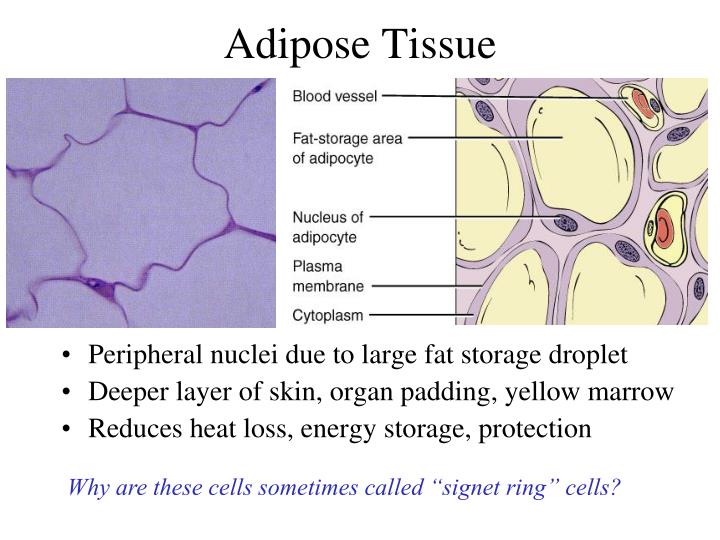
Adipose, or fat, tissue is loose connective tissue composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides
Triglyceride
A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose fr…
Adipose tissue
In biology, adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immun…
| Definition | A type of specialized connective tissue whose main functions are to store the energy, protect the organs and contribute to the endocrine profile of the body |
|---|---|
| Structure | Adipocytes (white, brown and beige) Thin extracellular matrix consisting of reticular fibers |
What are the different types of adipose tissue?
Types
- White adipose tissue: White adipose tissue (WAT) provides your body with energy, insulation, and protection, and is generally found around the hips, thighs, belly, or buttocks.
- Brown adipose tissue. A small amount of fat in your body is brown adipose tissue (BAT). ...
- Beige adipose tissue. ...
What does adipose tissue feel like?
What does adipose tissue feel like? Fat necrosis feels like a firm, round lump (or lumps) and is usually painless, but in some people it may feel tender or even painful. The skin around the lump may look red, bruised or occasionally dimpled.
What is the structure and function of adipose tissue?
What is the structure of adipose tissue? Lying three layers deep under the skin, the adipose tissue is composed of a loose collection of specialized cells, called adipocytes, embedded in a mesh of collagen fibers. Its main role in the body is function as a fuel tank for the storage of lipids and triglycerides.
Which section of the skin contains adipose (fat) tissue?
Adipose tissue is distributed within two compartments of the human body: Parietal or subcutaneous fat, which is embedded in the connective tissue under the skin ; Visceral fat, which surrounds the internal organs, such as eyeballs (periorbital fat) or kidneys (perirenal fat capsule).; Like every other tissue, adipose tissue consists of cells and extracellular matrix.

What are the characteristics of adipose tissue quizlet?
White adipose tissue is the predominant type in adult humans. It is subcutaneous fat, lying below the epithelial layer and CT. Its main functions are energy storage, cushioning and insulation. Brown adipose tissue is brown fat that is present in a baby, but lost with age, as well as in hibernating animals.
What are three adipose tissue functions?
Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, and insulate the body.
Which best describes adipose tissue?
Which is the best description of adipose tissue? It forms a tough, flexible network that provides support and resists distortion. Consisting of all of the cell types found in other forms of connective tissue proper, this tissue functions as the general packing material in the body.
What is the main role of adipose tissue?
The adipose tissue is a critical regulator of systemic energy homeostasis by acting as a caloric reservoir. In excess nutrient conditions, the adipose tissue stores surplus nutrients in the form of neutral lipids, whereas in nutrient deficit conditions, it supplies nutrients to other tissues through lipolysis (1).
Where is adipose tissue found and what is its function?
