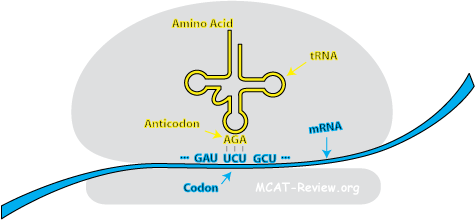
Both codon and Anticodon are specialized to work in pairs in the placement of amino acids and the process of protein synthesis. They are the languages that communicate together and give a byproduct of polypeptides. Specific base pairing initiates the process of codon and anticodon pairing and the stop codon helps in terminating it.
What is the step by step process of protein synthesis?
What are the 9 steps of protein synthesis?
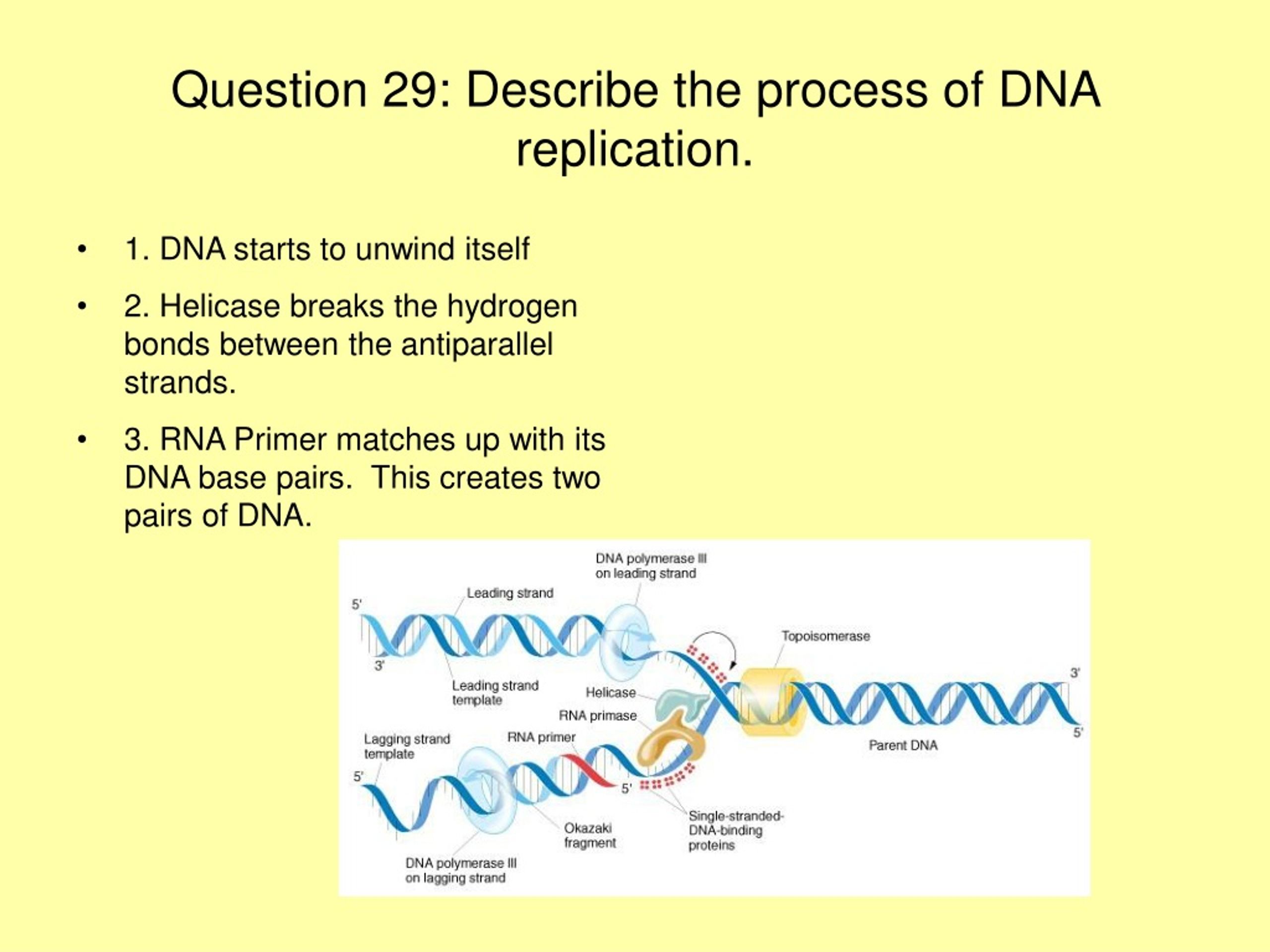
- DNA unravels, exposing code.
