What is a deep rooted plant? When soil is sparse, dry or extremely wet, shrubs and trees tend to root deeper. In the garden or landscape, deep-rooting small bushes can be used to stabilize an area of poor soil or conditions.
Full Answer
What do plants have deep root systems?
Plants that have deep, extensive root systems can successfully grow on hillsides. Deep roots help to prevent erosion by stabilizing the soil. Some plants produce a large central root called the taproot. Others have a fibrous root system which lacks a taproot.
How deep do these plant/tree roots go?
As the tree roots grow, some of the larger roots near the soil surface may emerge from the ground. Additionally, how deep do tree roots go into the ground? Under ideal soil and moisture conditions, roots have been observed to grow to more than 20 feet (6 meters) deep.
Are desert plants roots deep or spreaded out?
typical desert plants, such as the Mesquite bushes of America and the Acacia scrub of the African deserts have wide-spread, much branched root systems. A common fallacy is that desert plants must have extremely deep roots, so that they can reach the water table, the level at which standing water will always be found. This
What are the example of rooted floating plants?
Plants such as waterlilies, lotus, watershield, and spatterdock are floating-leaved plants. Trailing Floating - These plants are rooted into the shallow areas nearest the bank and have a 'trailing' or 'creeping' growth habit which allows them to form floating mats that extend out over the water surface.

What are plants with deep roots?
Deep-Rooted PlantsTomatoes.Asparagus.Winter squash.Pumpkins.Parsnips.
What garden plants have the deepest roots?
Deeply-Rooted Vegetables Vine crops including pumpkins, winter squash and watermelons are deep-rooted, with roots that extend 24 to 36 or more inches. These plants and their roots support long vine structures over long growing seasons. Heat-loving artichokes, okra, sweet potatoes and tomatoes are also deep rooted.
What are deep roots called?
These roots are called: Oblique Roots (Heart Roots) Lateral Roots. Sinker Roots, and. Secondary Roots or Fine Roots.
What are deep roots for?
Even though a distinct classification of “deep roots” is missing to date, deep roots provide important functions for individual plants such as nutrient and water uptake but can also shape plant communities by hydraulic lift (HL).
Which shrubs have deep roots?
Other deep-rooted shrubs that grow well on hillsides include cascara and Hooker willow. According to the Washington State Department of Ecology, cascara produces black berries which attract birds, and Hooker willow resists disease and tolerates salt.
Which flowers have the deepest roots?
The chrysanthemum has deep roots.
What are the 3 types of roots?
The different types of root systems are: Taproots. Fibrous roots. Adventitious roots.
What is the strongest rooted tree?
The neem tree has the strongest taproot system underground. It has one primary root that goes deeper into the soil, while the other secondary roots, emerging from it, have lateral growth habit. The primary root can go deeper twice the height of the tree to absorb water and minerals.
What are the 4 types of roots?
Types of RootsFibrous Roots. Fibrous roots are found in monocot plants. ... Taproots. Taproots are found in the majority of dicot plants. ... Adventitious Roots. Adventitious roots are similar to the fibrous roots. ... Creeping Roots. ... Tuberous Roots. ... Water Roots. ... Parasite Roots.
Why are deeper roots better?
Plant roots complete a cycle in the soil. The deeper they go, the more benefits they provide to soil fertility and stable carbon storage in soils. While alive and active, roots redistribute carbon and nutrients throughout the soil profile.
What fruit trees have deep roots?
The fig tree, for example, features a voracious root system that will expand far beyond the tree's crown in its search for water and nutrients. The Meyer lemon features a less aggressive root system that will not grow as far out but can reach deep into the ground.
Do tomatoes have deep roots?
Taproots are famous for going straight down provided there are no obstacles in the way. Tomatoes, due to their taproot system, have a deep root going down up to 3 feet (90 cm) in extreme cases, which happens when the plant is in search of water or nutrients in poor but loose soil conditions.
How deep do tomato plant roots go?
The ideal depth would be greater than 2 feet (60 cm) because, in general, tomato roots can grow anywhere between 2 and 3 feet, even though around 2 feet is more common.
How deep do most garden vegetable roots grow?
Crop rooting depth is categorized as shallow, moderate, or deep. Shallow-rooted crops root to a depth of 12 to 18 inches. Moderate-rooted crops develop roots to a depth of 18 to 24 inches. Deep-rooted crops develop a root system to a depth of 24 or more inches.
Which plant has long roots that can reach the soil under the water?
Deep-rooted plants, cacti have an underground structure called a taproot, which is a long, thick, tapered root that grows down straight from the base of the plant. These taproots allow cacti to access water deep below the surface of the ground.
Do perennials have deep roots?
Perennial plants have very deep roots. Perennial vegetables such as artichokes and asparagus have roots that extend much deeper than 4 feet (120cm), far deeper than annual vegetables, and tree roots can run as deep as the height of the tree itself. The deepest recorded depth that tree roots can run is 60m.
Where do trees have roots?
Plants or Trees That Have Deep Roots. Most trees do not develop deep roots, commonly referred to as tap roots, below the tree's trunk . Most trees and plants only develop roots in the top portion of the soil. However, pine and oak trees growing in well-drained soil can develop tap roots.
How tall is a wild rose?
Wild rose is also known as prickly rose, which is a deciduous shrub that reaches heights of 4 feet. Wild rose develops fine roots in the top of soil and deep roots often extend more than 55 inches. Pink flowers bloom on stems covered with prickles.
What is a pin oak tree?
Northern pin oak is a member of the Fagaceae family and is also known as jack oak, Hill's oak and upland pin oak. Reaching heights of 69 feet at maturity, this tree is known for the deep root system it develops in a short period of time. For this reason, the Northern pin oak is not easily transplanted. Northern pin oak is most commonly grown for its wood, which is often used to make flooring, furniture, pulp and fuel. A wide variety of wildlife feasts on the acorns of this tree, including deer and squirrel. Northern pin oak is found in the Great Lakes, Wisconsin, Michigan, Illinois, Iowa, Ohio, Indiana, North Dakota and Arkansas.
Why do Native Americans use wild roses?
Native Americans often used wild rose in teas to treat stomach ailments and sore throats. Certain Native American tribes believed the wild rose kept away evil spirits.
Do oak trees have deep roots?
Most trees do not develop deep roots, commonly referred to as tap roots, below the tree's trunk. However, pine and oak trees growing in well-drained soil can develop tap roots.
Can oak trees grow tap roots?
However, pine and oak trees growing in well-drained soil can develop tap roots.
Does Mugo Pine have deep roots?
The southern pine known as mugo pine develops deep roots unless it is planted on shallow, poorly drained soil.
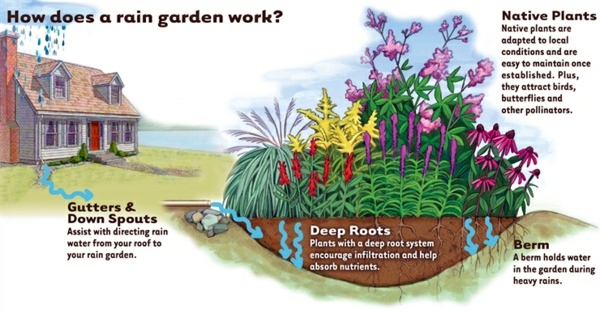
How do native plants help?
. . a 50 percent improvement in creativity after just a few days in nature.” 1. Native plants aid in crime reduction. Buildings in Chicago with the most green views saw 48 percent fewer property crimes and 56 percent fewer violent crimes.” 2.
How do plants get carbon dioxide?
Native plants take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, and their deep roots put it back in the ground (where it belongs!) in a process called carbon sequestration (also called carbon capture or carbon trapping). As plants respire, they absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen back into it. The carbon dioxide is broken down by plants, ...
Why are native plants important to the ecosystem?
Native plants are foundational in ecosystems. Through photosynthesis, they convert energy from the sun into forms that are usable for all other living things. Native plants provide nectar, shelter, and sustenance for butterflies, pollinators, and birds.
How do native plants help the water cycle?
Native Plants manage water flow with their strong root networks. Their deep roots slow down the flow of water, preventing soil erosion and reducing stormwater runoff. Once established, native plants thrive without the use of irrigation, but they’re also regenerative. Native plants and rain gardens help clean water naturally because their deep root systems act as filters for the dirty runoff from streets, parking lots and rooftops.
Do native plants grow in the prairie?
Over the years, people have associated native plants with native prairies and other beautiful, rugged, untamed places. Native landscapes at home don’t have to look wild and wooly unless you want them to. With good design and maintenance, native plants can also thrive in traditional gardenscapes.
How deep do bushes root?
When you dig out a planted shrub, you can ascertain its root depth. An average root depth for a small bush would be between one-quarter and one-third of the plant's height above ground.
Why do small bushes have deep roots?
Small Bushes With Deep Roots. When soil is sparse, dry or extremely wet, shrubs and trees tend to root deeper. In the garden or landscape, deep-rooting small bushes can be used to stabilize an area of poor soil or conditions. If you are trying to control soil erosion on sloping ground, deep-rooting bushes can be helpful.
How tall do salal trees grow?
Salal (Gaultheria shallon) is hardy in USDA zones 7 to 10 and roots moderately deeply in dry soil. It typically grows to a maximum height of 4 to 6 feet. The edible, black berries produced by salal attract birds, small mammals and bears. Cascara buckthorn (Rhamnus purshiana) can flourish in full shade, preferring dry to moist soil. Cascara buckthorn is hardy in USDA zones 4 through 9. Although it can grow 20 feet tall, you can keep it smaller through regular pruning.
What bushes can help with erosion?
If you are trying to control soil erosion on sloping ground, deep-rooting bushes can be helpful. Some of the smaller varieties of bushes or shrubs with deep roots offer unusual foliage, textures, flowers or berries.
