What is the receptor found in the dermal papillae?
To begin, you’ll need:
- Himalayan or Celtic sea salt
- Powdered activated charcoal
- Ginger
- Cucumber
- Lemon juice
- A juicing machine (or a blender and muslin cloth)
What is the dermal papilla nourished by?
The dermal papilla is fed by the bloodstream, which carries nourishment to produce new hair. The growth of your hair depends on your age, gender, hair colour, and ethnic background. Scalp hair grows on average of 1cm per month.
What does function do dermal papillae have?
The dermal papillae formed, substantially increase the surface area of the dermis layer. Since dermal papillae lie in the dermo-epidermal junction, one of their functions is to keep the dermis and the epidermis layer well-connected. In simple words, dermal papillae help in strengthening the dermal-epidermal connectivity.
What are dermal cells?
The dermis is composed of three major types of cells: fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells. Apart from these cells, the dermis is also composed of matrix components such as collagen (which provides strength ), elastin (which provides elasticity ), and extrafibrillar matrix , an extracellular gel-like substance primarily composed of glycosaminoglycans (most notably hyaluronan ), proteoglycans , and glycoproteins .

What is the dermal papilla and what is its function?
The dermal papilla (DP) of the hair follicle is both a chemical and physical niche for epithelial progenitor cells that regenerate the cycling portion of the hair follicle and generate the hair shaft.
What is dermal papilla made of?
Papillae is composed of thick collagen fibers whereas the reticular layer, situated near the surface of the skin, is formed from a thin and delicate fibers.
What are two functions of the dermal papillae?
The papillary dermis (PD) contains vascular networks that have two important functions. The first being to support the avascular epidermis with vital nutrients and secondly to provide a network for thermoregulation.
Are dermal papilla cells stem cells?
One population of mesenchymal cells in the skin, known as dermal papilla (DP) cells, is the focus of intense interest because the DP not only regulates hair follicle development and growth, but is also thought to be a reservoir of multi-potent stem cells.
What are dermal papillae quizlet?
dermal papillae. a fingerlike projection of the dermis that may contain blood capillaries or Meissner corpuscles (of touch) hair follicle.
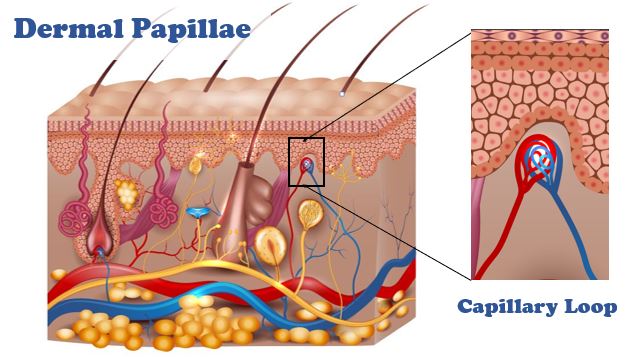
Where is the dermal papillae?
The dermal papillae are part of the uppermost layer of the dermis, the papillary dermis, and the ridges they form greatly increase the surface area between the dermis and epidermis.
Do dermal papillae make fingerprints?
Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and persist over a whole human lifespan. These ridges are caused by the underlying dermal papillae (small, nipple-like extensions of the uppermost layer of the dermis) into the epidermis.
What is the function of the dermal papillae at the base of the hair follicle quizlet?
What is the purpose of dermal papillae? They increase the area of contact between the dermis and epidermis, allowing for a stronger connection between the two layers. Each dermal papillae contains the capillaries that supply nutrients to the epidermal cells.
What is the dermal papilla?
The dermal papilla is a population of mesenchymal cells that reside just under the hair follicle. Several studies have suggested that during hair growth, the stem cells of the hair follicle are in close proximity to the dermal papilla, and signaling molecules including Wnts, BMPs, noggin, and FGFs from the dermal papilla activate HFSCs ...
What is the term for the projection of dermal papillae above the surface of the skin?
Papillomatosis refers to the projection of dermal papillae above the surface of the skin, resulting in an irregular undulating configuration of the epidermis. Often associated with epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis is also seen with chronic inflammatory and neoplastic dermatoses.