- mRNA comes in.
- transcription (copying genetic code from DNA)
- mRNA exits nucleus, goes to ribosome.
- translation (gives message to ribosome)
- tRNA brings in specific amino acids (anticodons)
- protein synthesis begins.
- peptides.
What are the 2 steps of protein synthesis?
Steps of protein synthesis process: There are 5 major steps of the protein synthesis process are: Activation of amino acids. Transfer of amino acids to tRNA. Initiation of the polypeptide chain. Chain termination and. Translocation of the protein molecule.
What is the correct order of protein synthesis?
- Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon.
- Elongation: The tRNA transfers an amino acid to the tRNA corresponding to the next codon.
- Termination: When a peptidyl tRNA encounters a stop codon, then the ribosome folds the polypeptide into its final structure.
How would you describe the steps in protein synthesis?
The transcription process is the first step of protein synthesis. This step transfers genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes of the cytoplasm or rough endoplasmic reticulum. Transcription is divided into three phases: initiation, elongation and termination. Initiation requires two special protein groups.
What is the codon in DNA?
Where are codons and anticodons found?
What is the name of the RNA that is attached to amino acids?
How many codons are in a sequence?
What is the sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA molecule that encodes a specific?
How many codons are there in the human body?
What is the first step in converting DNA to protein?
See 2 more
About this website

What are codons and Anticodons?
anticodon – a sequence of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that bond to a complementary sequence on an mRNA molecule. The anticodon sequence determines the amino acid that the tRNA carries. codon– a sequence of three nucleotides on a mRNA molecule that encode a specific amino acid.
What is a codons role in protein synthesis?
A codon is a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides (a trinucleotide) that forms a unit of genomic information encoding a particular amino acid or signaling the termination of protein synthesis (stop signals). There are 64 different codons: 61 specify amino acids and 3 are used as stop signals.
What is relationship between codon and anticodon?
Codons are trinucleotide units that present in mRNA and codes for a particular amino acid in protein synthesis. Anticodon is trinucleotide units that present in tRNA. It is complementary to the codons in mRNA. Codons transfer the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes where protein synthesis takes place.
Where are codons and Anticodons found?
Codons are present on an mRNA or DNA. They are sequences of three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid. Anticodons are present on the tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules that help transfer or bring in the amino acids to the mRNA during the translation process.
What is a codon simple definition?
Listen to pronunciation. (KOH-don) A sequence of three consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid.
How does protein synthesis work?
Protein synthesis is the process in which cells make proteins. It occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. Transcription is the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus. It includes three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
What is a codon and anticodon quizlet?
A codon is the triplet sequence in the messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript which specifies a corresponding amino acid (or a start or stop command). An anticodon is the corresponding triplet sequence on the transfer RNA (tRNA) which brings in the specific amino acid to the ribosome during translation.
What is the relationship between a codon and an anticodon quizlet?
A codon is on an mRNA molecule. The anticodon on a tRNA molecule is complementary to the mRNA codon and brings in the needed amino acid. A codon is a 3-nucleotide "unit" that "codes" for an amino acid.
What is an anticodon example?
genetic code expression three unpaired nucleotides, called an anticodon. The anticodon of any one tRNA fits perfectly into the mRNA codon that codes for the amino acid attached to that tRNA; for example, the mRNA codon UUU, which codes for the amino acid phenylalanine, will be bound by the anticodon AAA.
What is protein synthesis answer?
Protein synthesis(translation) is the production of a polymer of a chain of amino acids which produces a functioning protein. It involves reading the information from mRNA (messenger RNA) to put together a chain of amino acids. Ribosomes are the structures that synthesize the protein chain.
How many codons are there?
The three-letter nature of codons means that the four nucleotides found in mRNA — A, U, G, and C — can produce a total of 64 different combinations. Of these 64 codons, 61 represent amino acids, and the remaining three represent stop signals, which trigger the end of protein synthesis.
What is a codon quizlet?
codon. A sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. Codon.
Which best describes a codon?
Answer: Codon the sequence of three bases that codes for a specific amino acid.
What is the relationship between DNA codons and protein?