Adipose tissue is found directly beneath the skin, between muscles, around the kidneys and heart, behind the eyeballs, and abdominal membranes. It serves as a layer of protection, absorbing shock potentially sustained by the tissue.
What is the function of adipose tissue around the heart?
Cardiac adipose tissue is a metabolically active organ and plays an active role in lipid and energy homeostasis. Not only does it act as a source of energy for the myocardium, it also acts as a buffer in the context of excess circulating free fatty acids (FFAs).
What is an example of adipose tissue?
In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), around internal organs (visceral fat), in bone marrow (yellow bone marrow), intermuscular (Muscular system) and in the breast (breast tissue).
What are the functions of adipose tissue class 9?
The adipose tissue's main function is to store energy in the form of fat.
What is adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes...
How is adipose tissue classified?
Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fet...
Where is adipose tissue found?
Adipose tissue can be found in a number of different places throughout the body. White adipose tissue is the most abundant type of fat in humans. I...
What is the function of adipose tissue?
The main function of white adipocytes is to store excess energy in the form of fatty molecules, mainly triglycerides. Fat storage is regulated by s...
What are the most important facts to know about adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue is a specialized connective tissue mainly composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes can be subdivided into three cell ty...
What is adipose tissue?
Definition. A type of specialized connective tissue whose main functions are to store the energy, protect the organs and contribute to the endocrine profile of the body. Types.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
As it comprises about 20-25% of total body weight in healthy individuals, the main function of adipose tissue is to store energy in the form of lipids (fat). Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the skin) ...
Why do brown adipocytes have sponges?
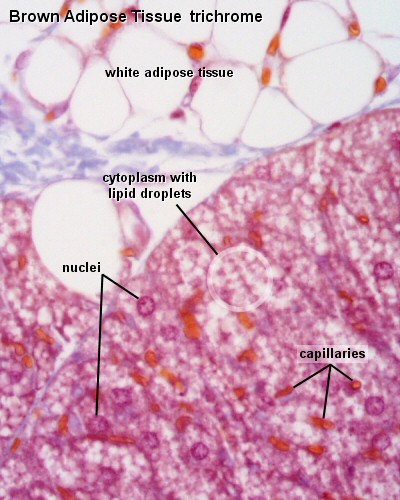
In contrast to white adipocytes, brown adipocytes have the appearance of a sponge due to the multiple droplets in the cytoplasm. Groups of adipocytes are divided into lobules by connective septa, which contain a substantial amount of blood vessels and unmyelinated nerve fibers. The extracellular matrix between individual cells within the lobules is sparse.
Why do adipocytes appear empty?
This is described as "signet ring" appearance of the unilocular tissue. This is because the intracellular fat droplet gets dissolved when dyed with standard histology staining methods (H&E staining).
What are the two types of fat tissue?
Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the skin) and visceral (surrounding organs ). Depending on adipocyte morphology, there are two types of adipose tissue: White adipose tissue - mainly found in adults. Brown adipose tissue - mainly found in newborns.
Why are adipocytes important?
The strong external membrane of adipocytes is of key importance for resilience to mechanical stress and disruption.
Where is adipose tissue located?
Adipose tissue is distributed within two compartments of the human body: Parietal or subcutaneous fat, which is embedded in the connective tissue under the skin. Visceral fat, which surrounds the internal organs, such as eyeballs (periorbital fat) or kidneys (perirenal fat capsule).
What are the different types of adipose tissue?
There are three types of adipose tissue: white, brown, and beige adipose. White adipose stores energy and helps to insulate the body. Brown and beige adipose tissue burn energy and generate heat. Their color is derived from the abundance of blood vessels and mitochondria in the tissue.
Why is adipose tissue important?
In addition to storing fat, adipose tissue also produces endocrine hormones which regulate adipocyte activity and are necessary for the regulation of other vital bodily processes. Adipose tissue helps to cushion and protect organs, as well as insulate the body from heat loss.
What is the function of adipocytes?
Adipose, or fat, tissue is loose connective tissue composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides. These cells swell as they store fat and shrink when the fat is used for energy. Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, ...