What are the feathers that make up the body?
the contour feathers, which are the main body feathers including a wide variety of wing and tail feathers; the filoplumes, which are fine thread-like feathers closely associated with contour feathers. All these definitive feathers are formed from the dermal papillae laid down in the embryo.
How are down feathers pushed out of the follicle?
The down feathers are pushed out of the follicle by the apices of the juvenile feathers, which are similar in structure to the adult feathers. For a morphological description of the embryonic down feathers, see Matulionis (1970). Adult feathers are of three types: Sign in to download full-size image. Text-Figure 86.
Is papillomatosis a chronic inflammatory disease?
Often associated with epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis is also seen with chronic inflammatory and neoplastic dermatoses. Villi are dermal papillae, covered by 1 to 2 layers of epidermal cells, that project into a vesicle or bulla. Villi are occasionally seen in actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the dermal papilla?
At early anagen, the dermal papilla (DP) is just proximal to the hair germ and bulge. As anagen progresses, stem cells in the hair germ are activated first by signals from the dermal papilla to proliferate and form a transit amplifying population that moves downward to reconstitute the matrix.
What is the hair follicle?
Hair follicles are epidermal invaginations that project into the dermis ( Fig. 3.2). The proximal tip of the follicle is invaginated to form a cap over the dermal papilla, a condensation of dermal fibroblasts associated with the follicle (Hardy, 1992 ).
How thick is the dermis?
Depending on the skin area, the dermis is on average 1–4 mm thick [13]. The upper layer, the stratum papillare, is a loose structure of fine connective tissue fibers that fill the papillary dermis and supplies the epidermis by means of capillary loops The density of the dermal papillae decreases with age, which results in a flattening of the dermal epidermal junction [14]. The lower dermal layer, the stratum reticulare, is a dense fibrous structure containing coarse collagen fibers forming a three-dimensional network providing the tensile cutaneous strength.
What are the layers of the skin?
The skin consists of three main layers: the epidermis (epidermis with hair), the dermis and subcutaneous tissue ( Figure 6.3 ). The dermis contains dermal papillae and reticular. Hair follicles and sweat glands reside between these layers. Papillae is composed of thick collagen fibers whereas the reticular layer, situated near the surface of the skin, is formed from a thin and delicate fibers. Papillae, which adheres to the epidermis, has a very tight arrangement of fibers forming the face of the skin. Collagen (60-80% of dry weight) 2 is the primary protein which forms skin. All other skin components are not useful and they are removed in the process of tanning.
How do hair germ cells proliferate?
In the first step, the hair germ cells proliferate, followed in the second step by proliferation of bulge cells, pushing the dermal papilla downward to reconstitute the hair bulb and matrix. A new hair shaft and inner root sheath are then differentiated from matrix transit amplifying cells.
Which cells regenerate hair?
Stem cells in the lower and middle bulge regenerate the hair, while stem cells in the upper bulge and isthmus renew the non-hair parts of the follicle ( Brownell et al., 2011 ). Bulge and isthmus stem cells contribute together to the injury-induced regeneration of the interfollicular epidermis.
What is the hair on the abdomen?
Hairs are specialized epidermal derivatives that arise as the result of inductive stimuli from the dermis. There are many types of hairs, ranging from the coarse hairs of the eyelashes and eyebrows to the barely visible hairs on the abdomen and back. Regional differences in morphology and patterns of distribution are imposed on the epidermis by the underlying dermis.
Where are dermal papillae located?
Human Hair Dermal Papilla Cells. The dermal papillae are a highly active group of cells derived from the dermis mesenchyme. Located at the base of the hair follicles, the dermal papillae play a crucial role in hair growth cycle by inducing follicle development from the epidermis to produce hair fiber [1].
What is HHDPC characterized by?
HHDPC are characterized by their mesenchymal cell morphology and immunofluorescence with antibodies specific to fibronectin and CD105. HHDPC are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fungi. HHDPC are guaranteed to further expand for 5 population doublings under the conditions provided by ScienCell Research Laboratories.
