41 major life stressors
| Life event | Life change units |
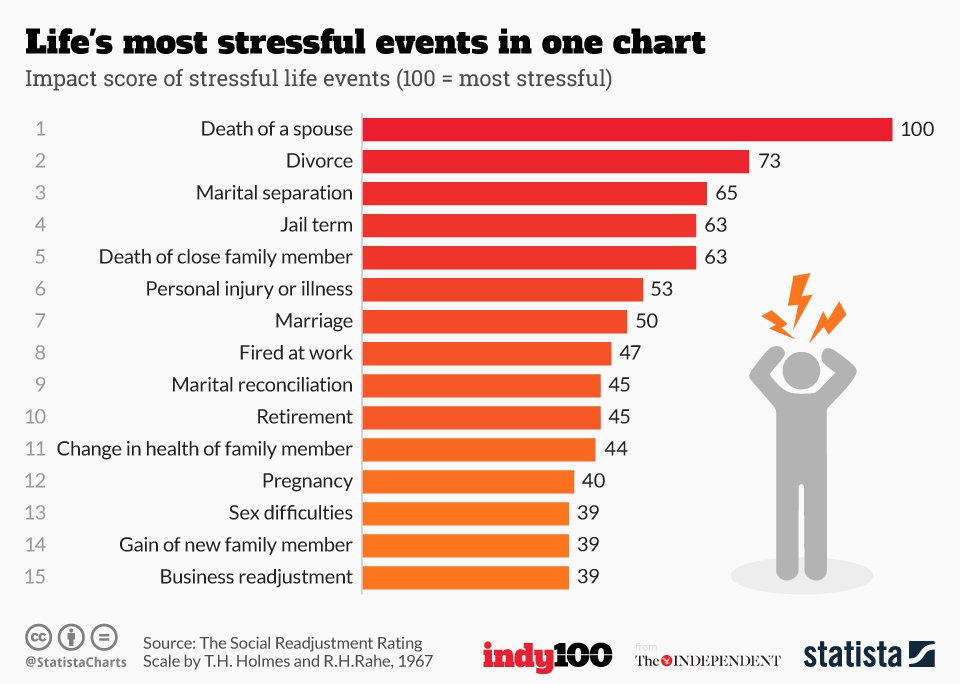
| Death of a spouse | 100 |
| Divorce | 73 |
| Marital separation | 65 |
| Imprisonment | 63 |
What are the top 10 stressors?
What are the top 10 stressors?
- Death of a loved one.
- Divorce.
- Moving.
- Major illness or injury.
- Job loss.
Are daily hassles and stressors the same?
The fourth hypothesis tests for cross-domain effects of chronic stressors and daily hassles. Findings indicate that chronic stressors and daily hassles are distinct types of stressors with unique contributions to psychological distress.
What are coping strategies are effective to manage stress?
What Coping Strategies Can Help Manage Stress?
- Calming Coping Strategies. First, it’s helpful to calm your physiology so you reverse your stress response. ...
- Emotion-Focused Coping Strategies. ...
- Solution-Focused Coping Strategies. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
What are the major stressors in life?
- Death of a loved one. The death of a spouse or other loved one tops the list of the most stressful things we experience.
- Separation or divorce. Separation and divorce are another two of life's most stressful events.
- Getting married.
- Starting a new job.
- Workplace stressors.
- Financial problems.

What are 3 daily stressors?
These can include:Losing a job (or starting a new one).Your child leaving or returning home.The death of your spouse.Divorce or marriage.Illness or injury for you or a close family member.Money problems.Having or adopting a baby.
What are 10 examples of stressors?
Life eventsDeath of a loved one.Losing a job.Illness.Starting university.Work promotion.Birth of a child.Marriage.Winning the lottery.
What are 5 common stressors?
The Top 5 Most Stressful Life Events and How to Handle ThemDeath of a loved one.Divorce.Moving.Major illness or injury.Job loss.
What are the top 20 stressors in life?
Examples of life stresses are:The death of a loved one.Divorce.Loss of a job.Increase in financial obligations.Getting married.Moving to a new home.Chronic illness or injury.Emotional problems (depression, anxiety, anger, grief, guilt, low self-esteem)More items...•
What are 15 stressors?
Top 15 grad school stressorsAcademic responsibilities or pressures. 68 percent.Finances or debt. 64 percent.Anxiety. 61 percent.Poor work/school-life balance. 59 percent.Family issues. 45 percent.Research responsibilities or pressures. 43 percent.Burnout or compassion fatigue. ... Professional isolation or lack of social support.More items...
What are the top 10 stressors in life?
