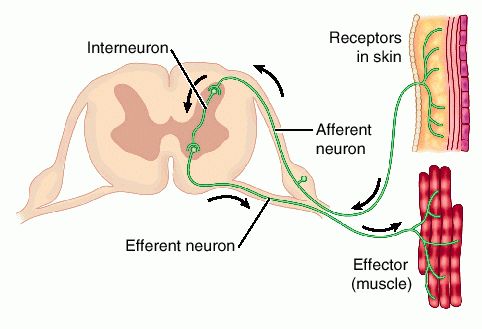
A cranial reflex is a fast, involuntary response to a stimulus. It uses the brain stem as an integrating center (the brain receives sensory information and generates a response).
Does cranial reflex involve spinal cord?
Location - cranial reflexes have the central nervous system part of their circuit in the brain, while spinal reflexes have it in the spinal cord. Also the cranial reflexes have the peripheral nervous system part of their circuit in cranial nerves, while spinal reflexes have it in spinal nerves. One may also ask, what are the types of reflexes?
What cranial nerves are involved in pupillary light reflex?
- The trigeminal nerve has two roots, one motor and the other sensory, arising from the pons. ...
- The sensory fibers convey pain, temperature, touch, and pressure information from the eye, face,
- each temple of the participant and asking the participant to clench his or her teeth several times. ...
Is reflex action and reflex arcs are same?
Reflexes, or reflex actions, are involuntary, almost instantaneous movements in response to a specific stimulus. Reflex arcs that contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron, are considered monosynaptic. Examples of monosynaptic reflex arcs in humans include the patellar reflex and the Achilles reflex.
Can reflex action controlled by spinal cord?
Within the spinal cord, simple reflexes can function without higher input from the brain. Slightly more complex spinal control occurs when central pattern generators function during repetitive movements like walking. The motor and premotor cortices in the brain are responsible for the planning and execution of voluntary movements.
What are the two types of cranial reflexes?
There are two types: autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs) and somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles).
What is the role of cranial reflex?
Reflexes are involuntary responses to peripheral nerve stimulation. A reflex that is mediated by cranial nerves is called cranial reflex such as blinking of eyes, masseter reflex, etc. Cranial reflexes control the movement of the eyeball, tongue, face, head, etc.
What's the difference between cranial and spinal reflexes?
During a spinal reflex, information may be transmitted to the brain, but it is the spinal cord, not the brain, that is responsible for the integration of sensory information and a response transmitted to motor neurons. Some reflexes are cranial reflexes with pathways through cranial nerves and the brainstem.
Do cranial reflexes involve the brain?
This quick response is called a reflex, and reflexes occur without conscious thinking or planning, meaning the brain is not involved in them.
What are some examples of reflexes?
Examples of reflexes that last into adulthood are: Blinking reflex: blinking the eyes when they are touched or when a sudden bright light appears. Cough reflex: coughing when the airway is stimulated. Gag reflex: gagging when the throat or back of the mouth is stimulated.
What reflexes are centered in the brain and involve cranial nerves?
A&P lab 2QuestionAnswer__ Reflexes are centered in the brain and involve cranial nervesCranialLymphatic tissue containsmainly lymphocytesThe large lymphatic organ found in the left hypochondriac region is thespleenthe lymph from tissues of lower limbs is conducted by thethoracic ducts36 more rows
Which is not an cranial reflex?
During a spinal reflex, information may be provided to the brain, but it is the spinal cord, not the brain, that is in charge of the integration of sensory information and a response transmitted to motor neurons. Hence, the correct option is (B) Scratching.
What are 3 main differences between spinal nerves and cranial nerves?
Spinal nervesCranial nervesAll of the spinal nerves are mixed nerves so that each nerve consists of both ventral that is motor and dorsal root that is sensory components.Except for olfactory, optic, and vestibulocochlear nerves, all other cranial nerves are purely mixed nerves.2 more rows
What is the difference between cranial nerves and peripheral nerves?
The cranial nerves are considered components of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), although on a structural level the olfactory, optic and terminal nerves are more accurately considered part of the central nervous system (CNS).
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
In our discussion we will examine four major reflexes that are integrated within the spinal cord: the stretch reflex, the Golgi tendon reflex, the withdrawal reflex and the crossed extensor reflex.
What part of the brain is responsible for reflexes?
brainstemYour brainstem helps regulate some body functions, including your breathing and heart rate. The brainstem also controls your balance, coordination and reflexes.
What part of the brain do reflexes come from?
The brain stem, which consists of the medulla (an enlarged portion of the upper spinal cord), pons and midbrain (lower animals have only a medulla). The brain stem controls the reflexes and automatic functions (heart rate, blood pressure), limb movements and visceral functions (digestion, urination).
What is the purpose of the rooting reflex?
Your baby's rooting reflex is an involuntary muscle response to stimulation of their mouth. It helps your baby find a nipple to feed. Your baby was born with this and other newborn reflexes to help them survive.
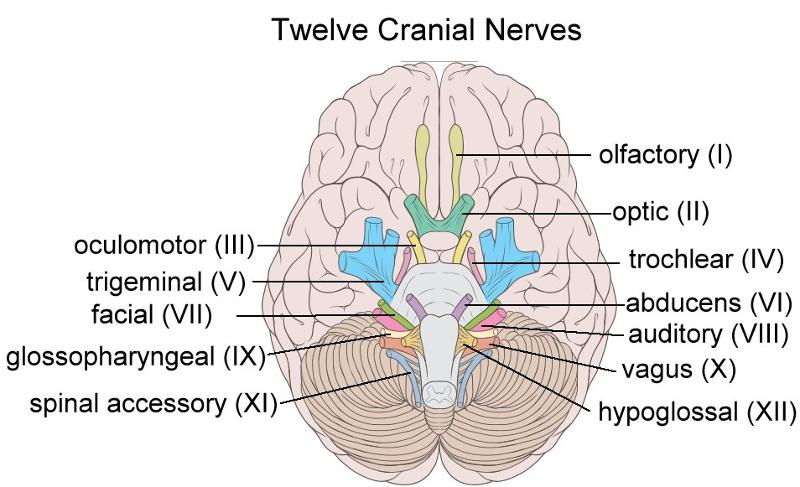
What are cranial nerves?
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
What cranial nerve is responsible for cough reflex?
The cough reflex starts with stimulation of irritant receptors with afferents in the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X).
Which cranial nerve is responsible for sucking?
The sucking motions of a premature newborn are generated by the coordinated action of muscle fibres of at least 26 muscle pairs and 5 pairs of cranial nerves, including the trigeminal nerve (V), the facial nerve (VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), the vagus nerve (X), the hypoglossal nerve (XII) and the cervical ...
What is the cranial reflex?
A type of cranial, SOMATIC reflex. Stimulated by rotation of head. Includes vestibulocochlear nerve (afferent) and II, Iv and VI (efferent). Central synapse at motor nuclei controlling eye muscles. Responds by opposite movement of eyes to stabilize field of vision
Which nerve is responsible for the sensory function of the lower eyelid?
A branch of the trigeminal nerve. Has a sensory function at lower eyelid; superior lip, gums, and teeth; cheek, nose (part), palate, and pharynx (part). Goes through foramen rotundum on sphenoid.
What nerve is responsible for the motor function of the tongue?
A branch of teh trigeminal nerve. Has a sensory function at inferior gums, teeth, lips, palate (part) and tongue (part). Has a MOTOR function at muscles of mastication. Goes through foramen ovale of the sphenoid