
Key Takeaways
- A common shareholder is someone who has purchased at least one common share of a company.
- Common shareholders have a right to vote on corporate issues and are entitled to declared common dividends.
- Common shareholders are paid out last in the event of bankruptcy after debtholders and preferred shareholders.
Full Answer
How many types of shareholders are there?
There are basically two types of shareholders: the common shareholders. Common Stock Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership of equity in a company. There are other terms – such as common share, ordinary share, or voting share – that are equivalent to common stock. and the preferred shareholders.
What is a common shareholder in a stock?
A stock is a form of security that indicates the holder has proportionate ownership in the issuing corporation. A common shareholder owns part of a company via share ownership. They can vote on the direction of the company and have rights to declared common dividends.
What is a shareholder?
What is a Shareholder? A shareholder can be a person, company, or organization that holds stock (s) in a given company. A shareholder must own a minimum of one share in a company’s stock or mutual fund to make them a partial owner.
What is the difference between a common shareholder and noncumulative shareholder?
A common shareholder owns part of a company via share ownership. They can vote on the direction of the company and have rights to declared common dividends. Noncumulative, as opposed to cumulative, refers to a type of preferred stock that does not pay the holder any unpaid or omitted dividends.

What is a common shareholder?
A common shareholder is someone who has purchased at least one common share of a company. Common shareholders have a right to vote on corporate issues and are entitled to declared common dividends.
What is the meaning of common shares?
Share. Common shares are issued to business owners and other investors as proof of the money they have paid into a company. Of all shareholders, common shareholders have the least claim on a company's assets.
What are the 3 types of shareholders?
Types of Shareholders:Equity Shareholder:Preference Shareholder:Debenture holders:
What are common and preferred shareholders?
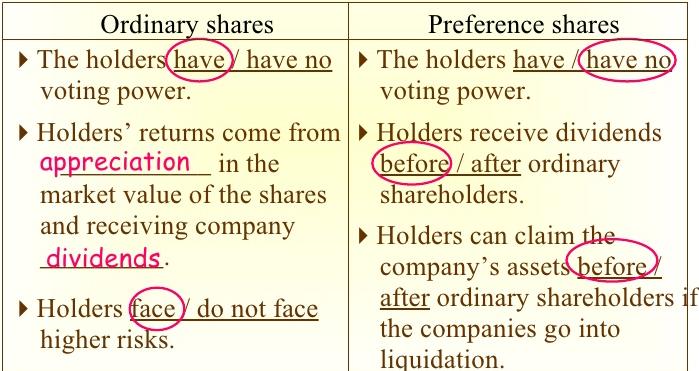
Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line when it comes to company assets, which means they will be paid out after creditors, bondholders, and preferred shareholders.
How do common shares work?
Common stock is a security that represents ownership in a corporation. Holders of common stock elect the board of directors and vote on corporate policies. This form of equity ownership typically yields higher rates of return long term.
Do common shares pay dividends?
Similar to fixed-income bonds, preferred shares often come with a guaranteed dividend (or at least the guarantee of preferential treatment ahead of common shareholders). Legally, preferred shareholders could be paid a dividend whereas common equity holders are issued nothing.
What are the 4 types of shares?
What are the different types of shares in a limited company?Ordinary shares.Non-voting shares.Preference shares.Redeemable shares.
What are the two types of shareholders?
Shareholders of a company are of two types – common and preferred shareholder. As their name suggests, they are the owners of a company's common stocks. These individuals enjoy voting rights over matters concerning the company.
Is a shareholder an owner?
A shareholder is a person, company, or institution that owns at least one share of a company's stock or in a mutual fund. Shareholders essentially own the company, which comes with certain rights and responsibilities. This type of ownership allows them to reap the benefits of a business's success.
Do common shares have voting rights?
Common stock ownership always carries voting rights, but the nature of the rights and the specific issues shareholders are entitled to vote on can vary considerably from one company to another.
What is an example of common stock?
Alphabet (Google) is one example of this. The company's class A shares (NASDAQ:GOOGL) have voting rights, while its class C shares (NASDAQ:GOOG) do not. Image source: Getty Images.
Why is preferred stock better than common?