Which cells are derived from precursor cells that develop into one of three types of adipose tissue?
Other types of cells that comprise adipose tissue include fibroblasts, white blood cells, nerves, and endothelial cells . Adipocytes are derived from precursor cells that develop into one of three types of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, ...
Where is adipose tissue located?
Adipose Tissue Location. Adipose tissue is found in various places in the body. Some of these locations include the subcutaneous layer under the skin; around the heart, kidneys, and nerve tissue; in yellow bone marrow and breast tissue; and within the buttocks, thighs, and abdominal cavity.
Where is brown fat found?
In adults, small deposits of brown fat are found on the upper back, the side of the neck, the shoulder area, and along the spine. Infants have a greater percentage of brown fat than do adults. This fat can be found on most of the back region and is important for generating heat.
Why is adipose tissue important?
Adipose tissue is an organ that performs a lot of significant physiological functions, which is why its excess in the body results in pathological states in many of its organs and systems. Adipose tissue is not only a tissue which stores fat and plays a protective role. It is an important endocrine organ where signals sent from different tissues ...
What is the morphological and biochemical characteristic of different depots?
Adipose tissue - morphological and biochemical characteristic of different depots. Adipose tissue is an organ that performs a lot of significant physiological functions, which is why its excess in the body results in pathological states in many of its organs and systems. Adipose tissue is not only a tissue which stores fat ...
What is adipose tissue?
Identified by Conrad Gessner in 1551, adipose tissue is a loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes and part of stromal vascular fraction which includes preadipocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages and vascular endothelial cells. Adipose tissue is mainly derived from preadipocytes and its main role is to store energy in the form of body lipids or fats. There are two types of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue (WAT), for energy storage, and brown adipose tissue (BAT), for generating body heat. Adipose deposits in different body parts have different biochemical profiles but the cumulative gene
What is the function of adipose tissue?
As it comprises about 20-25% of total body weight in healthy individuals, the main function of adipose tissue is to store energy in the form of lipids (fat). Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the skin) and visceral (surrounding organs ). Depending on adipocyte morphology, there are two types of adipose tissue:
What is the fatty tissue?
Adipose tissue, or fatty tissue, connective tissue consisting mainly of fat cells (adipose cells, or adipocytes), specialized to synthesize and contain large globules of fat, within a structural network of fibres .
What is the term for loose connective tissue?
Adipose tissue is loose connective tissue. It stores fat, provides cushion and insulation to the body.
What is connective tissue?
Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body. ... Connective tissue is made up of cells, fibers, and a gel-like substance. Types of connective tissue include bone, cartilage, fat, blood, and lymphatic tissue.
How many clinical trials are there for adipose derived cells?
So I see there are currently 42 Clinical Trials in the US using Adipose-derived cells for various indications. Most appear to be treating liposuction material with collagenase, and spinning out the stromal vascular cells for things like critical limb ischemia.
Is adipocyte a connective tissue?
Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix, and has only a few fibers. Adipose tissue is composed of cells called adipocytes that collect and store fat in the form of triglycerides for energy metabolism.
Adipose Tissue Composition
Adipose Tissue Location
- Adipose tissue is found in various places in the body. Some of these locations include the subcutaneous layer under the skin; around the heart, kidneys, and nerve tissue; in yellow bone marrow and breast tissue; and within the buttocks, thighs, and abdominal cavity. While white fat accumulates in these areas, brown fat is located in more specific areas of the body. In adults, s…
Adipose Tissue Endocrine Function
- Adipose tissue acts as an endocrine system organ by generating hormones that influence metabolic activity in other organ systems. Some of the hormones produced by adipose cells influence sex hormone metabolism, blood pressure regulation, insulin sensitivity, fat storage and use, blood clotting, and cell signaling. A major function of adipose cells is to increase the body's …
Sources
- "Adipose Tissue." You and Your Hormones, Society for Endocrinology,
- Stephens, Jacqueline M. "The Fat Controller: Adipocyte Development." PLoS Biology, vol. 10, no. 11, 2012, doi: