
What are Deferred Income
Deferred income
Deferred income (also known as deferred revenue, unearned revenue, or unearned income) is, in accrual accounting, money received for goods or services which have not yet been delivered. According to the revenue recognition principle, it is recorded as a liability until delivery is made, at which time it is converted into revenue.
What are the tax advantages of deferring income?
Tax Advantages. Many times, the contributions you make to your deferred compensation plan will not be taxed. Your dividends and interest are also less likely to get taxed as well. The amount that you withdraw is the only taxable amount. Once you withdraw the money from a deferred compensation plan, you will be taxed at your income tax rate.
What do you mean by deferred taxes?
Deferred tax is the tax that is levied on a company, that has either been deducted in advance or is eligible to be carried over to the succeeding financial years. Know more about its types, calculation, and scenarios in which it is recorded.
What do you mean by deferred income?
Deferred income is also known as deferred revenue or unearned income. As the name suggests, it refers to income that you have received or not earned yet. Usually, this is because a customer or client has made an advance payment for services that have not yet been rendered or goods that have not yet been delivered.
How to defer income from taxes?
“Okay, so how do you defer taxes?” After successfully filing your taxes, set up a short- or long-term payment installation plan with the IRS. First, try to pay as much as you can up front. Then, pay the rest on the plan. Apply for the short-term payment plan if you can pay your full tax payment in less than 120 days.
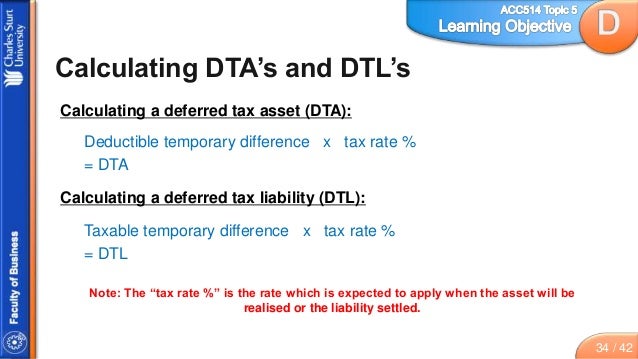
What is deferred tax in simple terms?
IAS 12 defines a deferred tax liability as being the amount of income tax payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences. So, in simple terms, deferred tax is tax that is payable in the future.
What is deferred income tax example?
A common example of tax-deferred liabilities for individuals is a 401(k). A 401(k)s is a deferred tax retirement plan. You pay no taxes on contributions to the 401(k) until years or decades later when you make a withdrawal.
How are deferred income taxes calculated?
It is calculated as the company's anticipated tax rate times the difference between its taxable income and accounting earnings before taxes. Deferred tax liability is the amount of taxes a company has "underpaid" which will be made up in the future.
What is deferred taxation?
The term deferred tax, in essence, refers to the tax which shall either be paid or has already been settled due to transient inconsistency between an organisation's income statement and tax statement. As per this definition, there are two types of deferred tax-deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability.
What is the benefit of deferred tax?
What Is a Deferred Tax Asset? A deferred tax asset is an item on a company's balance sheet that reduces its taxable income in the future. Such a line item asset can be found when a business overpays its taxes. This money will eventually be returned to the business in the form of tax relief.
What is exempt from deferred tax?
Deferred tax is not recognised if it arises on initial recognition of assets/liabilities in a transaction which is not a business combination and, at the time of the transaction, affects neither accounting profit nor taxable profit (IAS 12.15/24).
Do Deferred taxes have to be paid back?
One-half of the deferred taxes must be paid no later than December 31, 2021, with the remaining balance due by December 31, 2022.
Does deferred income count as earned income?
Is deferred compensation considered earned income? Deferred compensation is typically not considered earned, taxable income until you receive the deferred payment in a future tax year. The use of Roth 401(k)s as deferred compensation, for example, is an exception, requiring you to pay taxes on income when it is earned.
How do you identify deferred tax?
Deferred Tax (DT) Deferred tax is recognised on all timing differences – Temporary and Permanent. With respect to timing differences related to unabsorbed depreciation or carry forward losses, DTA is recognised only if there is future virtual certainty.
What are examples of tax-deferred accounts?
Tax-deferred accounts include IRAs, 401(k)s, I bonds, and whole life plans.
What is the difference between tax-deferred and taxable?
In the taxable scenario, taxes are applied annually while in the tax-deferred scenario, the investment is not taxed until the money is withdrawn. In the tax-free scenario, the money is an investment that is not subject to Federal or State tax.
What are examples of tax-deferred accounts?
Tax-deferred accounts include IRAs, 401(k)s, I bonds, and whole life plans.
What is an example of a deferred expense?
Other examples of deferred expenses are as follows: Interest costs that are capitalized as part of a fixed asset for which the costs were incurred. Insurance paid in advance for coverage in future months. The cost of a fixed asset that is charged to expense over its useful life in the form of depreciation.
Which of the following is an example of a deferral?
Here are some examples of deferrals: Insurance premiums. Subscription based services (newspapers, magazines, television programming, etc.) Prepaid rent.
What is deferred tax with example in India?
Example of Deferred Tax Asset and Liability For the purpose of tax profit, bad debts will be allowed in future when it's actually written off. Hence taxable income after this disallowance will be Rs. 1200 and let's say income tax rate is 20% then the entity will pay taxes on Rs. 1200 i.e (1200*20%) Rs.
What is deferred income tax?
Deferred income tax is a balance sheet item which can either be a liability or an asset as it is a difference resulting from recognition of income between the accounting records of the company and the tax law because of which the income tax payable by the company is not equal to the total expense of tax reported.
What is deferred liability?
Deferred tax liability is created when the Company underpays the tax, which it will have to pay in the near future. The liability is created not due to Company defaulting on its tax liabilities but due to timing mismatch or accounting provisions, which causes less tax outgo than required by the Company.
How does deferred tax affect cash flows?
Deferred tax impacts the future cash flows for the Company Cash Flows For The Company Cash Flow is the amount of cash or cash equivalent generated & consumed by a Company over a given period . It proves to be a prerequisite for analyzing the business’s strength, profitability, & scope for betterment. read more – while deferred tax assets lower the cash outflow, deferred tax liability increases the cash outflow for the Company in the future
How does deferred income affect tax?
Deferred Income tax affects the tax outgo to the authorities for the financial year. If there is a deferred tax asset, the Company will have to pay less tax in the particular year, whereas, if there is a deferred tax liability, it will have to pay more tax. How to Provide Attribution?
What is deferred tax asset?
Deferred tax asset is created when the Company has already paid the tax. The benefit of deferred tax assets is that the Company will have less tax outgo in the future subsequent years.
What is LIFO accounting?
LIFO accounting means inventory acquired at last would be used up or sold first. read more. . It created a temporary difference of $ 50,000, and if the tax rate is 30% would create a tax liability of $ 15,000.
How to look for changes in deferred taxes?
Analysts should look for changes in deferred taxes by reading the footnotes to the financial statements Financial Statements Financial statements are written reports prepared by a company's management to present the company's financial affairs over a given period (quarter, six monthly or yearly). These statements, which include the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flows, and Shareholders Equity Statement, must be prepared in accordance with prescribed and standardized accounting standards to ensure uniformity in reporting at all levels. read more, which could include information about the warranty, bad debts, write-downs, policy on capitalizing or depreciating assets, policy on amortizing financial assets, revenue recognition policy, etc.
Why is deferred income tax an asset?
Having said that, it is an asset. When income tax is deferred, it saves the taxpayer from paying a tax they may not be able to afford at this time in their life. 1031 exchanges are a prime example of this scenario. A rental house may make more money in the long-run than simply selling off the asset during a slow market. So, it may be in the taxpayer’s interest to roll the proceeds of an old rental into a new rental.
What is deferred tax?
Deferred tax is the most simple terms is a liability (tax) which exists from the moment the income is earned but is delayed until the income accessed. In addition to 401 (k) plans, the deferred tax is often used in 1031 exchanges. Not familiar with the term? Plenty of people know what they are even if they don’t know their name. Ever hear on the news if a house is sold and the proceeds of the house are rolled into another house before the end of the year, no tax is due? It’s a bit more complex than that but the principle is the same.
How much tax liability is 401(k) distribution?
When it comes to 401 (k) plans, deferred taxes come down to tax brackets. 401 (k) distributions are treated like income. Therefore, the tax liability must be calculated as such. Receive over $100,000 in 401 (k) normal distributions? 24% tax liability. However, most taxpayers hold out 30% if they have any other income sources or investments.
What is the problem with deferred income tax?
The problem with deferred income tax is the amount of misinformation out there. Deferred income tax applies to numerous tax situations. However, this article will focus on four common deferred income tax scenarios: installment sales, section 1031 exchanges, qualified retirement plans, and depreciation. While installment sales, section 1031 exchanges, and depreciation are technically deferred capital gains tax, they have become incredibly more popular since the pandemic. It’s become a priority for individuals and companies to defer tax liabilities until a time the wallets are little more flush.