What shrubs are used to prevent erosion of waterway banks?
Certain shrubs will root deep in wet soil conditions such as creek beds or wetlands. Red osier dogwood (Cornus stolonifera) roots deep and is commonly used to prevent erosion of waterway banks. The deciduous leaves are dark green in spring and summer, turning red and purple in the fall.
What is the best soil for a cascara buckthorn?
Cascara buckthorn (Rhamnus purshiana) can flourish in full shade, preferring dry to moist soil. Cascara buckthorn is hardy in USDA zones 4 through 9. Although it can grow 20 feet tall, you can keep it smaller through regular pruning.
What are the deep roots of prairie grass?
Weaver, in particular, is well known for his illustrations of long roots extending below prairie plants. That root depth is frequently held up as a major factor that influences the resilience of prairies in the face of summer drought. After all, deep roots allow those plants to draw water from far down in the soil profile when rainfall becomes scarce. It’s one of the defining components of prairie ecosystems.
How deep do shrubs draw water?
What about woody vegetation? Jesse’s students have found that shrubs pull water from much deeper in the soil than grasses and forbs, starting at about 18 inches and reaching down to 8 or 10 feet. As with forbs, shrubs can draw water from shallower depths during times of plenty, but they seem focus mainly water from depths below what grasses and forbs can reach. This, by the way, applies to shrub species such as sumac ( Rhus sp) and dogwood ( Cornus sp), but not to more forb-like shrubs such as leadplant ( Amorpha canescens) or New Jersey tea ( Ceanothus sp).
How do shrubs share water?
Some of those shrubs have an additional advantage because they are clonal and can share water between the multitude of their aboveground stems, which are connected by underground rhizomes. The Nippert lab has shown that the more mature stems in the center of clone can pull water from deep in the soil and then transport it to the more shallow-rooted stems along the expanding outer edge of the clone. In that way, the young stems on the outside are better able to outcompete surrounding vegetation and allow the overall shrub clone to grow larger. As if that wasn’t enough, Jesse says it also appears that the big thick roots of shrubs alter water infiltration, speeding the passage of rainwater down through the soil to where only shrub roots can access it. This is especially true after those roots die and leave open channels behind.
Where do prairie grasses grow?
Prairie grasses have a dense mass of roots in the upper reaches of the soil profile. They dominate the access to water within that zone, especially during times of drought.
Do shrubs have water infiltration?
As if that wasn’t enough, Jesse says it also appears that the big thick roots of shrubs alter water infiltration, speeding the passage of rainwater down through the soil to where only shrub roots can access it. This is especially true after those roots die and leave open channels behind.
Do prairie plants pull water from great depths?
In addition, the idea that prairie plants are pulling water from great depths is just an attractive – and logical – story. The accompanying illustrations are also really compelling.
Do prairie grasses have deep roots?
Yes, prairie grasses and wildflowers have very deep roots, but research over the last decade or so has built a strong case against the idea that those plants use their deep roots to find moisture during times of scarcity. In fact, they might not be using them to draw moisture at all.
What is the best plant for erosion control?
The Spruce / Autumn Wood. The best plants for erosion control are those ground covers or shrubs that are vigorous, attractive, and have a root system effective at holding back soil on a hill. They should have spreading foliage to slow the velocity of heavy rain. If you live in deer country they should also be plants that deer tend not to eat.
What zone is Phlox subulata in?
When you see the blossoms on this short (6 inches) creeping plant for zones 3 to 9, you know that spring is underway.
Is Pachysandra terminalis a ground cover?
Like creeping myrtle, Pachysandra terminalis is a short (6 in ches), evergreen ground cover for shade. Japanese spurge (zones 4 to 8) is considered a foliage plant. Although it does put out small, white flowers, they add little value. The leaves have a leathery feel and look that lends further interest to your property.
Can creeping myrtle take shade?
In contrast with creeping juniper, creeping myrtle ( Vinca minor) is one of the ground covers that can take shade. 2 But, like creeping juniper, it's a short (3 to 6 inches) evergreen.
DEEP ROOTS NATIVES
Our mission is to promote the conservation, preservation, and restoration of ecosystems; and of the rich multi-cultural history of Durham and surrounding areas.
Nursery Hours
The Deep Roots Natives plant nursery sells over 50 species of native plants as well as non-invasive pollinator and edible plants, fruit trees and architectural trees.
How long does it take for root killer to reach the plant base?
Otherwise, it will take about two weeks for the root killer to reach the plant's base.
Is landscape design labor intensive?
" Landscape design is very labor intensive. Don't bite off more than you can chew," cautions Yost , who recommends homeowners map out a plan that outlines their goals. "Draw something out, even if it's on the back of an envelope, or put together a shopping list with the tools you need." Adds Yost, "Know where you're starting and where you're going so that you get somewhere in the end."
Can root killer be used on leaves?
"It needs to be taken up by the leaves and then go down to the roots," explains Yost. "If you chop all the leaves off, you can't use it, because there's no leaf surface.".