What are dermal papillae?
Dermal papillae are embedded in a laminin and collagen IV rich extracellular matrix at the base of the hair follicles. They are essential for the induction and maintenance of hair growth. Since they have androgen receptors, they can be used for in vitro screening of androgen blocking reagents.
Where are primary papilla cells from?
Primary Human Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells isolated from human dermis of the scalp, originating from the occipital or temple region.
What is HFDPC in human hair?
HFDPC are isolated from the hair papilla of normal human scalp hair follicles. Hair papilla in the adult hair follicle play a crucial role in the dermal-epidermal interactions that control hair production and in hair growth cycle events. The follicle dermal cells are cryopreserved at second passage and can be cultured for at least 10 population ...
Where are primary human folicular dermal papilla cells isolated?
Primary Human Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells (HFDPC) are isolated mainly from human dermis of the scalp, originating from the occipital or temple region. Information on donor hair and skin color is available on request. HFDPC stain positive for alkaline phosphatase.
What are some examples of cryopreserved cells?
Examples: HUVEC and HUAEC correspond to P1 after thawing; therefore the pellets are frozen in P2. SMC or keratinocytes or epithelial cells correspond to P2 after thawing; therefore the pellets are frozen in P3. In contrast, our blood cells are cryopreserved directly after cell isolation.
What are the cells that make up the DP?
Cells within the DP interact with numerous other cell types within the follicle, including epithelial stem cells, matrix cells, and melanocytes, regulating their function. The diameter of the DP is directly proportional to the width of the hair shaft, and a decrease in both cell number and DP size is observed in hair loss conditions such as ...
Where is the DP located?
The diameter of the DP is …. The dermal papilla (DP) is a cluster of mesenchymal cells located at the bottom of the hair follicle. Cells within the DP interact with numerous other cell types within the follicle, including epithelial stem cells, matrix cells, and melanocytes, regulating their function. The diameter of the DP is ….
What is the population of mesenchymal cells in the skin called?
One population of mesenchymal cells in the skin, known as dermal papilla (DP) cells, is the focus of intense interest because the DP not only regulates hair follicle development and growth, but is also thought to be a reservoir of multi-potent stem cells. In this article and the accompanying poster we review the origins ...
What is the precursor of the hair follicle?
The precursor of the hair follicle is a local thickening, also known as placode, of the embryonic epidermis , which is detectable at embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) of mouse development. Soon after, a local condensation (dermal condensate) of fibroblasts forms beneath the placode.
What are SKPs cells?
SKPs are cells that can be cultured to form nestin-positive spheres with the capacity to differentiate into neurons, glia, smooth muscle cells, adipocytes and other cell types ( Toma et al., 2001; Fernandes et al., 2004; Lavoie et al., 2009; Biernaskie et al., 2009 ).
Why are DP cells important?
The cells of the DP are not only essential for hair follicle development and function, but are also a reservoir of cells with the potential to differentiate into a range of cell types that are of potential therapeutic importance. Improved methods for culturing DP cells can be exploited to treat hair loss, and the ability to direct DP cells to differentiate into other lineages, in particular Schwann cells, could provide a source of cells to repair damaged nerves ( Biernaskie et al., 2007 ).
Do DP cells form fibroblasts?
DP cells not only retain the ability to form DP following in vitro culture, but they can also contribute to dermal sheath cells and non-follicle-associated fibroblasts during skin reconstitution and wound-healing ( Biernaskie et al., 2009; Rendl et al., 2008 ).
Do DP cells divide?
DP cells themselves are thought to not divide. However, the number of cells in the DP increases during anagen, possibly as a result of replenishment from neighbouring cells of the dermal sheath ( Tobin et al., 2003; Chi et al., 2010 ).
Can sheath cells produce SKPs?
Since Sox2 is also expressed in dermal sheath cells close to the DP, it is possible that sheath cells have the ability to form SKPs in culture. SKPs can be generated not only from rodent skin, but also from human hair follicle DP ( Hunt et al., 2008 ).