blocked by metal construction material.
How does a rebroadcast antenna work?
It works by pulling in weak signal, amplifying it multiple times, then rebroadcasts the boosted signal to an area in need.
Why does my cell phone call fade?
Did you just walk into a grove of trees? The leaf canopy can block some cell signals and cause your call to fade or drop altogether. If your home is surrounded by large, coniferous trees, these can be causing a massive drop in your cellular reception.
What are the factors that affect cell signal?
Your local environment - hills, buildings, being in a basement or underground will all affect your cell signal.
What affects cell phone signal?
The main thing that affects your cell signal is your carrier's coverage. If you're literally stood next to one of their cell towers you'll have a perfect signal. But if you're a long way from a tower, that signal may come and go. This can affect your data download speeds, or result in dropped calls.
What is signal checker?
Our Signal Checker shows the coverage and signal strength for your zip code and helps you see which carrier will give you the best service. We check all the main carriers at once, saving you the time and effort of having to visit them all individually.
Why is my cell phone signal inconsistent?
This is because you're constantly moving out of the range of one cell tower, and into range of another, and your phone has to keep switching connections between them.
What to know before signing up for a new phone carrier?
Before you sign up with a new carrier, you need to be sure that you can get good reception - both good coverage and a reliable signal - where you live and work. If you can't, you might not be able to make calls, send messages, or use apps when you need to.
How fast is 4G?
It has over 90% coverage around the US, and all modern smartphones support it. You can get speeds over 150Mbps.
Do modern phones support all types of cell phone service?
Most modern phones do support them all. For voice calls, the situation also used to be complicated. Carriers used one of two types of cellular tech - GSM or CDMA - and you needed a phone that was compatible with whichever service your carrier used. However, this only applies to 2G and 3G connections.

Overview
Three Stages of Cell Signaling
- At its core cell signaling can simply be described as the production of a “signal” by one cell. This signal is then received by a “target”cell. In effect, signal transduction is said to have three stages: 1. First, reception, whereby the signal molecule binds the receptor 2. Then, signal transduction, which is where the chemical signal results in a series of enzyme activations 3. Finally, the respo…
Types of Cell Signaling Pathways
- Cell signaling serves a vital purpose in allowing our cells to carry out life as we know it. Moreover, thanks to the concerted efforts of our cells via their signaling molecules, our body is able to orchestrate the many complexities that maintain life. These complexities, in effect, demand a diverse collection of receptor-mediated pathways that execute their unique functions. In general…
Cell Signaling Ligands
- Typically, cell signaling is either mechanical or biochemical and can occur locally. Additionally, categories of cell signaling are determined by the distance a ligand must travel. Likewise, hydrophobic ligands have fatty properties and include steroid hormones and vitamin D3. These molecules are able to diffuse across the target cell’s plasma memb...
Types of Cell Signaling Molecules
- Signaling molecules are currently assigned one of five classifications. 1. Intracrineligands are produced by the target cell. Then, they bind to a receptor within the cell. 2. Autocrineligands are distinct in that they function internally and on other target cells (ex. Immune cells). 3. Juxtacrineligands target adjacent cells (often called “contact-dependent” signaling). 4. Paracrine…
How Does Insulin Signal A Cell to Take in Glucose?
- A great (and well-used) example of a cell signaling pathway is seen in the balancing actions of insulin. Insulin, a small protein produced by the pancreas, is released when glucose levels in the blood get far too high. First, the high glucose levels in the pancreas stimulate the release of insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin finds its way to the cells of the body, where it attaches to th…
Bibliography
- Bruice, P. Y. (2011). Organic chemistry(6th ed). Boston: Prentice Hall. Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2008). Lehninger principles of biochemistry(5th ed). New York: W.H. Freeman. Lodish, H. F. (Ed.). (2008). Molecular cell biology(6th ed). New York: W.H. Freeman.