When depreciating an asset to reduce tax liability, is it critical to remember the deferred tax will catch?
When depreciating any asset to reduce tax liability, it is critical to remember the deferred tax will catch up when the asset is sold. For example, first year bonus depreciation was 50% until the enactment of Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (TCJA) in the end of 2018 which changed the bonus depreciation to 100%. For example, if a taxpayer depreciates out a semi-truck which is used for work until the depreciation reaches zero ($0), when they sale the truck, the deferred tax will be recaptured. If the semi-truck is sold for $40,000 and it is three years old, the taxpayer will owe the deferred tax. In other words, taking the bonus depreciation on earlier tax returns allowed the taxpayer to not pay the tax. But once the asset is sold off, the IRS wants their share of the tax.
What is a 1031 exchange?
To prevent owing tax on the sale, as the individual intends to continue as a landlord, the individual hires a professional 1031 exchange firm to act as their qualified intermediary. While the individual works on closing on the house, the firm holds onto the money until the closing period when they pay the money directly to the seller of the property thus allowing the money never touch the individual’s hands.
When deferring the proceeds of a 1031 exchange, is it critical to remember the taxes are not due on?
When deferring the proceeds of a sale through a 1031 exchange, it is critical to remember the taxes are not due on the proceeds of the sale but rather the profit. For example, if a rental house was purchased for $120,000 and later sold for $160,000. The initial profit will appear to be $40,000 (but depreciation of the house will have to be calculated which will reduce the taxpayer’s basis in the house).
What Is a Deferred Tax Asset?
A deferred tax asset is an item on a company's balance sheet that reduces its taxable income in the future.
What Is a Deferred Tax Asset vs. a Deferred Tax Liability?
A deferred tax asset represents a financial benefit, while a deferred tax liability indicates a future tax obligation or payment due.
Why are deferred assets important?
This asset helps in reducing the company’s future tax liability.
When do deferred taxes exist?
For example, deferred taxes exist when expenses are recognized in a company's income statement before they are required to be recognized by the tax authorities or when revenue is subject to taxes before it is taxable in the income statement. 2
When is deferred tax asset recognized?
It is important to note that a deferred tax asset is recognized only when the difference between the loss-value or depreciation of the asset is expected to offset future profit. 1 . A deferred tax asset can conceptually be compared to rent paid in advance or refundable insurance premiums; while the business no longer has cash on hand, ...
Why does my company get refunded?
This may occur simply because of a difference in the time that a company pays its taxes and the time that the tax authority credits it. Or, it may indicate that the company overpaid its taxes. In that case, the money will be refunded.
What happens to the tax rate when the tax rate goes up?
If the tax rate goes up, it works in the company’s favor because the assets’ values also go up , therefore providing a bigger cushion for a larger income. But if the tax rate drops, the tax asset value also declines. This means that the company may not be able to use the whole benefit before the expiration date.
What Is Deferred Income Tax?
Deferred income tax is when a company defers paying tax on income for a period of time. There are numerous reasons why this may occur. For example, a company may recognize revenue at a time where tax laws were changing, and needed to defer this liability as they were unprepared for this change. The way a company depreciates assets may also be a culprit.
Why Are Tax Deferrals Important?
Tax deferrals are important because it allows an individual or company to increase their purchasing power at a faster rate. Following the example we went over above, where the individual invested $100,000 and earned a 10% return in year one, imagine if the individual had to pay a 25% tax on that $10,000 profit. Instead of being able to invest $110,000 in year 2, they would only be able to invest $107,500. That would reduce how much profit one could potentially earn in year two.
What Is the Difference Between Tax Free and Tax Deferral?
No tax is paid at retirement, because the tax is paid upfront when deposited. A tax deferral is when the tax liability is postponed to a later date.
What are some examples of tax deferrals?
There are numerous examples of tax deferrals you may be familiar with. These include, 401 (k) plans, 403 (b) plans, and various IRA accounts.
How long do you have to withdraw an annuity to get tax deferred?
These annuities also allow your money, and interest, to grow tax deferred until withdrawing it at 59 ½. If withdrawn earlier, you’ll need to pay full tax on your profit.
What is a fixed deferred annuity?
A fixed deferred annuity is an annuity product issued by an insurance agency or investment firm. Unlike a variable rate annuity, a fixed annuity will provide a fixed rate of return for a given period of time, which is arguably both the greatest advantage and disadvantage of this investment vehicle.
Why do companies benefit from tax deferrals?