Preferred shares have a higher dividend yield than common stockholders or bondholders usually receive (very compelling with low interest rates). Preferred shares have a greater claim on being repaid than shares of common stock if a company goes bankrupt.
What are the 4 types of shares?
What are the different types of shares in a limited company?Ordinary shares.Non-voting shares.Preference shares.Redeemable shares.
What is common stock with example?
In other words, it's a way to divide up the ownership of a company; so one share of common stock represents a percentage ownership share of a corporation. For instance, if a company had 100 shares outstanding, one share would be equal to one percent ownership of the company.
Are common shares a good investment?
If a company does well, or the value of its assets increases, common stock can go up in value. On the other hand, if a company is doing poorly, a common stock can decrease in value. Common stock allows investors to share in a company's success over time, which is why they can make great long-term investments.
Is common shares the same as common stock?
Similar Terminology. Of the two, "stocks" is the more general, generic term. It is often used to describe a slice of ownership of one or more companies. In contrast, in common parlance, "shares" has a more specific meaning: It often refers to the ownership of a particular company.
What is a common shareholder?
Common shareholders are those that own a company’s common stock. They are the more prevalent type of stockholders and they have the right to vote on matters concerning the company. As they have control over how the company is managed, they have the right to file a class-action lawsuit against the company for any wrongdoing that can potentially harm the organization.
What are the two types of shareholders?
There are basically two types of shareholders: the common shareholders . Common Stock Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership of equity in a company. There are other terms – such as common share, ordinary share, or voting share – that are equivalent to common stock. and the preferred shareholders.
What is dividend in business?
Dividend A dividend is a share of profits and retained earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders. When a company generates a profit and accumulates retained earnings, those earnings can be either reinvested in the business or paid out to shareholders as a dividend. if the company does well and succeeds.
What is a shareholder in a company?
A shareholder is an owner of a company as determined by the number of shares they own. A stakeholder does not own part of the company but does have some interest in the performance of a company just like the shareholders. However, their interest may or may not involve money.
What is senior debt?
Senior and subordinated debt refer to their rank in a company's capital stack. In the event of a liquidation, senior debt is paid out first. and financial obligations incurred by the company, which means creditors cannot compel stockholders to pay them.
What are the responsibilities of a shareholder?
Roles of a Shareholder. Being a shareholder isn’t all just about receiving profits, as it also includes other responsibilities. Let’s look at some of these responsibilities. Brainstorming and deciding the powers they will bestow upon the company’s directors, including appointing and removing them from office.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred Shares Preferred shares (preferred stock, preference shares) are the class of stock ownership in a corporation that has a priority claim on the company’s assets over common stock shares. The shares are more senior than common stock but are more junior relative to debt, such as bonds. .
What Is a Shareholder?
A shareholder, also referred to as a stockholder, is a person, company, or institution that owns at least one share of a company's stock, known as equity. Because shareholders essentially own the company, they reap the benefits of a business's success. These rewards come in the form of increased stock valuations or financial profits distributed as dividends.
What is a shareholder in a company?
A shareholder, also referred to as a stockholder, is a person, company, or institution that owns at least one share of a company’s stock, which is known as equity. Because shareholders are essentially owners in a company, they reap the benefits of a business’ success. These rewards come in the form of increased stock valuations, ...
What Are Some Key Shareholder Rights?
Shareholders have the right to inspect the company's books and records, the power to sue the corporation for the misdeeds of its directors and/or officers, and the right to vote on critical corporate matters, such as naming board directors. In addition, they have the right to decide whether or not to greenlight potential mergers, the right to receive dividends, the right to attend annual meetings, the right to vote on crucial matters by proxy, and the right to claim a proportionate allocation of proceeds if a company liquidates its assets.
Why are there two types of stock?
The vast majority of shareholders are common stockholders, primarily because common stock is cheaper and more plentiful than preferred stock. While common stockholders enjoy voting rights, preferred stockholders generally have no voting rights due to their preferred status, which affords them first crack at dividends before common stockholders are paid. Furthermore, the dividends paid to preferred stockholders are generally more significant than those paid to common stockholders.
What happens to shareholders in bankruptcy?
In the case of bankruptcy, shareholders can lose up to their entire investment.
