Common Causes
What are the Similarities Between Tissue and Cell?
- Cell and tissue are two levels of the cellular organization of a multicellular organism.
- Importantly, the tissue is a collection of cells working together.
- Tissues and cells are found in living organisms.
- Also, both cell and tissue fulfil different functions inside an organism.
Related Conditions
Types of tissues
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Nervous tissue.
What is the difference between cells and tissues?
What are 5 types of cells?
- Stem cells. Stem cells are cells that are yet to choose what they are going to become. …
- Bone cells. There are at least three primary types of bone cell:
- Blood cells. There are three major types of blood cell:
- Muscle cells. …
- Sperm cells. …
- Female egg cell. …
- Fat cells. …
- Nerve cells.
What are the 4 types of tissues and their functions?
Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are four main tissues in the body – epithelium, muscle, connective tissue and nervous tissue. I. EPITHELIUM
What are the 4 different types of cells?
How many tissues are in the human body?
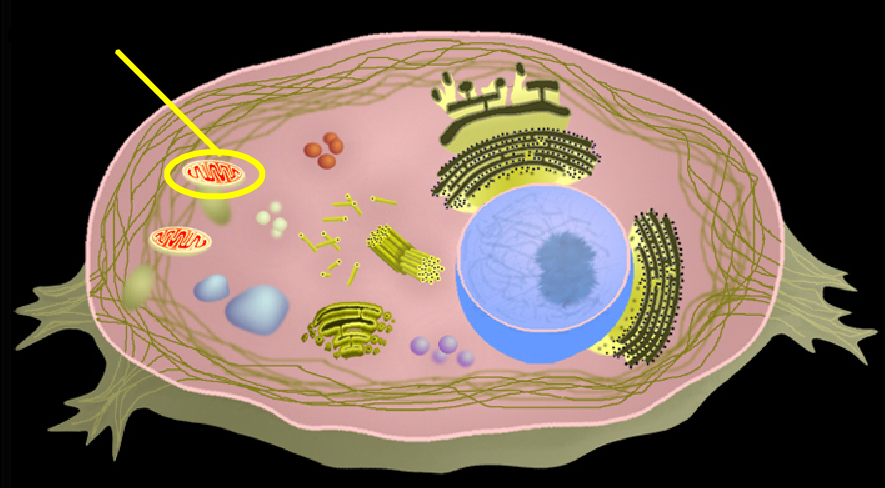
What is a tissue?
Tissue is a group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit. A nonliving material, called the intercellular matrix, fills the spaces between the cells. This may be abundant in some tissues and minimal in others.
What are cells?
(sel) In biology, the smallest unit that can live on its own and that makes up all living organisms and the tissues of the body. A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell.
What are tissues called?
There are 4 basic types of tissue: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Connective tissue supports other tissues and binds them together (bone, blood, and lymph tissues). Epithelial tissue provides a covering (skin, the linings of the various passages inside the body).
What is cell example?
Trees in a forest, fish in a river, horseflies on a farm, lemurs in the jungle, reeds in a pond, worms in the soil — all these plants and animals are made of the building blocks we call cells. Like these examples, many living things consist of vast numbers of cells working in concert with one another.
What are the 4 types of cells?
The Four Main Types of CellsEpithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another. ... Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication. ... Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction. ... Connective Tissue Cells.
What is cell for Class 7th?
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life's processes.” Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.
What are 5 types of cells?
What Are The 5 Types Of Cells?Blood cells.Stem cells.Fat cells.Skin cells.Endothelial cells.
What makes a cell a cell?
What is a cell? A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks.
What is the difference between a cell and a tissue?
Cell and Tissue – Differences. Cells are the smallest, structural and functional unit of an organism, which is characteristically microscopic. Tissues are the distinct types of material consisting of specialized cells and their products. Found in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
What is tissue in biology?
Tissues are groups of similar cells, working together to perform a specific function. They are structurally and functionally similar to the cells. The word tissue is mainly derived from a Latin word meaning weave.
What are the two types of tissues in the plant kingdom?