Top 10 Stressful Life EventsDeath of a spouse.Divorce.Marital separation from mate.Detention in jail or other institution.Death of a close family member.Major personal injury or illness.Marriage.Being fired at work.More items...•
What are the 6 stressors?
Here are six of the most common stressors along with a few quick tips to build your stress resilience:You are frequently late. ... You are often angry or frustrated. ... You are unsure of your ability to do something. ... You feel lonely. ... You are burned out. ... You are overextended.More items...•
What are the top 5 stressors for teens?
Some sources of stress for teens include:School demands and frustrations.Negative thoughts or feelings about themselves.Changes in their bodies.Problems with friends and/or peers at school.Unsafe living environment/neighborhood.Separation or divorce of parents.Chronic illness or severe problems in the family.More items...
What are the top 10 stressors in life?
Top 10 Stressful Life EventsDeath of a spouse.Divorce.Marital separation from mate.Detention in jail or other institution.Death of a close family member.Major personal injury or illness.Marriage.Being fired at work.More items...•
What are the 7 stressors?
The 7 Most Stressful Life Changes (and How to Cope With Them)Death of a spouse. You probably aren't surprised to hear that the death of a spouse is the most stressful event on this list. ... Divorce. ... Marital separation. ... Detention in jail or prison. ... The death of a close family member. ... A major injury or illness. ... Marriage.
What are the top 10 causes of stress?
Top 10 Causes Of Stress And How To Beat ThemNot having enough time. ... Unhealthy lifestyle. ... Taking on too much. ... Conflicts in the workplace or at home. ... Inability to accept things as they are. ... Failure to take time out and relax. ... Non-work-related issues. ... Failure to see the humour in situations.More items...
What are the 4 stressors?
Albrecht's four common types of stress are:Time stress.Anticipatory stress.Situational stress.Encounter stress.
What is a DISE checklist?
The DISE is an outgrowth of previous checklist approaches to the assessment of daily stress. The Daily Life Experiences (DLE) checklist comprises a list of 78 events that represent various domains in daily life, and scales for obtaining subjective ratings of the desirability and meaningfulness of each experienced event (Stone & Neale, 1982). Brantley and Jones (1989) developed a similar measure, the Daily Stress Inventory, which assesses 58 minor events as well as a subjective rating of how stressful each event was. Similarly, DeLongis and colleagues (DeLongis et al., 1992) Hassles Scale includes 53 items, assessing domains similar to those mentioned above. Zautra and colleagues (Zautra et al., 1986) have also shown that a shorter 18-item checklist, the Inventory of Small Life Events (ISLE), can be effectively adapted for use in a daily diary design. The approach of administering event checklists on a daily basis has important implications for the assessment of daily stressors. The repeated daily assessment of individuals using checklists allows for improved precision in characterizing the typical days of individuals as the day is the unit of analysis. Checklists such as the DLE and ISLE also include subjective ratings about each event that provide more information than whether an event simply occurred, adding multidimensional data about events, days, and individuals. A potential limitation of the daily checklist approach that the experience of a broad range of events is obtained at the expense that the experience of a broad range of events is obtained at the expense of obtaining intimate, and potentially useful, in-depth knowledge that is captured in the DISE.
How are stressors assessed?
Daily stressors are often assessed via self-reports of specific events over multiple days. These events represent tangible, albeit minor interruptions that may have a more proximal effect on well-being than major life events such as job loss and divorce. .
What are the daily stressors?
Daily Stressors are defined as routine challenges of day-to-day living, such as the everyday concerns of work, caring for other people, and commuting between work and home. They may also refer to more unexpected small occurrences such as arguments with children, unexpected work deadlines, and malfunctioning computers that disrupt daily life.
What are the stressors at work?
Job Issues. Pretty much everyone is going to run into stressors at work. It could be a heavy workload, a bully co-worker or a boss. If these people are haggling you and getting on your nerves, there is a good chance that they’re going to cause you significant stress.
How to avoid traumatic childhood?
The good news is that there are some things you can do to avoid the stress of a traumatic childhood. Speaking with a counselor is highly recommended. Once you’re able to overcome your past trauma, you’ll be able to avoid the stress now. 3. Job Issues.
Why is it important to learn how to prevent stress?
Since stress is pretty much unavoidable, you need to learn how to prevent stressors from taking over your life so you’re not constantly on edge and filled with anxiety.
Why do people worry about their health?
There are many people who sit around and worry about their health. They feel ill, so they’re concerned that they might have a serious disease. Many people always believe that it is the worst-case scenario possible.
How to deal with stress due to health problems?
If you’re dealing with stress due to health problems, you should get to the bottom of the problem as quickly as possible. Go ahead and visit the doctor for a checkup. There is a good chance that it is nothing. If there is a problem, finding out as soon as possible is best.
