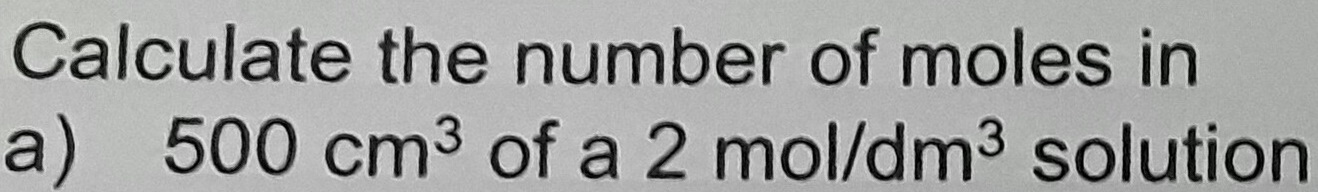
Chemical Quantities
- Chemical Quantities Definition. It is a systematic method to express quantities of the given chemical substance into scientific units.
- Overview of Chemical Quantities. Suppose you want to buy your favorite gum from a store, now, in how many ways could you buy gum? ...
- Mole and Avogadro’s Number. ...
- Molar Mass. ...
- Mass-Mole conversions. ...
How do you measure the amount of a substance?
Chapter 10 – Chemical Quantities Jennie L. Borders Section 10.1 – The Mole: A Measurement of Matter You often measure the amount of something by count, by mass, or by volume. A mole (mol) of a substance is 6.02 x 1023representative particles of that substance.
Why do chemists count molecules by the dozen?
Visible quantities of a substance must therefore have a large number of molecules, atoms, or ions. *Rather than using numbers of this size, chemist use a unit to count large numbers of particles. As we count eggs by the dozen, we count chemical particles (molecules, atoms, and ions) by the mole.
What is stoichiometry in chemistry?
The study of the numerical relationships between the reactants and the products in balanced chemical reactions is called stoichiometry. (Back to the Top) 6.6 Mole-Mass and Mass-Mass Problems In this section you will learn to convert from mass or moles of one substance to mass or moles of another substance in a chemical reaction.
How many atoms and molecules are in a chemical reaction?
So far, we have talked about chemical reactions in terms of individual atoms and molecules. Although this works, most of the reactions occurring around us involve much larger amounts of chemicals. Even a tiny sample of a substance will contain millions, billions, or a hundred billion billions of atoms and molecules.

What is the chemical quantity?
It is a systematic method to express quantities of the given chemical substance into scientific units.
What units are chemical quantities?
Chemists use the mole unit to represent 6.022 × 10 23 things, whether the things are atoms of elements or molecules of compounds. This number, called Avogadro's number, is important because this number of atoms or molecules has the same mass in grams as one atom or molecule has in atomic mass units.
What is the quantity of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in each atom, and defines the element. For example, all carbon atoms contain 6 protons in their atomic nucleus; so the atomic number of carbon is 6.
What are molar quantities in chemistry?
CHEMISTRY GLOSSARY Molar quantity is often convenient to express an extensive quantity (e.g., volume, enthalpy, heat capacity, etc.) as the actual value divided by the amount of substance (number of moles). The resulting quantity is called molar volume, molar enthalpy, etc.
How do you do chemical quantities?
1:2012:13The Mole and Chemistry Quantities - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAs one mole per 6.02 times 10 to the 23. Things or 6.02 times 10 to the 23. Things per one mole theMoreAs one mole per 6.02 times 10 to the 23. Things or 6.02 times 10 to the 23. Things per one mole the one we want to use will cancel the old unit and leave us with the new unit.
What is an example of a chemical quantity used to measure chemicals?
Amount concentration (moles per liter) The SI unit of this quantity is the mole (of the substance) per liter (of the solution). Thus, for example, the amount concentration of sodium chloride in ocean water is typically about 0.599 mol/L.
What are the 4 types of elements?