In the plant kingdom, tissues are divided into two different types: Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue.
What are some examples of multicellular organisms?
Plants, animals, human beings, birds are examples of multicellular organisms. There are two different types of cells, the prokaryotic cells and the eukaryotic cells and these differences are mainly based on the presence and absence of the nucleus in their cell.
Which organisms are unicellular?
These unicellular organisms include amoeba, algae, bacteria, fungi, Protista etc. Multicellular organisms consist of different types of cells which have specialized functions.
What is the smallest unit of life?
The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life. There is no living creature existing on the planet earth without the cell. Therefore it is referred to as a fundamental unit of life. Every function of the body is executed through these minute cells.
What are some examples of nerve tissue?
Nervous Tissue: Brain, spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system are examples of Nervous Tissue. Epithelial Tissue: Surface of the skin, the reproductive tract, the airways, and the inner lining of the digestive tract are examples of Epithelial Tissue. Also Read: Discovery of Cells.
What are the parts of a cell?
Here is what we have learned from Cells, Tissues, and Membranes: Basically, a cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and between the two, the cytoplasm. The cell nucleus contains genetic material and regulates activities of the cell.
Which tissue is responsible for covering all body surfaces?
Epithelial tissues form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. Connective tissues bind structures together, form a framework and support for organs and the body as a whole, store fat, transport substances, protect against disease, and help repair tissue damage.
Which tissue is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities?
Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of body parts. Nervous tissue is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities. Body membranes are thin sheets of tissue that cover the body, line body cavities, and cover organs within ...
Where are the functions of cells carried out?
All of the functions for cell expansion, growth and replication are carried out in the cytoplasm of a cell. Tissue is a group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit. Primary types of body tissues include epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
What is the membrane of the body?
Body membranes are thin sheets of tissue that cover the body, line body cavities, and cover organs within the cavities in hollow organs.
What is the tissue of the body?from verywellhealth.com
Tissues. When cells of a certain type are grouped together, the resulting structure is called tissue. There is muscle tissue, which is made of strands of muscle cells. Adipose tissue is one layer of skin made of fat cells.
What are nerve cells?from verywellhealth.com
Nerve cells are long, thin and covered in myelin, natural insulation. Nerve cells conduct impulses, which are used to communicate. They're basically the telephone wires of the body, and they the part. Muscle cells are thick and elongated, like live rubber bands. Red blood cells are flat and oval-shaped.
What is the name of the organ that has connective tissue?from verywellhealth.com
Organs. When different types of tissues are organized together to perform a complex function, it's called an organ. The heart is an organ. It has muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nerve tissue all working together to pump blood. Organs can do more than one function and each function can be pretty complicated.
What are the shapes of muscle cells?from verywellhealth.com
Muscle cells are thick and elongated, like live rubber bands. Red blood cells are flat and oval-shaped. The shapes of the cells help them with their individual functions. Each cell serves a single purpose in the body. Muscle cells contract and nerve cells transmit impulses.
What are the functions of organs?from verywellhealth.com
Organs can do more than one function and each function can be pretty complicated. The eyes sense color, movement, and light. They move and focus. The biggest organ in (or on) the human body is the skin. It's a great example of layers of tissue working together to do several functions: 1 Holds in fluids 2 Regulates heat 3 Senses heat and pressure
What is the smallest unit of life?from verywellhealth.com
Cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. To understand what a cell looks like, picture a chicken egg. It has an outer membrane (in the case of an egg, it's a hard shell, but most cells aren't like that); it's filled with nutrient-rich fluid (whites of the egg versus cytoplasm in a cell) and has a nucleus (egg yolk).
What is the biggest organ in the human body?from verywellhealth.com
The biggest organ in (or on) the human body is the skin. It's a great example of layers of tissue working together to do several functions: Holds in fluids. Regulates heat. Senses heat and pressure. The organization of the anatomy starts with these three building blocks.
What is the difference between cells and tissues?