A codon is a sequence of three DNA or RNA nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis. DNA and RNA molecules are written in a language of four nucleotides; meanwhile, the language of proteins includes 20 amino acids.
What is a codon a level biology?
A codon is a specific sequence of nucleotides on an mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid or to a stop signal during protein translation. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of a nucleobase (or simply, base), a sugar, and a phosphate group.
When the 1st base of the anticodon is C or A, base pairing is specific?
When the 1st base of the anticodon is C or A, base pairing is specific & only one codon is identified by that tRNA.
How many codons are there in arginine?
Degeneracy: Occasionally called redundant although each codon that corresponds to a single amino acid, an amino acid given that may have more than one codon, for example, leucine, serine, arginine, etc have 6 different codons, however methionine and tryptophan have one codon.
What is the coding language in mRNA?
Codons are presented in the mRNA that language of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), uracil (U). Their nucleotide sequence is every time in a 5’ – 3’ direction.
What are the consequences of altering the nucleotide sequence?
Consequences of altering the nucleotide sequence: Silent mutation: The codon that containing the altered base may code for the same amino acid. For example, if the serine codon UCA is given a different third base—U—to turn out to be UCU, it still codes for serine. Missense mutation:
Why is translation important in prokaryotes?
translation beginning before transcription is accomplished, this is because of the lack of nuclear membrane in prokaryotes. There are actual steps in protein synthesis are the following;
What is the pathway of protein synthesis called?
The pathway of protein synthesis is called translation because the language of the nucleotide course on the mRNA is translated into the language of the amino acid sequence. The genetic information which is stored in the chromosome are finally translated into proteins and are the end products of most information pathway.
What happens when mutations occur at splice locations?
Mutations at splice locations can alter or change the way in which introns are removed from pre-mRNA molecules, which producing aberrant proteins.
What is the codon in DNA?
A codon is a portion of DNA or RNA which has the information necessary to identify a single unique amino acid in the sequence of a protein. As you should know the “"genetic code” is embodied by the sequence in DNA molecules of four bases, Adenine, Guanine, Thiamine, and Cytosine, usually listed only by their first letters: A, T, G, or C. The “code” consists of strings of codons in a continuous line making up a single gene, so for example AAT GAC TTC AAA GTG etc (this is not a real sequence, I just made something up). Each codon represents an amino acid and the sequence of codons dictates the order of the amino acids in the linear sequence of the protein.
Where are codons and anticodons found?
Codons are found in mRNA. Anticodons are found in tRNA. The two match during translation of mRNA into protein in the ribosome.
What is the name of the RNA that is attached to amino acids?
Anticodons the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains requires the presence of second type of RNA know as tRNA. The tRNA becomes attached to it's particular kind of amino acids. In this way tRNA molecules transfer the appropriate amino acids to the ribosomes and align them with respect to the mRNA codons. It is achieved by marching the tRNA anticodons.
How many codons are in a sequence?
It then has codons in sequence that gives instructions on the amino acids to use to build a protein, and it then has a stop codon to signal when the protein assembly is complete. Normally, there is one initiation codon and three stop codons, and most amino acids are represented by more than one codon.
What is the sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA molecule that encodes a specific?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA molecule that encodes a specific amino acid. The codons transfer the genetic information from the nucleus where the DNA is located to the ribosomes where the pro
How many codons are there in the human body?
There are 64 possible codons, each composed of three of the four possible nucleotides, but only 20 amino acids are found in most biological systems. Accordingly, there is a great deal of redundancy, such as the amino acid valine with four codons. Only tryptophan and methionine have only one codon each. The codon for methionine is the same as the start codon, which is interpreted based on context.
What is the first step in converting DNA to protein?
I want to note that it sometimes appears that people confuse stop codons as transcription terminators. Transcription is the first step of converting DNA to protein and it is done via the RNA polymerase enzyme, which sits directly before a gene sequence on the DNA. This process is initiated by promoter transcription factors and terminated via terminator sequences located after the gene sequen
How do anticodons work?
How Anticodons Work. When genetic information is to be turned into a protein, the sequence of events goes like this: Genetic information in the cell’s genome is transcribed into mobile pieces of RNA using base-pairing rules. Each nucleotide has only one other nucleotide which pairs up with it.
What is an anticodon?
Anticodon Definition. Anticodons are sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. They are found in tRNAs, and allow the tRNAs to bring the correct amino acid in line with an mRNA during protein production. During protein production, amino acids are bound together into a string, much like beads on a necklace.
