- Contractionary monetary policy is a strategy used by a nation’s central bank during booming growth periods to slow down the economy and control rising inflation.
- The Federal Reserve uses three main contractionary monetary tools: increasing interest rates, increasing banks’ reserve requirement, and selling government securities.
What is the overall goal of contractionary policies?
What is the overall goal of contractionary policies? Contractionary Policy as a Monetary Policy The goal is to reduce inflation by limiting the amount of active money circulating in the economy. It also aims to quell unsustainable speculation and capital investment that previous expansionary policies may have triggered.
What are the negative effects of monetary policy?
What are the monetary policy implications? Looking forward, a prolonged period of negative interest rates may be expected to hurt bank performance. In turn, lower bank profitability may reduce lending by banks and hamper the transmission of monetary policy stimulus. The design of monetary policy can take this into account.
How does contractionary fiscal policy affect the economy?
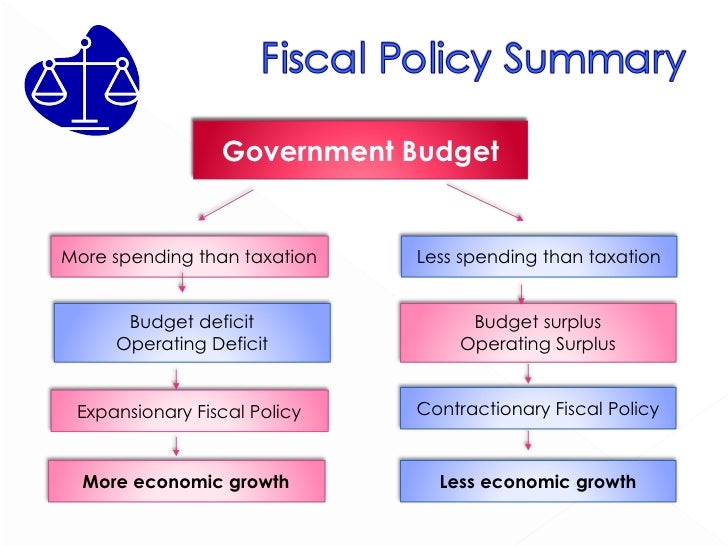
The opposite of expansionary fiscal policy, contractionary fiscal policy raises taxes and cuts spending. As consumers pay more taxes, they have less money to spend, and economic stimulation and growth slow. Under contractionary fiscal policies, the economy usually grows by no more than 3% per year.
What does contractionary fiscal policy includes?
Contractionary fiscal policy is a form of fiscal policy that involves increasing taxes, decreasing government expenditures or both in order to fight inflationary pressures. Due to an increase in taxes, households have less disposal income to spend.
What are 5 examples of contractionary monetary?
A contractionary monetary policy utilizes the following variations of these tools:Increase the short-term interest rate (discount rate) ... Raise the reserve requirements. ... Expand open market operations (sell securities) ... Reduced inflation. ... Slow down economic growth. ... Increased unemployment.
What are 3 examples of contractionary monetary policies?
The Federal Reserve uses three main contractionary monetary tools: increasing interest rates, increasing banks' reserve requirement, and selling government securities.
What is contractionary and expansionary monetary policy?
Expansionary monetary policy is simply a policy which expands (increases) the supply of money, whereas contractionary monetary policy contracts (decreases) the supply of a country's currency.
What is contractionary monetary policy and when is it used?
Contractionary monetary policy aims to slow down economic growth or even contract the economy in order to keep inflation at bay. It dampens growth primarily by raising interest rates and reducing the supply of money. Higher interest rates cause consumers to reduce spending, especially through the use of credit cards.
What is contractionary monetary policy quizlet?
Contractionary Monetary Policy involves decreasing the money supply in order to increase interest rates and decrease Consumption and Investment.
What are examples of contractionary fiscal policy?
When the government uses fiscal policy to decrease the amount of money available to the populace, this is called contractionary fiscal policy. Examples of this include increasing taxes and lowering government spending.
What is an example of expansionary monetary policy?
Purchasing Treasuries from banks increases their reserves, which makes it easier for them to lend out money to customers, making it easier for people to buy homes, cars, etc, and businesses to start or expand.
How does contractionary monetary policy reduce inflation?
Central banks use contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation. They reduce the money supply by restricting the volume of money banks can lend. The banks charge a higher interest rate, making loans more expensive. Fewer businesses and individuals borrow, slowing growth.
How is contractionary monetary policy implemented?
To implement a contractionary policy, the Fed sells these Treasurys to its member banks. The bank must pay the Fed for the Treasurys, reducing the credit on its books. As a result, banks have less money available to lend. With less money to lend, they charge a higher interest rate.
How does contractionary monetary policy affect the economy?
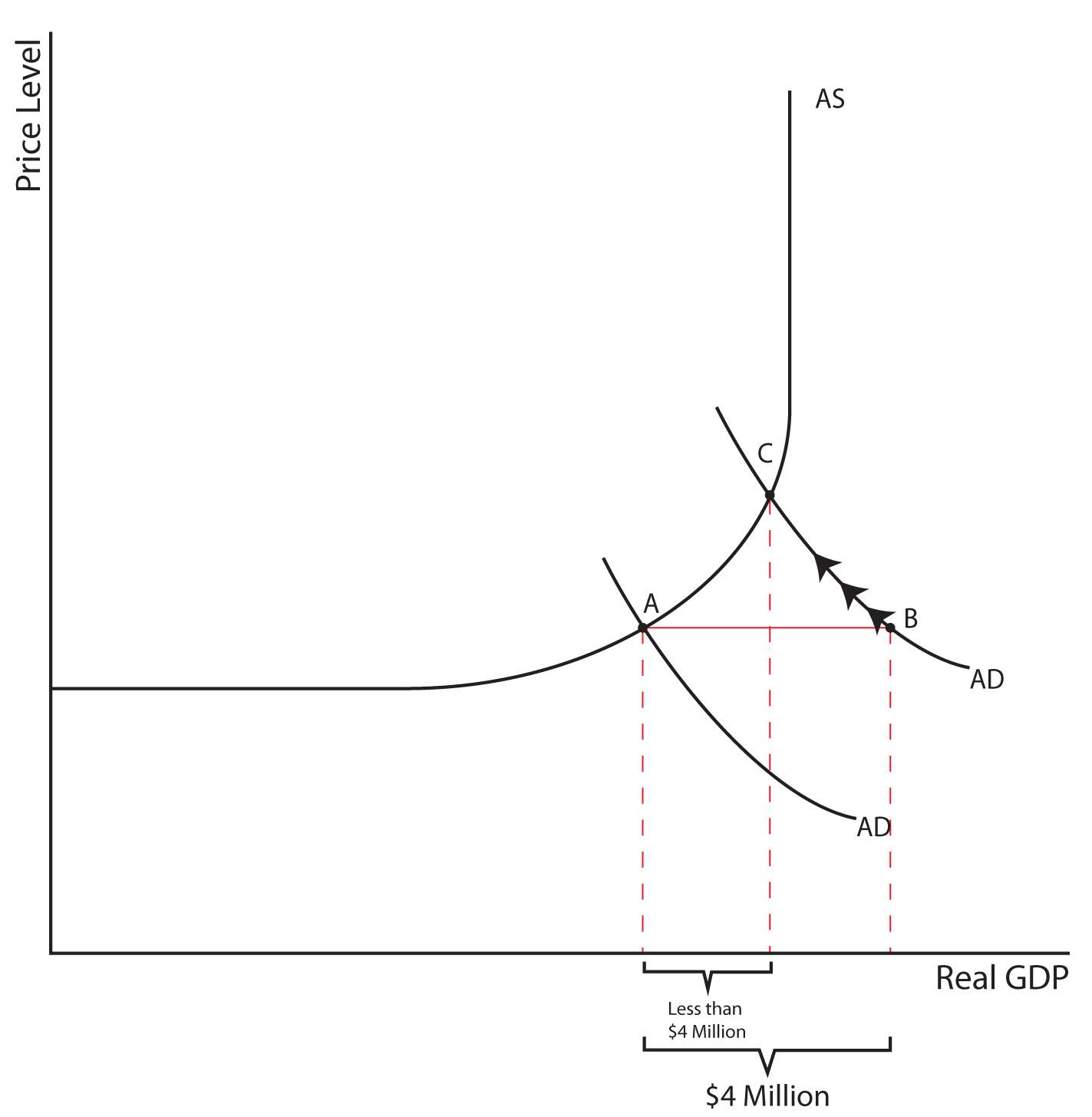
Contractionary monetary policy is driven by increases in the various base interest rates controlled by modern central banks or other means producing growth in the money supply. The goal is to reduce inflation by limiting the amount of active money circulating in the economy.