While they are both important parts of our body, they serve different purposes. Cells make up tissue and our bones, muscles, organs, and other structures in the body. Tissues are made up of many cells that work together to form particular shapes or functions, such as skin or cartilage.
What Is Tissue?
Tissues are made up of many cells that work together to form particular shapes or functions. Skin, bone, cartilage, and muscle are examples of tissues with different cell types to carry out their function. Much like cells, tissues also vary in size and shape. Cartilage is a tough but flexible tissue that covers our joints to allow them to move freely without causing damage or inflammation. The skin, on the other hand, is more elastic with an elastic layer of fat underneath it for insulation purposes.
What is the most basic criteria for differentiation between cells and tissues?
Cartilage is a tough but flexible tissue that covers our joints to allow them to move freely without causing damage or inflammation. It is considered as the major and most basic criteria to differentiate between cells and tissues.
How do cells differ from other cells?
For example, brain cells don’t look like skin cells or muscle cells. Cells can be differentiated by their shapes and what they do for the organism. You can also differentiate between cells and tissues with their shape. Brain cells will not function as blood cells because they have specialized features that will not allow them to do so. For a better understanding of cells, take a look at the diagram of a cell to understand the structure and functions of the Cell
Why is cartilage soft?
While this type of tissue may appear soft because it contains fluid-filled spaces between its cells, it is actually very tough and can withstand a lot of pressure.
What is the nervous tissue that extends outward?
This type of tissue is mostly made up of cell bodies containing dendrites and axons that extend outward to other cells to carry messages from one place to another.
How many types of cells are there in the human body?
When you learn about what a cell is, you need to know how many types of cells are present in your body. There are billions of different cell types within our body. These include brain, skin, and muscle cells, to name a few, with each type performing a specific function that is crucial for keeping us healthy.
What is the cell?
cell. cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature.
What is the skeletal system of an animal?
Skeleton, the supportive framework of an animal body. The skeleton of invertebrates, which may be either external or internal, is composed of a variety of hard nonbony substances. The more complex skeletal system of vertebrates is internal and is composed of several different types of tissues that...
What is the digestive system?
The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms absorbable into the bloodstream. ... Encyclopedia / Cells, Organs & Tissues. Written By.
What is the function of a cooperative assembly of similar cells?
Cooperative assemblies of similar cells form tissues, and a cooperation between tissues in turn forms organs, which carry out the functions necessary to sustain the life of an organism.
What is the reproductive system of plants?
plant reproductive system, any of the systems, sexual or asexual, by which plants reproduce. In plants, as in animals, the end result of reproduction is the continuation of a given species, and the ability to reproduce is, therefore, rather conservative, or given to only moderate change, during...
What is the system that transports nutrients, respiratory gases, and metabolic products throughout a living organism?
Circulatory system. Circulatory system, system that transports nutrients, respiratory gases, and metabolic products throughout a living organism, permitting integration among the various tissues. The process of circulation includes the intake of metabolic materials, the conveyance of these materials throughout the...
Which organ system produces urine?
Renal system. Renal system, in humans, organ system that includes the kidneys, where urine is produced, and the ureters, bladder, and urethra for the passage, storage, and voiding of urine. In many respects the human excretory, or urinary, system resembles those of other mammalian species, but it has its own...
What is tissue A?
A is a group of cells that share a function. The cells within a tissue may differ from each other, but they all contribute to a particular function. I’m going to introduce three types of tissues in this lecture: dermal, cortex, and vascular tissues.
How many types of cells are in phloem tissue?
Phloem tissue also has four types of cells:
What are the three types of vascular tissue?
There are three main types of vascular tissue: xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium. Xylem and phloem are composed of different types of cells which are listed below.
What is the primary cell wall?
This type of cell has a primary and secondary cell wall. The primary cell wall, on the outside of the cell, is rich in cellulose, just like other plant cell walls. Once the cell has reached its final size, a secondary cell wall is deposited just inside the primary wall. The secondary wall has a high concentration of lignin that gives the cell rigidity. This rigid, lignified secondary cell wall is responsible for sclerenchyma’s hardness and strengthening properties. Sclerenchyma comes in two types:
Where are sclerenchyma cells located?