The elements are classified as metal, non-metal, and metalloid.The extreme left side elements in the periodic table are metals, for example, sodium, calcium, caesium, etc.However, elements on the right side are generally referred to as non-metals, carbon, chlorine, oxygen, etc.More items...
How many chemical elements are there?
118General observations. At present there are 118 known chemical elements.
What is human made of?
The human body is approximately 99% comprised of just six elements: Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, calcium, and phosphorus. Another five elements make up about 0.85% of the remaining mass: sulfur, potassium, sodium, chlorine, and magnesium.
How do you find the molar quantity?
0:133:51How to Calculate Molar Mass (Molecular Weight) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we go to the periodic. Table we find carbon and we find oxygen and we see the atomic mass thereMoreSo we go to the periodic. Table we find carbon and we find oxygen and we see the atomic mass there right below the element symbol to find the molar mass we add those two numbers together.
How do you find molar quantity?
1:3011:20How To Calculate The Molar Mass of a Compound - Quick & Easy!YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the atomic mass of oxygen is 16 if you multiply by 3 that's 48 so the molar mass of ozone o3 it'sMoreSo the atomic mass of oxygen is 16 if you multiply by 3 that's 48 so the molar mass of ozone o3 it's 48 grams per mole.
How are molar quantities and mass quantities related?
We now come to the concept of molar mass, which relates the number of moles (i.e. number of atoms, molecules etc.) to a measurable physical quantity (mass). The molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance, which is equal to the sum of the masses of the component entities.
What is basic unit of chemistry?
The basic unit of all matter is the atom. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that can't be divided using any chemical means and the building block that has unique properties. In other words, an atom of each element is different from an atom of any other element.
What is standard unit in chemistry?
There are seven basic units in the SI system: the meter (m), the kilogram (kg), the second (s), the kelvin (K), the ampere (A), the mole (mol), and the candela (cd).
What are the units for mass in chemistry?
The standard unit of mass in the SI system is the kilogram (kg). A kilogram was originally defined as the mass of a liter of water (a cube of water with an edge length of exactly 0.1 meter).
How are SI units used in chemistry?
The International System of Units (SI) is system of units of measurements that is widely used all over the world. This modern form of the Metric system is based around the number 10 for convenience. A set unit of prefixes have been established and are known as the SI prefixes or the metric prefixes (or units).
Chemical Quantities Definition
It is a systematic method to express quantities of the given chemical substance into scientific units.
Overview of Chemical Quantities
Suppose you want to buy your favorite gum from a store, now, in how many ways could you buy gum? First, you can buy a piece of gum, second, you can buy 1 dozen of gum packets or third, you can buy a whole box of gum.
Mass-Mole conversions
Conversion of a quantity from mass to mole requires the use of the molecular mass of a substance. 1 mole of carbon means it contains 12 grams of carbon (where 12 g is the molar mass of carbon). The formula one can use to calculate the number of moles is expressed as follows:
How much CH4 is in a mole?
Methane (CH4), known as natural gas, is used in gas stoves and gas heaters. 1 mole of CH4 = 16.0 g of CH4
How many atoms are in a mole?
A mole is a counting unit that contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms of an element (Avogadro’s number).
How many grams of CaCO3 are in a mole?
Step 3 Determine the molar mass and write conversion factors. 1 mole of CaCO3 = 100.1 g of CaCO3
How many liters of air does the human lung have?
An adult human lung has a volume of 2.9 liters. If its volume decreases to 1.2 liters and it contains 0.049 mole of air after it exhales, how many moles of air does it contain when full?
What is the density of glycerin?
The density of glycerin is 1.26 . How many is this? Use the conversion rates of and . Express your answer to the correct number of significant figures.
How much calcium carbonate can dissolve in water?
The solubility of calcium carbonate is 14 . This rate means that 14 milligrams of calcium carbonate can dissolve in 1 liter of water.