What is a majority shareholder?
In many cases, majority shareholders are company founders , and in older companies, majority shareholders are frequently descendants of company founders. In either case, by controlling more than half of a company's voting interest, majority shareholders wield considerable power to influence critical operational decisions, including replacing board members and C-level executives like chief executive officers ( CEOs) and other senior personnel. For this reason, companies often attempt to avoid having majority shareholders amongst their ranks.
Is a shareholder subject to capital gains?
Shareholders are subject to capital gains (or losses) and/or dividend payments as residual claimants on a firm's profits.
How Do Common Shares Work?
The name ‘common shares’ suggests that there are different types of shares, which is indeed true. We’ll get into that a bit later, but first, let’s take a closer look at how common shares work.
What is common stock?
Common shares, also known as common stock, are a type of security that represents ownership, or equity in a company. Common shares can be purchased by individual investors on a stock market, such as the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX), the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), or the Nasdaq.
What is mutual fund?
One is to purchase a mutual fund, which is like a basket of securities holding a variety of stocks and bonds. Mutual funds are professionally managed and are an easy way to achieve instant diversification without requiring large sums of money.
Why are dividends so attractive?
The ability to earn dividends is one of the things that make stock investing so attractive because they allow investors to continue to earn, even when the price of a stock drops and the value has gone down.
How is stock issued?
Stock is issued by companies through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). This provides important capital that can be used for expansion. There are specific steps companies must take to receive approval for the IPO. Eventually, the shares are introduced to the market and made available for purchase on the stock exchange.
Why do shareholders have the right to vote?
In most cases, shareholders receive one vote for every share owned. Because board members are the ones making the big decisions, voting gives common shareholders some control over the direction of a company. ...
How do shares fluctuate?
Share prices fluctuate up and down based on investor demand. In other words, the market dictates the price of shares. Of course, demand is influenced by several factors, such as a company’s financial performance, industry outlook, and company news, whether it’s negative or positive.
What are the sources of shareholder rights?
The main sources of shareholder rights are legislation in the company’s incorporation, corporate charter, and governance documents. Therefore, the rights of shareholders can vary from one jurisdiction to another and from one corporation to another.
What is common stock?
What is a Common Stock? Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership of equity in a company. Corporation A corporation is a legal entity created by individuals, stockholders, or shareholders, with the purpose of operating for profit. Corporations are allowed to enter into contracts, sue and be sued, own assets, ...
What is dividend in business?
The shareholders usually receive a portion of profits through dividends. Dividend A dividend is a share of profits and retained earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders. When a company generates a profit and accumulates retained earnings, ...
What is a board of directors?
Board of Directors A board of directors is a panel of people elected to represent shareholders. Every public company is required to install a board of directors. , as well as in voting regarding important corporate policies. Common stock owners can profit from the capital appreciation of the securities.
Do common stock holders own assets?
In addition, in case of a company’s liquidation, holders of common stock own rights to the company’s assets. However, since common shareholders are at the bottom of the priority ladder, it is very unlikely that they would receive compensation in the event of liquidation. Moreover, common shareholders can participate in important corporate decisions ...
Is a shareholder a shareholder?
Generally, a shareholder is a stakeholder of the company while a stakeholder is not necessarily a shareholder. Stockholders Equity. Stockholders Equity Stockholders Equity (also known as Shareholders Equity) is an account on a company's balance sheet that consists of share capital plus.
Is there a unified classification of common stock?
There is no unified classification of common stock. However, some companies may issue two classes of common stock. In most cases, a company will issue one class of voting shares and another class of non-voting (or with less voting power) shares. The main rationale for using dual classification is to preserve control over the company.
What Is Common Stock?
Common stock is a security that represents ownership in a corporation. Holders of common stock elect the board of directors and vote on corporate policies. This form of equity ownership typically yields higher rates of return long term. However, in the event of liquidation, common shareholders have rights to a company's assets only after bondholders, preferred shareholders, and other debtholders are paid in full. Common stock is reported in the stockholder's equity section of a company's balance sheet.
What happens to common stock in liquidation?
In a liquidation, common stockholders receive whatever assets remain after creditors, bondholders, and preferred stockholders are paid. There are different varieties of stocks traded in the market. For example, value stocks are stocks that are lower in price in relation to their fundamentals.