What are some schools that put pressure on students?
Many students are dealing with stress related to school. It is a fact that some schools, such as charter, magnet, private, boarding and universities, put a lot of pressure on students to perform up to par. And, this is not to mention the pressure put on the by their parents.
What is compassion fatigue?
There’s a condition called compassion fatigue which has to do with being so tied up with taking care of those around you that it stresses you out. Check out this article for tips on how to overcome compassion fatigue. 5. A Divorce.
What Situations Become Stressors?
While some things tend to stress many people—job demands, relationship conflicts, a hectic schedule —not every potential stressor causes stress for everyone.
What is Oken BS?
Oken BS, Chamine I, Wakeland W. A systems approach to stress, stressors and resilience in humans. Behav Brain Res. 2015;282:144-54. PMID:25549855
Why do people have different stressors?
Each person has different stressors because each of us has a unique set of resources, understanding of the world, and way of perceiving things.
What happens when you encounter stressors?
When one encounters stressors, the body’s stress response is triggered, and a series of physiological changes take place to allow the person to fight or run. If this sounds like stress, it's because sometimes when people talk about ‘stress’ in their life, they are really talking about stressors; stressors lead to the body’s stress response and ...
What is the toll of conflict in a relationship?
Relationship Stress: The Toll of Conflict : Conflict in a relationship is one of the heavier stressors people face in that conflict takes a bigger toll on us that most of the other stressors we face in life. Find out why, and what you can do to minimize the stress.
What is stressor in life?
Stressors are situations that are experienced as a perceived threat to one’s well-being or position in life, especially if the challenge of dealing with it exceeds a person’s perceived available resources. 1.
How to reduce stress?
An important first step is to begin thinking of stress as something that you can and should learn to manage, just as you'd take any other problem head-on. For now, here are some targeted resources for managing the stress from specific stressors: Top Causes of Stress: Are you stressed by ...
What are Stressors?
Stress is a bodily reaction, and stressors are what create that reaction. In other words, a stressor is any stimulus that produces mental or physical stress. Notice that we define stressors as stimuli. They are something that causes a stress reaction, but they aren't the stress itself. This is an important fact to keep in mind when you're dealing with stress because separating the stress from the stressor can help you understand what to do about it.
Why are stressors called stressors?
Stressors are so named because they cause a stress reaction. In other words, if something didn't cause you stress, it wouldn't be a stressor for you. So, what is this stress response like? Well, it can be a physical and/or mental response.
How does stress affect mental health?
The short-term mental effects may include a heightened sense of awareness and focus. However, the stress may also show up in more negative ways, such as: If the stressors don't go away and you don't learn to reduce your stress response, the long-term effects on your mental health can be extremely serious.
How does the body respond to stress?
How The Body Responds To Stress 1 The amygdala triggers the hypothalamus, the command center of the for the stress reaction, by sending a signal that tells your body you're in a threatening situation. 2 The adrenal glands sense the signals and release cortisol, noradrenaline, and adrenaline; this causes your heart rate and respiration to speed up. Blood vessels dilate in your arms and legs, and the digestive system starts increasing blood sugar levels. 3 The musculoskeletal system reads the stress signals and causes your muscles to become tense and taut. 4 The cardiovascular system causes your heart rate to speed up, and this also causes your heart to pump more blood through your large blood vessels and heart. 5 The endocrine system is signaled by the hypothalamus to produce stress hormones, which gives you energy and tells your digestive system to get to work to produce glucose in your liver. 6 The gastrointestinal system can cause you to eat more or eat different foods. Butterflies in your stomach start because your brain is in a state of heightened awareness and picks up the slightest sensations in your stomach. You may also have diarrhea or constipation because of the changed rate of digestion. 7 The reproductive system reacts differently in men and women. In men, this means a rush of testosterone and possibly heightened arousal. In women, PMS may include flair, menstruation may stop or become irregular, and arousal may decrease.
Why is it important to separate stress from the stressor?
This is an important fact to keep in mind when you're dealing with stress because separating the stress from the stressor can help you understand what to do about it. Stressors are the triggers behind the stress we face every day.
What are the triggers of stress?
Stressors are the triggers behind the stress we face every day. They're the things we're exposed to or the things we are dealing with internally. They are the signs that tell our minds and our bodies that something is happening that will require us to do something hard or difficult.
What happens when a stressor appears?
When a stressor appears, it triggers the body's nervous system. The nervous system sends several signals to the body, some of which trigger a 'flight or flight' response in the body. The body then shifts to focus on the threatening situation or event and continues to send signals.
What is a 150 score?