How many anticodons does a tRNA have?
Each tRNA carries one amino acid, and has one anticodon. When the anticodon successfully pairs up with an mRNA codon, the cellular machinery knows that the correct amino acid is in place to be added to the growing protein. Anticodons are necessary to complete the process of turning the information stored in DNA into functional proteins ...
What enzymes bind amino acids together?
Enzymes catalyze the bonding of amino acids together as tRNA anticodons bind to the correct mRNA codon. When the tRNA’s amino acid has been added to the protein chain, the tRNA leaves to pick up a new amino acid to bring to a new mRNA. Interestingly, this means that the tRNA anticodon has the RNA version of the same nucleotide sequence ...
How does RNA polymerase make protein?
By pairing the correct RNA nucleotide with each DNA nucleotide, RNA polymerase creates a strand of RNA that contains all the correct information to make the protein. This “messenger RNA,” or “mRNA,” then travels to a ribosome, the site of protein production.
Why does DNA use thymine instead of uracil?
It is thought that DNA uses Thymine instead of Uracil because, as the cell’s “master blueprints,” information stored in DNA must remain stable over a long period of time. RNAs are only copies of DNA made for specific purposes, and are used by the cell for only a short period of time before being discarded.
Why is it important to use amino acids in the correct places?
It’s important that the correct amino acids be used in the correct places, because amino acids have different properties. Putting the wrong one in a spot can render a protein useless, or even dangerous to the cell.
What is the codon in DNA?
A codon is a portion of DNA or RNA which has the information necessary to identify a single unique amino acid in the sequence of a protein. As you should know the “"genetic code” is embodied by the sequence in DNA molecules of four bases, Adenine, Guanine, Thiamine, and Cytosine, usually listed only by their first letters: A, T, G, or C. The “code” consists of strings of codons in a continuous line making up a single gene, so for example AAT GAC TTC AAA GTG etc (this is not a real sequence, I just made something up). Each codon represents an amino acid and the sequence of codons dictates the order of the amino acids in the linear sequence of the protein.
Where are codons and anticodons found?
Codons are found in mRNA. Anticodons are found in tRNA. The two match during translation of mRNA into protein in the ribosome.
What is the name of the RNA that is attached to amino acids?
Anticodons the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains requires the presence of second type of RNA know as tRNA. The tRNA becomes attached to it's particular kind of amino acids. In this way tRNA molecules transfer the appropriate amino acids to the ribosomes and align them with respect to the mRNA codons. It is achieved by marching the tRNA anticodons.
How many codons are in a sequence?
It then has codons in sequence that gives instructions on the amino acids to use to build a protein, and it then has a stop codon to signal when the protein assembly is complete. Normally, there is one initiation codon and three stop codons, and most amino acids are represented by more than one codon.
What is the sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA molecule that encodes a specific?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA molecule that encodes a specific amino acid. The codons transfer the genetic information from the nucleus where the DNA is located to the ribosomes where the pro
How many codons are there in the human body?
There are 64 possible codons, each composed of three of the four possible nucleotides, but only 20 amino acids are found in most biological systems. Accordingly, there is a great deal of redundancy, such as the amino acid valine with four codons. Only tryptophan and methionine have only one codon each. The codon for methionine is the same as the start codon, which is interpreted based on context.
What is the first step in converting DNA to protein?
I want to note that it sometimes appears that people confuse stop codons as transcription terminators. Transcription is the first step of converting DNA to protein and it is done via the RNA polymerase enzyme, which sits directly before a gene sequence on the DNA. This process is initiated by promoter transcription factors and terminated via terminator sequences located after the gene sequen
Overview of Protein Synthesis
The Genetic Code
- The genetic code is a glossary that defines the correspondence between a sequence of nucleotides bases in the body & the sequence of amino acids in humans. Each individual word in the code is composed of 3 specific nucleotide bases, these genetic words are called codons.
Codons
- Codons are presented in the mRNA that language of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), uracil (U). Their nucleotide sequence is every time in a 5’ – 3’ direction. There are 4 nucleotide bases that are implemented to produce 3 base codons. Therefore there are 64 different types of combinations of bases taking 3 at a time. There are four important codons which are the followi…
Components Required For Translation (Protein Synthesis)
- Aminoacid.
- Transfer RNA.
- Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
- Messenger RNA.