What is the largest stock exchange in the world?
NYSE had a market capitalization of $28.5 trillion in June 2018, making it the biggest stock exchange in the world by market cap. There are also several international exchanges for foreign stocks, such as the London Stock Exchange and the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
What is an unlisted stock?
There are also several international exchanges for foreign stocks, such as the London Stock Exchange and the Tokyo Stock Exchange. Companies that are smaller in size and unable to meet an exchange’s listing requirements are considered unlisted. These unlisted stocks are traded on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board (OTCBB) or pink sheets.
Why are stocks important?
They bear a greater amount of risk when compared to CDs, preferred stock, and bonds. However, with the greater risk comes the greater potential for reward. Over the long term, stocks tend to outperform other investments but are more exposed to volatility over the short term.
How to diversify portfolio?
Investors should diversify their portfolio by putting money into different securities based on their appetite for risk.
When was the first common stock invented?
The first-ever common stock was established in 1602 by the Dutch East India Company and introduced on the Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Larger US-based stocks are traded on a public exchange, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or NASDAQ.
How many votes does a shareholder have?
Alternatively, each shareholder may have one vote, regardless of how many shares of company stock they own. Shareholders can exercise their voting rights in person at the corporation's annual general meeting or other special meeting convened for voting purposes, or by proxy.
What does a shareholder vote on?
Shareholders typically have the right to vote in elections for the board of directors and on proposed operational alterations such as shifts of corporate aims and goals or fundamental structural changes . Shareholders also have the right to vote on matters that directly affect their stock ownership, such as the company doing a stock split ...
How does voting rights influence a company's decisions?
The Influence of Voting Rights in a Company's Decisions. Since the issues on which shareholders can vote , at least in part , determine the profitability of the company going forward , voting rights in such matters allow shareholders to influence the success of their investment.
Why do activist investors buy shares?
Because shareholders have a proportional influence per their stake, certain market movers or "hostile" activist investors will amass a large stake in a company through purchasing shares. When they have enough shareholder power to sway a vote, they will step in and direct the company in the direction that benefits them or they may purchase enough shares to become the majority shareholder of the company. When that happens, they can direct it more assertively.
What rights do shareholders have in 2021?
Updated Apr 30, 2021. Common stock shareholders in a publicly-traded company have certain rights pertaining to their equity investment , and among the more important of these is the right to vote on certain corporate matters. Shareholders typically have the right to vote in elections for the board of directors and on proposed operational alterations ...
Can shareholders vote in person?
Shareholders can exercise their voting rights in person at the corporation's annual general meeting or other special meeting convened for voting purposes, or by proxy. Proxy forms are sent to shareholders, along with their invitations, to attend the shareholders' meeting. These forms list and describe all the issues on which shareholders have the right to vote. A shareholder may elect to fill out the form and mail in their votes on the issues rather than voting in person.
Should shareholders analyze proposals being presented for a vote?
Shareholders should thoroughly analyze proposals being presented for a vote. For example, there may be proposals for the company to take action that amounts to creating a " poison pill " designed to thwart a possible takeover by another firm.
What rights do common shareholders have?
Common shareholders are granted six rights: voting power, ownership, the right to transfer ownership, dividends, the right to inspect corporate documents, and the right to sue for wrongful acts.
Why is it important to know your shareholders rights?
These rights are crucial for the protection of shareholders from poor management.
Why are bondholder rights determined differently?
The rights of bondholders are determined differently because a bond agreement, or indenture, represents a contract between the issuer and the bondholder. The payments and privileges the bondholder receives are governed by the indenture (tenets of the contract).
How does a shareholder rights plan work?
A shareholder rights plan might then stipulate that existing common shareholders have the opportunity to buy shares at a discount to the current market price (usually a 10% to 20% discount).
Do preferred stockholders have voting rights?
For example, a company’s charter typically states that only the common stockholders have voting privileges, and preferred stockholders must receive dividends before common stockholders.
Do common shareholders benefit from liquidation?