How does contractionary monetary policy affect interest rates?
A contractionary monetary policy will shift the supply of loanable funds to the left from the original supply curve (S0) to the new supply (S2), and raise the interest rate from 8% to 10%.
Why does contractionary monetary policy increase interest rates?
Contractionary policy reduces the amount of loanable funds in the economy. As with all goods, greater scarcity leads a greater price, so the interest rate, or the price of borrowing money, rises. An increase in the amount of available loanable funds means that there are more people who want to lend.
What is an example of contractionary economic policy quizlet?
An example of contractionary fiscal policy would be to decrease government spending on goods and services.
What is contractionary policy used for quizlet?
What is contractionary policy used for? To fight rapid inflation in the economy.
What are examples of expansionary fiscal policy?
The two major examples of expansionary fiscal policy are tax cuts and increased government spending. Both of these policies are intended to increase aggregate demand while contributing to deficits or drawing down budget surpluses.
Which of the following would be an example of monetary policy?
Which of the following is an example of monetary policy that can help put the economy back toward equilibrium? Increasing the money supply to reduce interest rates to encourage more spending and investment.
What Is a Contractionary Policy?
Contractionary policy is a monetary measure referring either to a reduction in government spending—particularly deficit spending—or a reduction in the rate of monetary expansion by a central bank. It is a type of macroeconomic tool designed to combat rising inflation or other economic distortions created by central banks or government interventions. Contractionary policy is the polar opposite of expansionary policy .
How does contractionary policy affect the economy?
If contractionary policy reduces the level of crowding out in the private markets, it may create a stimulating effect by growing the private or non-governmental portion of the economy. This bore true during the Forgotten Depression of 1920 to 1921 and during the period directly following the end of World War II when leaps in economic growth followed massive cuts in government spending and rising interest rates.
How does the government engage in contractionary fiscal policy?
Governments engage in contractionary fiscal policy by raising taxes or reducing government spending. In their crudest form, these policies siphon money from the private economy, with hopes of slowing down unsustainable production or lowering asset prices. In modern times, an increase in the tax level is rarely seen as a viable contractionary ...
Why does the Fed raise reserve requirements?
The Fed may also raise reserve requirements for member banks, in a bid to shrink the money supply or perform open-market operations, by selling assets like U.S. Treasuries, to large investors . This large number of sales lowers the market price of such assets and increases their yields, making it more economical for savers and bondholders.
Is tax increase a contractionary measure?
In modern times, an increase in the tax level is rarely seen as a viable contractionary measure. Instead, most contractionary fiscal policies unwind previous fiscal expansion, by reducing government expenditures—and even then, only in targeted sectors.
What is contractionary monetary policy?
Better knowledge. Sharper Insight. What’s it: A contractionary monetary policy is a monetary policy aimed at reducing the money supply’s growth rate in the economy. Its aim is to reduce the pressure caused by high inflation and to cool the economy. High inflation can lead to hyperinflation if it is not controlled.
What is the difference between expansionary and contractionary monetary policy?
Difference between the expansionary monetary policy and the contractionary monetary policy. Expansionary monetary policy is the opposite of contractionary monetary policy. Under the expansionary policy, the central bank expands the money supply. The aim is to encourage economic growth by stimulating aggregate demand.
How does the central bank prevent overheating?
To avoid overheating the economy, the central bank will adopt a contractionary monetary policy. Contractive monetary policy pushes down aggregate demand. In this case, the central bank reduces the growth rate of the money supply in the economy. As the money supply slows down, interest rates go up.
How does inflation affect the economy?
If the contractionary policy is effective, it weakens aggregate demand in the economy. Inflation moves at a lower rate. As demand weakens, producers also moderate the pace of their production, leading to slower economic growth.
What are the three instruments of contractionary policy?
To carry out a contractionary policy, the central bank has several options. Three common monetary instruments are raising the policy rate, open market operations by selling government debt securities and increasing the reserve requirement ratio.
Why do interest rates rise when the money supply is slow?
People becomes more challenged to find the money. Therefore, interest rates will rise because supply is more limited. For this reason, we call contractionary monetary policy tighter monetary policy because the money supply is tighter than before.
What are the main tools of monetary policy?
The main monetary policy tools are the benchmark interest rate, open market operations, and reserve requirement. Contractionary monetary policy uses one or a combination of the following: Raising the policy rate. Selling government securities through open market operations.
What is contractionary monetary policy?