Score 150-: Only has a slight risk of illness.
Who created the stress scale?
As far back as 1967, two psychiatrists, Thomas Holmes and Richard Rahe, researched the causal link between stress and illness. What they came up with is called (you guessed it) the Holmes and Rahe stress scale. It lists life events in order of the stress levels they cause. Below is the scale.
Is stress bad for health?
For many people, stress levels go hand-in-hand with getting ill. Some stress is good for us, but when it is prolonged, stress is very bad for our health. We are simply not put together to deal with the kind of stressors that modern life often imposes on us.
Definition
Daily stress is defined as mundane hassles, strains, or annoyances associated with routine daily activities and transactions of everyday life. Daily stress is relatively minor, but has the potential to disrupt the flow of everyday life and add to overall levels of stress.
Description
Daily stressors are not inherently stressful events, but they are events that people might appraise as stressful. The experience of feeling stressed depends on what events one notices and how one...
References and Readings
Cooper, C. L., & Derre, P. (2007). Stress: A brief history from the 1950s to Richard Lazarus. In A. Monat, R. S. Lazarus, & G. Reevy (Eds.), The Praeger handbook on stress and coping (2007th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 7–31). Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing. Google Scholar
What are some situations that require coping?
However, some situations that require coping are likely to elicit (bring out) similar coping responses from most people. For example, work-related stressors are more likely to elicit problem-solving strategies. Stressors that are perceived to be changeable are more likely to elicit problem-solving strategies while stressors perceived ...
How to deal with stress?
It's especially important to evaluate your overall lifestyle when encountering significant stress. Engage in stress-reducing activities to help your overall approach to coping with stressors. Try to: 1 Get enough good quality sleep. 2 Eat a well-balanced diet. 3 Exercis e on a regular basis. 4 Take brief rest periods during the day to relax. 5 Take vacations away from home and work. 6 Engage in pleasurable or fun activities every day. 7 Practice relaxation exercises such as yoga, prayer, meditation or progressive muscle relaxation. 8 Avoid use of caffeine and alcohol.
Why does coping get worse?
In some cases, physical illnesses may develop or get worse when a person's capacity to adapt to change is overwhelmed by too much change. Coping involves adjusting to unusual demands, or stressors. This requires giving a greater effort and using greater energy than what's needed in the daily routines of life.
What is the meaning of "coping"?
Coping usually involves adjusting to or tolerating negative events or realities while you try to keep your positive self-image and emotional equilibrium. Coping occurs in the context of life changes that are perceived to be stressful.
What is the difference between rigidity and flexibility in coping?
These differences in coping styles usually reflect differences in personality. Rigidity in coping is less likely to help than is flexibility in coping — being able to fit the most appropriate coping strategy to the demands of different situations.
What are the effects of prolonged mobilization of effort?
Prolonged mobilization of effort can contribute to elevated levels of stress-related hormones and to eventual physical breakdown and illness. Stressors that require coping may be acute, like moving to a new home or experiencing the onset of marriage problems.
What can we do to protect ourselves against stress and enhance our prospects for successful coping?
What can we do to protect ourselves against stress and enhance our prospects for successful coping? Perhaps the most important strategy is to maintain emotionally supportive relationships with others. A vast field of research demonstrates that emotional support buffers individuals against the negative impact of stress.
What are some examples of stressful events?
Stressful events included arguing or almost arguing with someone; experiencing a stressful event at work, home, or school; experiencing discrimination based on race, gender, or age; having something bad happen to someone you’re close to; or experiencing any other bad or stressful events.
How long after a stressful event do you have health issues?
Researchers found that people who continued to have negative feelings about a stressful event the next day were more likely to have health issues ten years later.
When was the NIA study published?
The research was supported by NIH’s National Institute of Aging (NIA). Results were published in Psychological Science on March 19, 2018. For eight days, participants answered questions about the number and type of daily stressors they experienced over the past 24 hours.
Does stress help physical health?
Those who continued to experience negative feelings the day after a stressful event—on days without a stressful event occurring—had more chronic physical health conditions and limitations in their day-to-day activities 10 years later. The findings suggest that the ability to recover from stress may help improve long-term physical health outcomes.
Is stress a physical or mental illness?
Stress is a normal, often useful feeling. It’s a physical and emotional reaction that people experience as they encounter changes in life. But stress that’s extreme or chronic (persists over time) can carry physical and mental health risks. Some people may cope with stress more effectively or recover from stressful events more quickly than others.
Can stress be a long term health problem?
Some people may cope with stress more effectively or recover from stressful events more quickly than others. Studies have linked a person’s emotional response to daily stressors with long-term health effects, including mental disorders, physical illness, and even death.