Common shareholders are still part owners of the business, and if the business can turn a profit, common shareholders benefit. The liquidation preference we described above makes logical sense. Shareholders take on greater risk as they receive next to nothing if the firm goes bankrupt, but they also have a greater reward potential through exposure to share price appreciation when the company succeeds. In contrast, preferred stocks generally experience less price fluctuation.
What are Common Shares?
When someone refers to a share in a company, they are usually referring to common shares. Those who buy common shares will be essentially purchasing shares of ownership in a company. A holder of common stocks will receive voting rights, which increases proportionally with the more shares the holder owns.
When are preferred shareholders paid out?
Because preferred shares are a combination of both bonds and common shares, preferred shareholders are paid out after the bond shareholders but before the common stockholders. In the event that a company goes bankrupt, the preferred shareholders need ...
What happens if Company A misses the $2 dividend for preferred shares in Quarter 2?
Going back to the example, if Company A misses the $2 dividend for preferred shares in Quarter 2, they will need to pay $4 ($2 x 2) in Quarter 3.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates go up?
It is a static value. , which is affected by interest rates. When the interest rates go up, the value of preferred shares declines. When the rates go down, the value of preferred shares increases. Similar to common shareholders, those who purchase preferred shares will still be buying shares of ownership in a company.
What is dividend in stock?
A dividend typically comes in the form of a cash distribution that is paid from the company's earnings to investors. differs in nature. For common shares, the dividends are variable and are paid out depending on how profitable the company is.
What is preferred share?
Like bonds, preferred shares receive a fixed amount of income through a recurring dividend. Par Value Par Value is the nominal or face value of a bond, or stock, or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. It is a static value. , which is affected by interest rates.
How long does it take for a preferred share to mature?
Corporate Bonds Corporate bonds are issued by corporations and usually mature within 1 to 30 years. These bonds usually offer a higher yield than government bonds but carry more risk.
Roles of A Shareholder
- Being a shareholder isn’t all just about receiving profits, as it also includes other responsibilities. Let’s look at some of these responsibilities. 1. Brainstorming and deciding the powers they will bestow upon the company’s directors, including appointing and removing them from office 2. Deciding on how much the directors receive for their salar...
Types of Shareholders
- There are basically two types of shareholders: the common shareholders and the preferred shareholders. Common shareholders are those that own a company’s common stock. They are the more prevalent type of stockholders and they have the right to vote on matters concerning the company. As they have control over how the company is managed, they have the right to file a c…
Can The Shareholder Be A Director?
- The shareholder and director are two different entities, though a shareholder can be a director at the same time. The shareholder, as already mentioned, is a part-owner of the company and is entitled to privileges such as receiving profits and exercising control over the management of the company. A director, on the other hand, is the person hired by the shareholders to perform resp…
Shareholder vs. Stakeholder
- Shareholder and Stakeholder are often used interchangeably, with many people thinking that they are one and the same. However, the two terms don’t mean the same thing. A shareholder is an owner of a company as determined by the number of shares they own. A stakeholder does not own part of the company but does have some interest in the performance of a company just like …
Shareholder vs. Subscriber
- Before a company becomes public, it starts out first as a private limited company that is run, formed, and organized by a group of people called “subscribers.” The subscribers are considered the first members of the company whose names are listed in the memorandum of association. Once the company goes public, their names continue to be written in the public register and the…
Additional Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Shareholder. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful: 1. Drag-Along Rights 2. Irrevocable Proxy 3. Owner’s Equity 4. Voting Trust
What Is A Shareholder?
Understanding Shareholders
- As noted above, a shareholder is an entity that owns one or more shares in a company's stock or mutual fund. Being a shareholder (or a stockholder as they're also often called) comes with certain rights and responsibilities. Along with sharing in the overall financial success, a shareholder is also allowed to vote on certain issues that affect the company or fund in which they hold shares…
Special Considerations
- There are a few things that people need to consider when it comes to being a shareholder. This includes the rights and responsibilities involved with being a shareholder and the tax implications.
Types of Shareholders
- Many companies issue two types of stock: common and preferred. Common stock is more prevalent than preferred stock. Generally, common stockholders enjoy voting rights, while preferred stockholders do not. However, preferred stockholders have a priority claim to dividends. Furthermore, the dividends paid to preferred stockholders are generally more significant than th…