Contractionary Monetary Policy. The goal of a contractionary monetary policy is to decrease the money supply in the economy. It can be achieved by raising interest rates, selling government bonds, and increasing the reserve requirements for banks. The contractionary policy is utilized when the government wants to control inflation levels.
What are contractionary policies?
1. Inflation. Monetary policies can target inflation levels. A low level of inflation is considered to be healthy for the economy. If inflation is high, a contractionary policy can address this issue. 2. Unemployment. Monetary policies can influence the level of unemployment in the economy. For example, an expansionary monetary policy generally ...
What are the primary objectives of monetary policy?
The primary objectives of monetary policies are the management of inflation or unemployment, and maintenance of currency exchange rates. Fixed vs. Pegged Exchange Rates Foreign currency exchange rates measure one currency's strength relative to another. The strength of a currency depends on a number of factors such as its inflation rate, ...
How does monetary policy affect unemployment?
For example, an expansionary monetary policy generally decreases unemployment because the higher money supply stimulates business activities that lead to the expansion of the job market.
What is the measure of the value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents and businesses?
Gross National Product Gross National Product (GNP) is a measure of the value of all goods and services produced by a country’s residents and businesses. It. Quantitative Easing Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy of printing money, that is implemented by the Central Bank to energize the economy.
What is inflation in economics?
Inflation Inflation is an economic concept that refers to increases in the price level of goods over a set period of time. The rise in the price level signifies that the currency in a given economy loses purchasing power (i.e., less can be bought with the same amount of money). and unemployment.
How does the central bank influence interest rates?
A central bank can influence interest rates by changing the discount rate. The discount rate (base rate) is an interest rate charged by a central bank to banks for short-term loans. For example, if a central bank increases the discount rate, the cost of borrowing for the banks increases.
Purpose of Monetary Policy
- The purpose of a restrictive or tight monetary policyis to ward off inflation. A little inflation is healthy. A 2% annual price increase is actually good for the economy because it stimulates demand. People expect prices to be higher later, so they may buy more now. That's why many central banks have an inflation target of around 2%. If inflation gets much higher, it's d…
How Central Banks Implement Contractionary Policy
- Central banks have lots of monetary policy tools. The first is open market operations. Here's how the Federal Reserve tools are used in the U.S. The Fed is the official bank for the federal government. The government deposits U.S. Treasury notes at the Fed like you deposit cash. To implement a contractionary policy, the Fed sells these Treasurys to its member banks. The ban…
Effects and Examples
- Higher interest rates make loans more expensive. As a result, people are less likely to buy houses, autos, and furniture. Businesses can't afford to expand. The economy slows. If not exercised with care, the contractionary policy can push the economy into a recession. There aren't many examples of contractionary monetary policy for two reasons. First, the Fed wants the economy t…
How Contractionary Differs from Expansionary Policy
- Expansionary monetary policy stimulates the economy. The central bank uses its tools to add to the money supply. It often does this by lowering interest rates. It can also use expansionary open market operations, called quantitative easing. The result is an increase in aggregate demand. It boosts growth as measured by gross domestic product. It low...
What Is A Contractionary Policy?
A Granular View of Contractionary Policy
- Contractionary policies aim to hinder potential distortions to the capital markets. Distortions include high inflation from an expanding money supply, unreasonable asset prices, or crowding-out effects, where a spike in interest rates leads to a reduction in private investment spending such that it dampens the initial increase of total investment spending. While the initial effect of t…
Contractionary Policy as Fiscal Policy
- Governments engage in contractionary fiscal policy by raising taxes or reducing government spending. In their crudest form, these policies siphon money from the private economy, with hopes of slowing down unsustainable production or lowering asset prices. In modern times, an increase in the tax level is rarely seen as a viable contractionary measure. Instead, most contrac…
Contractionary Policy as A Monetary Policy
- Contractionary monetary policy is driven by increases in the various base interest rates controlled by modern central banks or other means producing growth in the money supply. The goal is to reduce inflation by limiting the amount of active money circulating in the economy. It also aims to quell unsustainable speculation and capital investment that previous expansionary policies may …
Contractionary Policy Example
- For an actual example of a contractionary policy at work, look no further than 2018. As reported by Dhaka Tribune, Bangladesh Bank announced plans to issue a contractionary monetary policy in an effort to control the supply of credits and inflation and ultimately maintain economic stability in the country.3 As the economic situation changed in subsequent years, the bank converted to …