These are sclerenchyma cells lying near the vessels and tracheids, and so are part of the vascular bundle. They are also strung together end to end like the vessels and tracheids, but unlike those water carriers they have no pits or perforations and instead have thick primary and secondary cell walls. They provide flexible support for the plant from within the vascular bundles.
What are some examples of plant fibers?
We extract these fibers from plants and use them in fabrics, carpets, and rope. Examples of plant fibers made up of sclerenchyma cells include jute, hemp, and flax (the fabric made of flax fibers is called linen). Not cotton though. Cotton is an epidermal fiber produced by the plant’s seed coats.
What are sclerids in plants?
Sclereids – cells with hard, tough cell walls. Sclereid cells can coalesce and cover other plant parts. For instance they form the hard covering around the seeds (the endocarp) of stone fruits (like cherry pits), the hard shell around walnuts, and the hard covering of coconut. Sclereids also make up the grit that crunches between your teeth when you eat a pear.
What are cells called?
CELLS are often called the microscopic building blocks of the body. They are active and dynamic, they continually grow and specialize, function, die, and
What is the difference between living things and cells?
1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are an organisms’ basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells come only from existing cells. 4. Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level. 5. Homeostasis at the level of the tissue, organ, organ system, and organism, reflects the combined and coordinated actions of billions of cells !
How many proteins are in the cell membrane?
The cell membrane also contains many different proteins which make up about half of its surface. Many of these proteins are embedded in the membrane but stick out on both sides. There are thousands of proteins and ion channels on each of the 37.2 Trillion cells in the body !!
How many types of cells are there in the human body?
As mentioned, there are 226 types of Body cells - some can form sheets like those in your skin or lining your mouth, while others can store or generate energy, such as fat and muscle cells. All cells have an outer membrane, a control center called a nucleus that contains our DNA, and tiny powerhouses called mitochondria.
How long does it take for a cell to divide into two cells?
The longer name for the final part of the process is Cytokinesis. It takes 2 hours for each cell to divide into 2 cells !! There is another type of cell division called Meiosis.
How many micrometers are in a cell?
Typical cells range from 5 –50 micrometers (microns) in diameter
How big is a cell?
Cells are considered as the basic unit of Life !! Cells are extremely small, typically only about 0.01 millimeter (.0004 or 4 ten-thousandths of an inch) across – even our largest cells are no bigger than the width of a human hair.
Why are cells called cella?
Robert Hook first discovered cells in 1665. He gave them their name because they resembled the cella (Latin for “small rooms”) where monks lived in monasteries.
How many nuclei are there in a cell?
There is normally one nucleus per cell, but this is not always the case, skeletal muscle cells, for instance, have two. The nucleus contains the majority of the cell’s DNA (a small amount is housed in the mitochondria, see below). The nucleus sends out messages to tell the cell to grow, divide, or die.
What is the difference between a sperm cell and a nerve cell?
For instance, a sperm cell resembles a tadpole , a female egg cell is spherical , and nerve cells are essentially thin tubes.
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly made of phospholipids, which prevent water-based substances from entering the cell. The plasma membrane contains a range of receptors, which carry out a number of tasks, including being: 1 Gatekeepers: Some receptors allow certain molecules through and stop others. 2 Markers: These receptors act as name badges, informing the immune system that they are part of the organism and not a foreign invader. 3 Communicators: Some receptors help the cell communicate with other cells and the environment. 4 Fasteners: Some receptors help bind the cell to its neighbors.
Why are daughter cells called diploids?
Both daughter cells have the same chromosomes as each other and the parent. They are referred to as diploid because they have two complete copies of the chromosomes.
What is the smallest unit of life that can replicate?
They function on their own, creating their own energy and self-replicating — the cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate. However, cells also communicate with each other and connect to create a solid, well stuck-together animal.
What is the membrane that keeps cells separate from their neighbor?
Plasma membrane. To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly made of phospholipids, which prevent water-based substances from entering the cell.