A company also benefits from tax deferrals as it gives more liquidity to the company in the present day. The company can use that liquidity, or cash, to generate a greater return, or make larger investments.
What Is an Example of Deferred Tax Liability?
The depreciation of fixed assets is a common example.
How is the anticipated tax rate calculated?
It is calculated as the company's anticipated tax rate times the difference between its taxable income and accounting earnings before taxes.
What is accelerated depreciation?
But for tax purposes, the company will use an accelerated depreciation approach. Using this method, the asset depreciates at a greater rate in its early years. A company may record a straight-line depreciation of $100 in its financial statements versus an accelerated depreciation of $200 in its tax books. In turn, the deferred tax liability would equal $100 multiplied by the tax rate of the company.
Why is a tax liability deferred?
The liability is deferred due to a difference in timing between when the tax was accrued and when it is due to be paid. For example, it might reflect a taxable transaction such as an installment sale that took place one a certain date but the taxes will not be due until a later date.
Why is deferred tax liability important?
A deferred tax liability records the fact the company will, in the future, pay more income tax because of a transaction that took place during the current period , such as an installment sale receivable.
What is the depreciation method for long-lived assets?
The depreciation expense for long-lived assets for financial statement purposes is typically calculated using a straight-line method, while tax regulations allow companies to use an accelerated depreciation method. Since the straight-line method produces lower depreciation when compared to that of the under accelerated method, a company's accounting income is temporarily higher than its taxable income.
What does it mean when a company says it has underpaid?
By saying it has underpaid doesn't necessarily mean that it hasn't fulfilled its tax obligations, rather it is recognizing that the obligation is paid on a different timetable. For example, a company that earned net income for the year knows it will have to pay corporate income taxes. Because the tax liability applies to the current year, ...
What is deferred tax liability?
In a fixed asset example where the book carrying value exceeds the corresponding tax basis, the deferred tax liability can represent the tax consequences of recovering or disposing of the asset at its book carrying value. In the case of disposal, a sales price equal to the book carrying value would result in a taxable gain, given the lower corresponding tax basis.
What is the basis of a fixed asset?
Example: Generally, the income tax basis in a fixed asset is the purchase price less tax depreciation previously allowed under the applicable tax law . The timing of the cost recovery of the fixed asset may differ between the tax law for a particular jurisdiction and the applicable accounting rules, which can result in a deferred tax asset or liability.
What are tax attributes?
Common tax attributes, including unutilized net operating losses or tax credit carryforwards generated in prior tax year (s), may be available to reduce cash tax obligations in future year (s), thu s representing a potential future tax benefit.
What is deferred tax?
A deferred tax often represents the mathematical difference between the book carrying value (i.e., an amount recorded in the accounting balance sheet for an asset or liability ) and a corresponding tax basis (determined under the tax laws of that jurisdiction) in the asset or liability, multiplied by the applicable jurisdiction’s statutory income tax rate.
What is deferred tax accounting?
While certain complexities exist, the fundamental objective of the deferred tax accounting model is to provide a complete measure of an enterprise’s net earnings by allowing the current and future tax consequences to be recognized in the same reporting period as the book income or loss is generated. This objective is met through the measurement of the basis difference in the book carrying value and tax basis of the enterprise’s underlying assets and liabilities. While there are limited exceptions, these differences in basis generally reverse as part of the enterprise’s normal course of operations according to well-established rules.
How long does it take for a timing difference to reverse?
Depending on the nature of the assets and liabilities involved, timing differences may reverse within a year (e.g., differences relating to certain assets and liabilities classified as current or short term on the balance sheet), or may take several years to reverse (e.g., certain long-lived assets). Moreover, other differences may not reverse until the related asset is disposed of or otherwise impaired for book purposes (e.g., certain non-amortizing book intangible assets, such as a trade name). For example, basis differences may exist between the book carrying value and tax basis in an enterprise’s investments, such as the stock of a corporation. The reversal of such investments would generally not occur until the investment is sold or otherwise recovered. While the timing of recovery may vary, importantly, deferred taxes will reverse as the financial statement asset is recovered or the financial statement liability is settled in the normal course of business.
What is the purpose of GAAP reporting?
Generally, the objective of general purpose financial reporting (e.g., US GAAP reporting standards) is to provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources to the entity. The focus is on the consolidated results of the reporting entity. In contrast, tax regimes are generally not similarly focused and often include aspects of tax policy that seek to incentivize certain behaviors. For example, accelerated cost recovery measures promote investment in a specific area or asset class. Other credits promote the investment in more clean energy sources.
